
For the graph shown in Fig 5-29,
a. give the vertex set.
b. give the edge list.
c. give the degree of each vertex.
d. draw a version of the graph without crossing points.
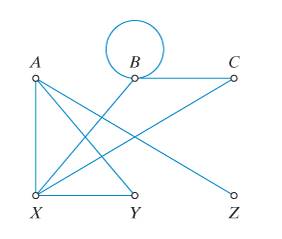
(a)
To find:
The vertex set of given graph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The vertex set is
Explanation of Solution
In the graphical representation of routes, the location is defined as a dot in the graph. Those dots are the vertices of the graph and the collection of vertices come under the vertex set.
Given:
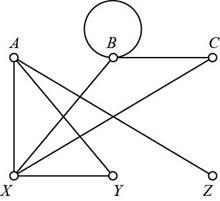
The given graph is,
From the given graph, the vertices are
(b)
To find:
The edge list of given graph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The list of edges is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
In the graphical representation of routes, the paths or routes are defined by the lines in the graph. Those lines are the edges of the graph.
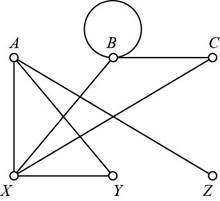
The given graph is,
From the given graph, the edges are
(c)
To find:
The degree of each vertex in given graph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The degree on vertices are
Explanation of Solution
In the graph theory, the degree of any vertex is the number of edge formed on that particular vertex.
The count for a loop on any vertex is two degree on that vertex.
Given:
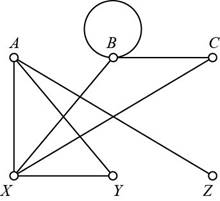
The given graph is,
From the given graph, the vertex A has 3 edges adjoined on it. The degree of vertex A is
The vertex B has 4 edges adjoined on it. The degree of vertex B is
The vertex C has 2 edges adjoined on it. The degree of vertex C is
The vertex X has 4 edges adjoined on it. The degree of vertex X is
The vertex Y has 2 edges adjoined on it. The degree of vertex Y is
The vertex Z has 1 edge adjoined on it. The degree of vertex Z is
Conclusion:
Thus, the degree on vertices are
(d)
To plot:
The version of the graph without crossing points
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The required graph is,
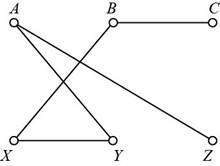
Explanation of Solution
Given:
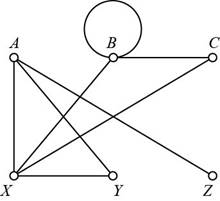
The given graph is,
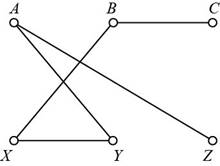
The required graph needs to have a route in which no vertex is taken again. From the given graph, the required graph is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Excursions in Modern Mathematics (9th Edition)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus (Standalone Book)
Precalculus
Beginning and Intermediate Algebra
Elementary Statistics ( 3rd International Edition ) Isbn:9781260092561
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- Definition: A topology on a set X is a collection T of subsets of X having the following properties. (1) Both the empty set and X itself are elements of T. (2) The union of an arbitrary collection of elements of T is an element of T. (3) The intersection of a finite number of elements of T is an element of T. A set X with a specified topology T is called a topological space. The subsets of X that are members of are called the open sets of the topological space.arrow_forward3) Let a1, a2, and a3 be arbitrary real numbers, and define an = 3an 13an-2 + An−3 for all integers n ≥ 4. Prove that an = 1 - - - - - 1 - - (n − 1)(n − 2)a3 − (n − 1)(n − 3)a2 + = (n − 2)(n − 3)aı for all integers n > 1.arrow_forwardDefinition: A topology on a set X is a collection T of subsets of X having the following properties. (1) Both the empty set and X itself are elements of T. (2) The union of an arbitrary collection of elements of T is an element of T. (3) The intersection of a finite number of elements of T is an element of T. A set X with a specified topology T is called a topological space. The subsets of X that are members of are called the open sets of the topological space.arrow_forward
- Definition: A topology on a set X is a collection T of subsets of X having the following properties. (1) Both the empty set and X itself are elements of T. (2) The union of an arbitrary collection of elements of T is an element of T. (3) The intersection of a finite number of elements of T is an element of T. A set X with a specified topology T is called a topological space. The subsets of X that are members of are called the open sets of the topological space.arrow_forwardDefinition: A topology on a set X is a collection T of subsets of X having the following properties. (1) Both the empty set and X itself are elements of T. (2) The union of an arbitrary collection of elements of T is an element of T. (3) The intersection of a finite number of elements of T is an element of T. A set X with a specified topology T is called a topological space. The subsets of X that are members of are called the open sets of the topological space.arrow_forward1) If f(x) = g¹ (g(x) + a) for some real number a and invertible function g, show that f(x) = (fo fo... 0 f)(x) = g¯¹ (g(x) +na) n times for all integers n ≥ 1.arrow_forward
- image belowarrow_forwardSolve this question and show steps.arrow_forwardu, v and w are three coplanar vectors: ⚫ w has a magnitude of 10 and points along the positive x-axis ⚫ v has a magnitude of 3 and makes an angle of 58 degrees to the positive x- axis ⚫ u has a magnitude of 5 and makes an angle of 119 degrees to the positive x- axis ⚫ vector v is located in between u and w a) Draw a diagram of the three vectors placed tail-to-tail at the origin of an x-y plane. b) If possible, find w × (ū+v) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. c) If possible, find v. (ū⋅w) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. d) If possible, find u. (vxw) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. Note: in this question you can work with the vectors in geometric form or convert them to algebraic vectors.arrow_forward
- Question 3 (6 points) u, v and w are three coplanar vectors: ⚫ w has a magnitude of 10 and points along the positive x-axis ⚫ v has a magnitude of 3 and makes an angle of 58 degrees to the positive x- axis ⚫ u has a magnitude of 5 and makes an angle of 119 degrees to the positive x- axis ⚫ vector v is located in between u and w a) Draw a diagram of the three vectors placed tail-to-tail at the origin of an x-y plane. b) If possible, find w × (u + v) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. c) If possible, find v. (ū⋅ w) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. d) If possible, find u (v × w) Support your answer mathematically or a with a written explanation. Note: in this question you can work with the vectors in geometric form or convert them to algebraic vectors.arrow_forward39 Two sides of one triangle are congruent to two sides of a second triangle, and the included angles are supplementary. The area of one triangle is 41. Can the area of the second triangle be found?arrow_forwardPls help ASAP botharrow_forward
 Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell





