
Concept explainers
Healthy Foods Inc. sells 50-pound bags of grapes to the military for
a. What is the break-even point in bags?
b. Calculate the profit or loss on 12,000 bags and on 25,000 bags.
c. What is the degree of operating leverage at 20,000 bags and at 25,000 bags? Why does the degree of operating leverage change as the quantity sold increases?
d. If Healthy Foods has an annual interest expense of
e. What is the degree of combined leverage at both sales levels?
a.
To calculate: The break-even point (BEP) of Healthy Foods Inc.
Introduction:
Break-even point (BEP):
It is a point of sale at which a company is in a no profit and no loss situation. The value of BEP is derived by dividing total fixed cost by the difference of revenue per unit and variable cost per unit.
Answer to Problem 12P
The BEP of Healthy Foods Inc. is 16,000 bags.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of BEP of Healthy Foods Inc.:
b.
To calculate: The profit or loss for Healthy Foods Inc. on 12,000 as well as 25,000 bags.
Introduction:
Profit or Loss:
It refers to the gain or loss arising from the commercial transactions during a specified period of time and is used to assess the company’s financial performance.
Answer to Problem 12P
Calculation of profit or loss on 12,000 bags and 25,000 bags for Healthy Foods Inc:
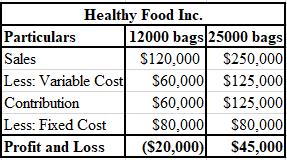
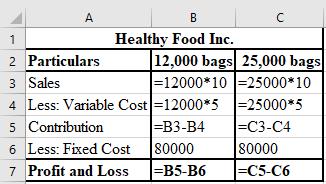
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the computation of profit or loss of 12,000 bags and 25,000 bags:
c.
To calculate: The DOL for 20,000 and 25,000 bags of Healthy Foods Inc. and also explain the reason behind the change of DOL with the increase in the quantity sold.
Introduction:
Degree of operating leverage (DOL):
It is a multiple measurement ratio which determines the quantity of change in operating income of the company with the change in sales value.
Answer to Problem 12P
The DOL for Healthy Foods Inc. for 20,000 bags is 5 times and for 25,000 bags is 2.78 times.
The reason behind this change of DOL is that the leverage has gone down and is far away from BEP. Hence, we can say that the leverage has decreased and the organisation is operating on a greater profit base.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of DOL for 20,000 bags:
Calculation of DOL for 25,000 bags:
d.
To calculate: The DFL of Healthy Foods Inc.for 20,000 bags as well as 25,000 bags.
Introduction:
Degree of financial leverage(DFL):
It is a multiple measurement ratio which determines the quantity of change in operating income of the company with the change in sales value.
Answer to Problem 12P
DFL for the company Healthy Foods Inc. for 20,000 bags is 2 times and for 25,000 bags is 1.29 times.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of DFL for 20,000 bags:
Calculation of DFL for 25,000 bags:
Working note:
Calculation of EBIT on 20,000 bags:
Calculation of EBIT on 25,000 bags:
e.
To calculate: The DCL of Healthy foods Inc. at 20,000 and 25,000 bags, respectively.
Introduction:
Degree of combined leverage (DCL):
It is a multiple measurement ratio which determines the quantity of change in operating income of the company with the change in sales value.
Answer to Problem 12P
DCL for the company Healthy Foods Inc. for 20,000 bags is 10 times and for 25,000 bags is 3.57 times.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Calculation of DCL on 20,000 bags:
Calculation of DCL on 25,000 bags:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Foundations of Financial Management Format: Loose-leaf
- How has AirBnb negatively affected the US and global economy? How has Airbnb negatively affected the real estate market? How has Airbnb negatively affected homeowners and renters market? What happened to Airbnb in the Tax Dispute in Italy?arrow_forwardHow has AirBnb positively affected the US and global economy? How has Airbnb positively affected the real estate market? How has Airbnb positively affected homeowners and renters market?arrow_forwardD. (1) Consider the following cash inflows of a financial product. Given that the market interest rate is 12%, what price would you pay for these cash flows? Year 0 1 2 3 4 Cash Flow 160 170 180 230arrow_forward
- Explain why financial institutions generally engage in foreign exchange tradingactivities. Provide specific purposes or motivations behind such activities.arrow_forwardA. In 2008, during the global financial crisis, Lehman Brothers, one of the largest investment banks, collapsed and defaulted on its corporate bonds, causing significant losses for bondholders. This event highlighted several risks that investors in corporate bonds might face. What are the key risks an investor would encounter when investing in corporate bonds? Explain these risks with examples or academic references. [15 Marks]arrow_forwardTwo companies, Blue Plc and Yellow Plc, have bonds yielding 4% and 5.3%respectively. Blue Plc has a credit rating of AA, while Yellow Plc holds a BB rating. If youwere a risk-averse investor, which bond would you choose? Explain your reasoning withacademic references.arrow_forward
- B. Using the probabilities and returns listed below, calculate the expected return and standard deviation for Sparrow Plc and Hawk Plc, then justify which company a risk- averse investor might choose. Firm Sparrow Plc Hawk Plc Outcome Probability Return 1 50% 8% 2 50% 22% 1 30% 15% 2 70% 20%arrow_forward(2) Why are long-term bonds more susceptible to interest rate risk than short-term bonds? Provide examples to explain. [10 Marks]arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardScenario one: Under what circumstances would it be appropriate for a firm to use different cost of capital for its different operating divisions? If the overall firm WACC was used as the hurdle rate for all divisions, would the riskier division or the more conservative divisions tend to get most of the investment projects? Why? If you were to try to estimate the appropriate cost of capital for different divisions, what problems might you encounter? What are two techniques you could use to develop a rough estimate for each division’s cost of capital?arrow_forwardScenario three: If a portfolio has a positive investment in every asset, can the expected return on a portfolio be greater than that of every asset in the portfolio? Can it be less than that of every asset in the portfolio? If you answer yes to one of both of these questions, explain and give an example for your answer(s). Please Provide a Referencearrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT



