
College Physics
OER 2016 Edition
ISBN: 9781947172173
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 19PE
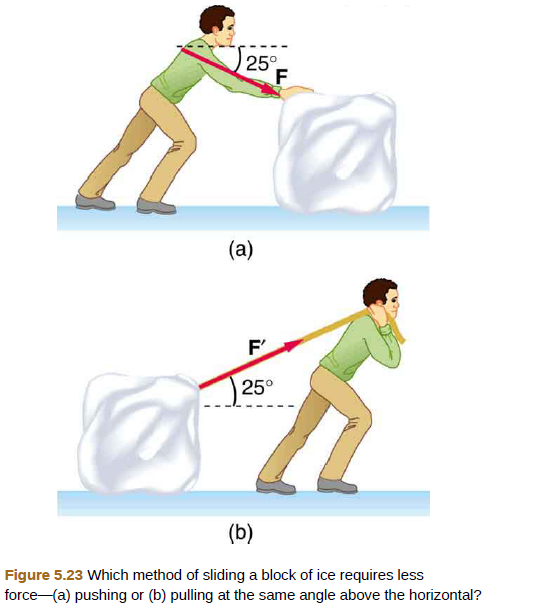
Repeat Exercise 5.18 with the contestant pulling the block of ice with a rope over his shoulder at the same angle above the horizontal as shown in Figure 5.23(b).
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A pendulum has a 0.4-m-long cord and is given a tangential velocity of 0.2 m/s toward the
vertical from a position 0 = 0.3 rad.
Part A
Determine the equation which describes the angular motion.
Express your answer in terms of the variable t. Express coefficients in radians to three significant figures.
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
vec
(t)=0.3 cos (4.95t) + 0.101 sin (4.95t)
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
× Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remaining
Part A
■Review
The uniform 150-lb stone (rectangular block) is being turned over on its side by pulling the
vertical cable slowly upward until the stone begins to tip.
(Figure 1)
If it then falls freely (T = 0) from an essentially balanced at-rest position, determine the speed at which the corner A strikes the pad at B. The stone does not slip at its corner C as it falls. Suppose that height of the stone is
L = 1.2 ft.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
?
ft
VA 10.76
S
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
× Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remaining
Consider the circuit shown in the figure. The battery has emf ε = 69 volts and negligible internal resistance. The inductance is L = 0.4 H and the resistances are R 1 = 12 Ω and R 2 = 9.0 Ω. Initially the switch S is open and no currents flow. Then the switch is closed. After leaving the switch closed for a very long time, it is opened again. Just after it is opened, what is the current in R 1?
Chapter 5 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 5 - Define normal force. What is its relationship to...Ch. 5 - The glue on a piece of tape can exert forces. Can...Ch. 5 - When you learn to drive, you discover that you...Ch. 5 - When you push a piece of chalk across a...Ch. 5 - Athletes such as swimmers and bicyclists wear body...Ch. 5 - Two expressions were used for the drag force...Ch. 5 - As cars travel, oil and gasoline leaks onto the...Ch. 5 - Why can a squirrel jump from a tree branch to the...Ch. 5 - The elastic properties of the arteries are...Ch. 5 - What are you feeling when you feel your pulse?...
Ch. 5 - Examine different types of shoes, including sports...Ch. 5 - Would you expect your height to be different...Ch. 5 - Why can a squirrel from a tree branch to the...Ch. 5 - Explain why pregnant women often suffer from back...Ch. 5 - An old carpenter's trick to keep nails from...Ch. 5 - When a glass bottle full of vinegar warms up, both...Ch. 5 - A physics major is cooking breakfast when he...Ch. 5 - (a) When rebuilding her car's engine, a physics...Ch. 5 - (a) What is the maximum frictional force in the...Ch. 5 - Suppose you have a 120-kg wooden crate resting on...Ch. 5 - (a) If half of the weight of a small 1.00103 kg...Ch. 5 - A team of eight dogs pulls a sled with waxed wood...Ch. 5 - Consider the 65.0-kg ice skater being pushed by...Ch. 5 - Show that the acceleration of any object down a...Ch. 5 - Show that the acceleration of any object down an...Ch. 5 - Calculate the deceleration of a snow boarder going...Ch. 5 - (a) Calculate the acceleration of a skier heading...Ch. 5 - If an object is to rest on an incline without...Ch. 5 - Calculate the maximum deceleration of a car that...Ch. 5 - Calculate the maximum acceleration of a car that...Ch. 5 - Repeat Exercise 5.14 for a car with four-wheel...Ch. 5 - A freight train consists of two 8.00105 -kg...Ch. 5 - Consider the 52.0-kg mountain climber in Figure...Ch. 5 - A contestant in a winter sporting event pushes a...Ch. 5 - Repeat Exercise 5.18 with the contestant pulling...Ch. 5 - The terminal velocity of a person falling in air...Ch. 5 - A 60-kg and a go-kg skydiver jump from an airplane...Ch. 5 - A 560-g squirrel with a surface area of 930 cm2...Ch. 5 - To maintain a constant speed, the force provided...Ch. 5 - By what factor does the drag force on a car...Ch. 5 - Calculate the speed a spherical rain drop would...Ch. 5 - Using Stokes' law, verify that the units for...Ch. 5 - Find the terminal velocity of a spherical...Ch. 5 - Stokes' law describes sedimentation of particles...Ch. 5 - During a circus act, one performer swings upside...Ch. 5 - During a wrestling match, a 150 kg wrestler...Ch. 5 - (a) The "lead" in pencils is a graphite...Ch. 5 - TV broadcast antennas are the tallest artificial...Ch. 5 - (a) By how much does a 65.0-kg mountain climber...Ch. 5 - A 20.0-m tall hollow aluminum flagpole is...Ch. 5 - As an oil well is drilled, each new section of...Ch. 5 - Calculate the force a piano tuner applies to...Ch. 5 - A vertebra is subjected to a shearing force of 500...Ch. 5 - A disk between vertebrae in the spine is subjected...Ch. 5 - When using a pencil eraser, you exert a vertical...Ch. 5 - To consider the effect of wires hung on poles, we...Ch. 5 - A farmer making grape juice fills a glass bottle...Ch. 5 - (a) When water freezes, its volume increases by...Ch. 5 - This problem returns to the tightrope walker...Ch. 5 - The pole in Figure 5.24 is at a 90.0° bend in a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 1TPCh. 5 - Prob. 2TPCh. 5 - Prob. 3TPCh. 5 - Prob. 4TP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. An object is subject to two forces that do not point in opposite directions. Is it possible to choose their ...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Which of the roll owing compounds have a dipole moment of zero?
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
MAKE CONNECTIONS Review the description of meiosis (see Figure 10.8) and Mendels laws of segregation and indepe...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Fibrous connective tissue consists of ground substance and fibers that provide strength, support, and flexibili...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Endospore formation is called (a) _____. It is initiated by (b) _____. Formation of a new cell from an endospor...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A capacitor with a capacitance of C = 5.95×10−5 F is charged by connecting it to a 12.5 −V battery. The capacitor is then disconnected from the battery and connected across an inductor with an inductance of L = 1.55 H . At the time 2.35×10−2 s after the connection to the inductor is made, what is the current in the inductor? At that time, how much electrical energy is stored in the inductor?arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Gravitational Force (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pxp1Z91S5uQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY