
Concept explainers
Purchase-related transactions using perpetual inventory system
The following selected transactions were completed by Niles Co. during March of the current year:
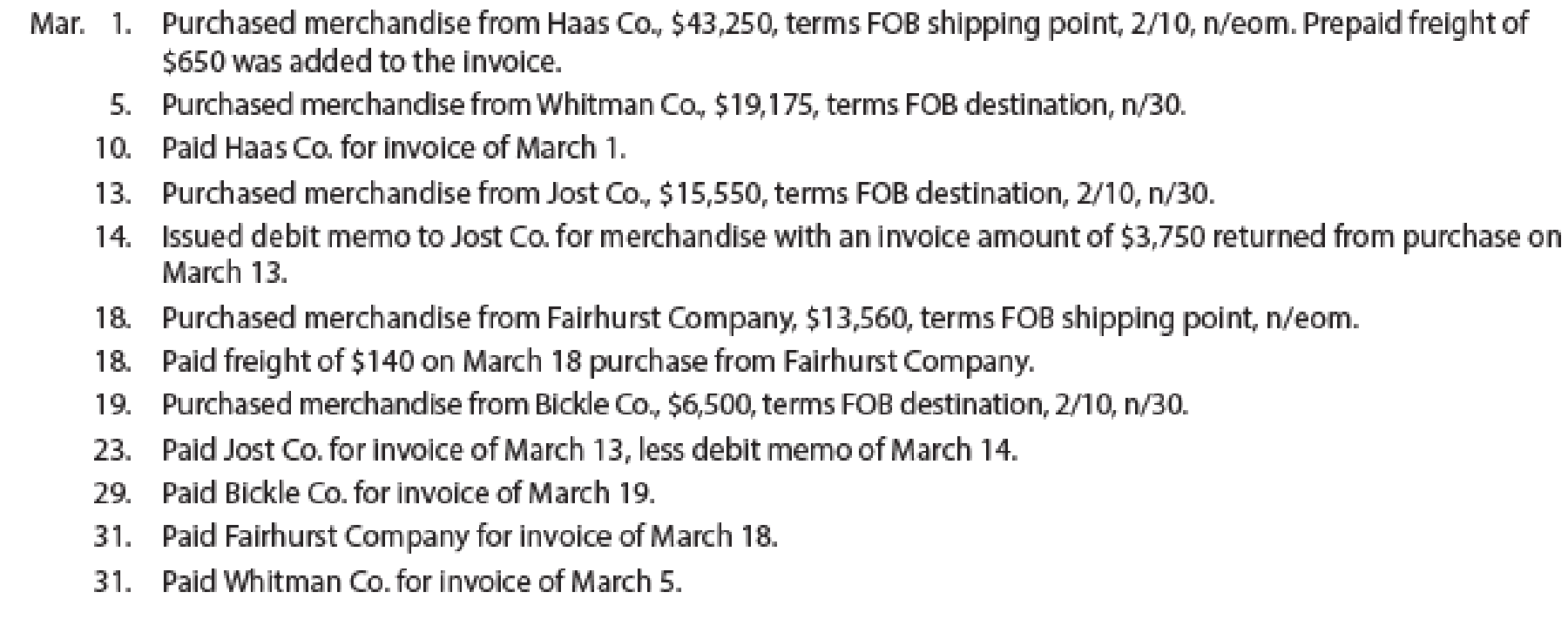
Instructions
Journal entry: Journal is the book of original entry whereby all the financial transactions are recorded in chronological order. Under this method each transaction has two sides, debit side and credit side. Total amount of debit side must be equal to the total amount of credit side. In addition, it is the primary books of accounts for any entity to record the daily transactions and processed further till the presentation of the financial statements.
The following are the rules of debit and credit:
- 1. Increase in assets and expenses accounts are debited. Decrease in liabilities and stockholders’ equity accounts are debited.
- 2. Increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equity accounts are credited. Decreases in all asset accounts are credited.
Prepare journal entries to record the transactions of Company N during the month of March using perpetual inventory system.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual Inventory System refers to the inventory system that maintains the detailed records of every inventory transactions related to purchases and sales on a continuous basis. It shows the exact on-hand- inventory at any point of time.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 1 | Inventory | 43,035 | ||
| Accounts payable | 43,035 (1) | |||
| (To record purchase on account) |
Table (1)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of accounts payable.
Purchases = $43,250
Discount percentage = 2%
Freight charges = $650
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $43,035. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $43,035.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased by $43,035. Therefore, credit accounts payable account with $43,035.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 5 | Inventory | 19,175 | ||
| Accounts payable | 19,175 | |||
| (To record purchase on account) |
Table (2)
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $19,175. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $19,175.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased by $19,175. Therefore, credit accounts payable account with $19,175.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 10 | Accounts payable | 43,035 | ||
| Cash | 43,035 | |||
| (To record the payment against accounts payable) |
Table (3)
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $43,035. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $43,035.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $43,035. Therefore, credit cash account with $43,035.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 13 | Inventory | 15,239 | ||
| Accounts payable | 15,239 (2) | |||
| (To record purchase on account) |
Table (4)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of accounts payable.
Purchases = $15,550
Discount percentage = 2%
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $15,239. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $15,239.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased by $15,239. Therefore, credit accounts payable account with $15,239.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 14 | Accounts payable | 3,675 (3) | ||
| Inventory | 3,675 | |||
| (To record purchase return) |
Table (5)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of accounts payable.
Purchases return = $3,750
Discount percentage = 2%
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $3,675. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $3,675.
- Inventory is an asset and it is decreased by $3,675. Therefore, credit Inventory account with $3,675.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 18 | Inventory | 13,560 | ||
| Accounts payable | 13,560 | |||
| (To record purchase on account) |
Table (6)
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $13,560. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $13,560.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased by $13,560. Therefore, credit accounts payable account with $13,560.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 18 | Inventory | 140 | ||
| Cash | 140 | |||
| (To record freight charges paid) |
Table (7)
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $140. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $140.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $140. Therefore, credit cash account with $140.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 19 | Inventory | 6,370 | ||
| Accounts payable | 6,370 (4) | |||
| (To record purchase on account) |
Table (8)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of accounts payable.
Purchases = $6,500
Discount percentage = 2%
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $6,370. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $6,370.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased by $6,370. Therefore, credit accounts payable account with $6,370.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 23 | Accounts payable | 11,564 (5) | ||
| Cash | 11,564 | |||
| (To record payment made in full settlement less discounts) |
Table (9)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of net accounts payable.
Inventory = $15,239 (2)
Purchase returns = $3,675 (3)
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $11,564. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $11,564.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $11,564. Therefore, credit cash account with $11,564.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 29 | Accounts payable | 6,370 | ||
| Cash | 6,370 | |||
| (To record payment made in full settlement less discounts) |
Table (10)
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $6,370. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $6,370.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $6,370. Therefore, credit cash account with $6,370.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 31 | Accounts payable | 13,560 | ||
| Cash | 13,560 | |||
| (To record payment made in full settlement less discounts) |
Table (11)
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $13,560. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $13,560.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $13,560. Therefore, credit cash account with $13,560.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 31 | Accounts payable | 19,175 | ||
| Cash | 19,175 | |||
| (To record payment made in full settlement less discounts) |
Table (12)
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $19,175. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $19,175.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $19,175. Therefore, credit cash account with $19,175.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Financial And Managerial Accounting
- Which of the following errors will cause the trial balance to not balance?A. Omission of a transactionB. Entry posted twiceC. Transposing digits in one sideD. Debiting one account and crediting anotherarrow_forwardMime Delivery Service is owned and operated by Pamela Kolp. The following selected transactionswere completed by Mime Delivery Service during October:1. Received cash from the owner as an additional investment, $7,500.2. Paid creditors on account, $815.3. Billed customers for delivery services on account, $3,250.4. Received cash from customers on account, $1,150.5. Paid cash to the owner for personal use, $500.Required:Indicate the effect of each transaction on the accounting equation elements (Assets, Liabilities,Owner’s Equity, Drawing, Revenue, and Expense) by listing the numbers identifying the transactions,(1) to (5). Also, indicate the specific item within the accounting equation element that is affected, i.e.(1) Asset (Cash) increases by $; Owner’s Equity (Pamela Kolp, Capital) increases by $.arrow_forwardWhen a company incurs an expense but does not yet pay it, what is the entry?A. Debit Expense, Credit CashB. Debit Liability, Credit ExpenseC. Debit Expense, Credit LiabilityD. No entry needed helparrow_forward
- When a company incurs an expense but does not yet pay it, what is the entry?A. Debit Expense, Credit CashB. Debit Liability, Credit ExpenseC. Debit Expense, Credit LiabilityD. No entry neededarrow_forwardDont use ai What is the effect of writing off an uncollectible account under the allowance method?A. Increases net incomeB. No effect on total assetsC. Decreases revenueD. Increases expensesarrow_forwardWhat is the effect of writing off an uncollectible account under the allowance method?A. Increases net incomeB. No effect on total assetsC. Decreases revenueD. Increases expensesi need help ..arrow_forward
- Get the Correct Answer with calculation of this General Accounting Questionarrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting problem using proper accounting guidelines.arrow_forward
- I am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forwardHello Dear Tutor Please Need Answer of this Question as possible fast and Correctarrow_forward15. The balance in the dividends account is closed to:A. CashB. RevenueC. Retained EarningsD. Common Stock dont use AIarrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning




