
Concept explainers
Suppose you are holding a box in front of you and away from your body by squeezing the sides, as shown in Figure Q5.10. Draw a free-body diagram showing all of the forces on the box. What is the force that is holding the box up, the force that is opposite the weight force?
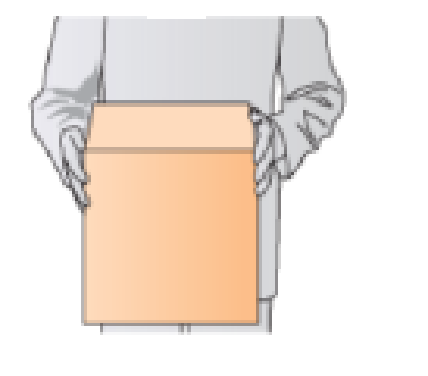
Figure Q5.10
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 5 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach Plus Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (4th Edition) (What's New in Astronomy & Physics)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- A projectile is fired with an initial speed of 40.2 m/s at an angle of 35.0 degree above the horizontal on a long flat firing range. Determine. please help and show work for them so i can understand.arrow_forwardpls helparrow_forwardJ K L The graph in the figure shows the position of an object as a function of time. The letters H-L represent particular moments of time. At which moments shown (H, I, etc.) is the speed of the object the greatest? + Position H I K Timearrow_forward
- 1. Two pendula of slightly different length oscillate next to each other. The short one oscillates with frequency 0.52 Hz and the longer one with frequency 0.50 Hz. If they start of in phase determine their phase difference after 75 s.arrow_forwardA mass is connect to a vertical revolving axle by two strings of length L, each making an angle of 45 degrees with the axle, as shown. Both the axle and mass are revolving with angular velocity w, Gravity is directed downward. The tension in the upper string is T_upper and the tension in the lower string is T_lower.Draw a clear free body diagram for mass m. Please include real forces only.Find the tensions in the upper and lower strings, T_upper and T_lowerarrow_forward2. A stone is dropped into a pool of water causing ripple to spread out. After 10 s the circumference of the ripple is 20 m. Calculate the velocity of the wave.arrow_forward
- 10. Imagine you have a system in which you have 54 grams of ice. You can melt this ice and then vaporize it all at 0 C. The melting and vaporization are done reversibly into a balloon held at a pressure of 0.250 bar. Here are some facts about water you may wish to know. The density of liquid water at 0 C is 1 g/cm³. The density of ice at 0 C is 0.917 g/cm³. The enthalpy of vaporization of liquid water is 2.496 kJ/gram and the enthalpy of fusion of solid water is 333.55 J/gram. A. How much energy does the ice absorb as heat when it melts? B. How much work is involved in melting the ice? C. What is the total change in energy for melting the ice? D. What is the enthalpy change for melting the ice? E. What is the entropy change for melting the ice? F. What is the change in Helmholtz energy for melting the ice? G. What is the change in Gibbs energy for melting the ice?arrow_forwardIn the figure Q = 5.7 nC and all other quantities are accurate to 2 significant figures. What is the magnitude of the force on the charge Q? (k = 1/4πε 0 = 8.99 × 109 N · m2/C2)arrow_forwardNow add a fourth charged particle, particle 3, with positive charge q3, fixed in the yz-plane at (0,d2,d2). What is the net force F→ on particle 0 due solely to this charge? Express your answer (a vector) using k, q0, q3, d2, i^, j^, and k^. Include only the force caused by particle 3.arrow_forward
- For a tornadoes and hurricanes, which of the following is most critical? an alert a watch a warning a predictionarrow_forwardWhen a warm front advances up and over a cold front, what is it called? front inversion stationary front cold front occlusion warm front occlusionarrow_forward1) Consider two positively charged particles, one of charge q0 (particle 0) fixed at the origin, and another of charge q1 (particle 1) fixed on the y-axis at (0,d1,0). What is the net force F→ on particle 0 due to particle 1? Express your answer (a vector) using any or all of k, q0, q1, d1, i^, j^, and k^. 2) Now add a third, negatively charged, particle, whose charge is −q2− (particle 2). Particle 2 fixed on the y-axis at position (0,d2,0). What is the new net force on particle 0, from particle 1 and particle 2? Express your answer (a vector) using any or all of k, q0, q1, q2, d1, d2, i^, j^, and k^. 3) Particle 0 experiences a repulsion from particle 1 and an attraction toward particle 2. For certain values of d1 and d2, the repulsion and attraction should balance each other, resulting in no net force. For what ratio d1/d2 is there no net force on particle 0? Express your answer in terms of any or all of the following variables: k, q0, q1, q2.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





