
Concept explainers
Isomers are molecules with the same elemental composition but a different atomic arrangement. Three isomers with the formula C4H8 are shown in the models below. The enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH°) of each isomer, determined using a calorimeter, is as follows:
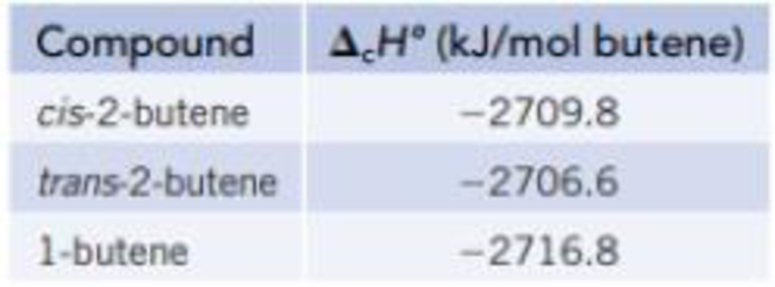
- (a) Draw an energy level diagram relating the energy content of the three isomers to the energy content of the combustion products, CO2(g) and H2O(ℓ).
- (b) Use the ΔcH° data in part (a), along with the enthalpies of formation of CO2(g) and H2O(ℓ) from Appendix L, to calculate the enthalpy of formation for each of the isomers.
- (c) Draw an energy level diagram that relates the enthalpies of formation of the three isomers to the energy of the elements in their standard states.
- (d) What is the enthalpy change for the conversion of cis-2-butene to trans-2-butene?
(a)
Interpretation:
The energy level diagram relating the energy content of the three isomers has to be determined
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of substance by 1K.Energy gained or lost can be calculated using the below equation.
Where, q= energy gained or lost for a given mass of substance (m), C =specific heat capacity,
The standard molar enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change
Explanation of Solution
The energy level diagram is given below
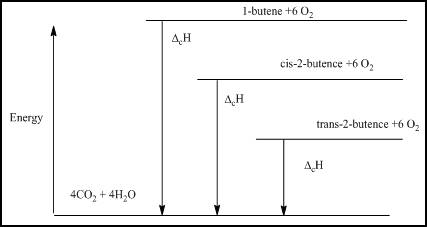
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The enthalpy of formation of
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1g substance by 1K.Energy gained or lost can be calculated using the below equation.
Where, q= energy gained or lost for a given mass of substance (m), C =specific heat capacity,
The standard molar enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is:
For cis-2-butene
Using the formula 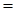
For trans-2-butene
Using the formula 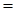
For 1-butene
Using the formula 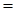
the enthalpy of formation for each of the isomers found out.
(c)
Interpretation:
The energy level diagram based on the enthalpy of formation has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of substance by 1K. Energy gained or lost can be calculated using the below equation.
Where, q= energy gained or lost for a given mass of substance (m), C =specific heat capacity,
The standard enthalpy change of combustion of a compound is the enthalpy change which occurs when one gram of the compound is burned completely in oxygen under standard conditions, and with everything in its standard state.
Explanation of Solution
The energy level diagram based on the enthalpy of formation is:
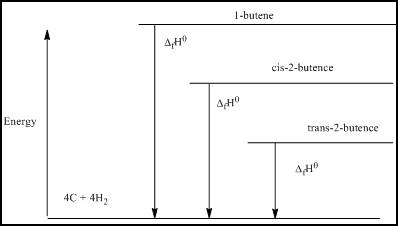
Figure 2
(d)
Interpretation:
The enthalpy change for the conversion of
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of substance by 1K. Energy gained or lost can be calculated using the below equation.
Where, q= energy gained or lost for a given mass of substance (m), C =specific heat capacity,
The standard enthalpy change of combustion of a compound is the enthalpy change which occurs when one gram of the compound is burned completely in oxygen under standard conditions, and with everything in its standard state.
Explanation of Solution
Form the question the values given are:
Enthalpy change of cis-2-butence to trans-2-butene
So, the enthalpy change for a conversion of cis-2-butence to trans-2-butene is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- < 10:44 5GW 10 Question 7/8 Show Answer Convert 46.0 mm to inches (1 inch = 2.54 cm) 46.0 DAM STARTING AMOUNT 1 cm 1 in 46.0 mm x ☑ 10 mm 10 cm ADD FACTOR DELETE x() X × = 1.81 in = 1 10 Dam ANSWER RESET ១ 2.54 0.0460 mm 10 1000 in 0.001 11.7 m 4.60 18.1 cm 100 1.81 0.394 1 0.1 46.0 0.01 Tap here for additional resourcesarrow_forward< 10:44 Question 6/8 5GW (10 Submit A cake recipe calls for 230.0 mL of buttermilk. How 230.0 many cups is this? DAL STARTING AMOUNT × 1 cups 230.0 mL x = 0.9722 cups 230.0 mL ADD FACTOR DELETE (( ) = 1 cups 230.0 DAE ANSWER RESET ១ 9.722 × 105 0.8706 cups 8.706 × 104 1 L 8.706 × 105 0.9722 quart 10 100 mL 0.001 0.1 6.076 × 103 0.01 9.722 × 104 230.0 0.06076 4 1.0567 1000 6.076 × 104 Tap here for additional resourcesarrow_forward< 10:44 Question 6/8 5GW (10 Submit A cake recipe calls for 230.0 mL of buttermilk. How 230.0 many cups is this? DAL STARTING AMOUNT × 1 cups 230.0 mL x = 0.9722 cups 230.0 mL ADD FACTOR DELETE (( ) = 1 cups 230.0 DAE ANSWER RESET ១ 9.722 × 105 0.8706 cups 8.706 × 104 1 L 8.706 × 105 0.9722 quart 10 100 mL 0.001 0.1 6.076 × 103 0.01 9.722 × 104 230.0 0.06076 4 1.0567 1000 6.076 × 104 Tap here for additional resourcesarrow_forward
- Show work in detailed of all the options. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardPredict the Product. Predict the major organic product for the following reaction:arrow_forwardPlease provide the complete mechanism for the reaction below including arrows, intermediates, and formal charges.arrow_forward
- Can you please explain this to me? Maybe color-code it in essence and highlight it.arrow_forwardCan you please color-code and explain this problem to me and is it because its spdf, and then it follows by higher numver so 3 first and so forth ...arrow_forwardapp aktv.com Alt Leaming App Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Problem 30 of 35 Na Select to Edit Arrows THE M 回 Na :0: 0% Donearrow_forward
- Can you explain this problem to me? I'm only given a PD table, so how can I determine the answer? I guess there’s a way to subtract the TI-84 EN values.arrow_forwardSapp ektiv.com Free Response Work-Aktiv Problem 2 of 35 Your Response Submit Aldehyde electrophiles generally react more quickly than ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions. Explain the difference in reactivity. Make a clear claim about these structures and the characteristics of this reaction. Briefly state the evidence and relate the evidence clearly to your explanation. Type in your prompt for the question. Click "Add Equation/Symbols" to insert symbols and expressions. 回 =Add Equation/Symbols Feb 15 9:54arrow_forwardCan you please color-code and explain how to solve this and any molecular orbital diagram given? I'm so confused; could you provide baby steps regardless of which problem type they gave me?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





