
Concept explainers
To analyze:
The variations in Po2 (in units of mmHg) in a typical open-close-fluttering cycle. Also explain the estimated mm Hg Po2 in the atmosphere and inside the tubes of trachea in all the three given experiments shown in figure B. Here, 1 kPa (kilopascal) = 7.5 mm Hg.
Given information:
The microscopic plastic tubes were inserted into the tracheae of the pupae of Attacus atlas moths by the researchers to study the tracheal function in the moths. The microtubes were attached to the sensors for recording the rate of CO2 that was released from the tracheae and also the intratracheal concentrations of O2.
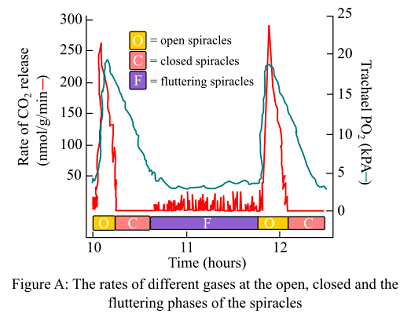
The pupae were placed in the chambers by the researchers and the normal atmospheric levels of the gases were maintained. Researchers then recorded the behavior of spiracles, rate of CO2 release, and O2 concentrations in the tracheae. The results are shown in figure A.
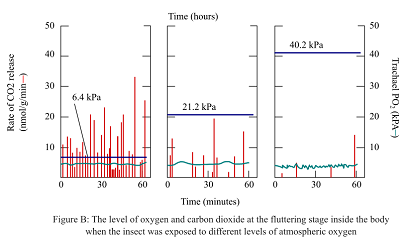
In order to examine the spiracles performance in the different atmospheric conditions and their effects on the rate of CO2 release and O2 concentrations, pupae were exposed to the different levels of atmospheric O2. The levels of the release of CO2 and O2 concentrations were calculated during the fluttering stage as shown in the figure B.
Introduction:
The insectys have a unique mechanism of air exchange in their bodies. The respiratory system of the insects consists of the tracheae that is responsible for the gaseous exchange in and out of tissues. There are spiracles present that guards the trachea. They are valve-like and either remains open, closed, or in a fluttering state.
Explanation of Solution
Intratracheal partial pressure of O2 during the open phase of the spiracles in the tracheae as shown in the figure is 20.4 kPa.
If 1 kPa = 7.5mm Hg, then, Po2 during the open phase will be,7.5*20.4 = 153 mm Hg.
During the closed phase, Po2 decreases to 4–5 kPa.
If 1 kPa = 7.5mm Hg, then, PO2 during the closed phase will be,7.5*5 = 37.5 mm Hg.
During the fluttering phase, if the oxygen concentration is changed as shown in figure B, the PO2 will be calculated as
Case1, If 1 kPa = 7.5mm Hg, 7.5*6.4 = 48 mm Hg.
Case2, If 1 kPa = 7.5mm Hg, 7.5*21.2 = 159 mm Hg.
Case3, If 1 kPa = 7.5mm Hg, 7.5*40.2 = 301.5 mm Hg.
Thus, it can be concluded that the changes in approximate mm Hg of PO2 in a typical open-close fluttering cycle are 153 mm Hg and 7.5 mm Hg during the open and closed phases, respectively. Also, in the tubes of the trachea, in all the three given cases, the pressure was 48 mm Hg, 159 mm Hg, and 301.5 mm Hg, respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 48 Solutions
LIFE:SCIENCE OF BIOL.(LL) >CUSTOM<
- What is the concept "calories consumed must equal calories burned" in regrads to nutrition?arrow_forwardYou intend to insert patched dominant negative DNA into the left half of the neural tube of a chick. 1) Which side of the neural tube would you put the positive electrode to ensure that the DNA ends up on the left side? 2) What would be the internal (within the embryo) control for this experiment? 3) How can you be sure that the electroporation method itself is not impacting the embryo? 4) What would you do to ensure that the electroporation is working? How can you tell?arrow_forwardDescribe a method to document the diffusion path and gradient of Sonic Hedgehog through the chicken embryo. If modifying the protein, what is one thing you have to consider in regards to maintaining the protein’s function?arrow_forward
- The following table is from Kumar et. al. Highly Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor (DR) Antagonists and Partial Agonists Based on Eticlopride and the D3R Crystal Structure: New Leads for Opioid Dependence Treatment. J. Med Chem 2016.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. You are a chef in a fancy new science-themed restaurant. You have a recipe that calls for 1 teaspoon of resinferatoxin, but you feel uncomfortable serving foods with "toxins" in them. How much capsaicin could you substitute instead?arrow_forwardWhat protein is necessary for packaging acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles?arrow_forward
- 1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forwardDetermine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forward
- Choose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. a) Which has a higher potency? b) Which is has a higher efficacy? c) What is the approximate Kd of capsaicin in uM? (you can round to the nearest power of 10)arrow_forwardWhat is the rate-limiting-step for serotonin synthesis?arrow_forward
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning- Case Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
 Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781337794909Author:Des Jardins, Terry.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781337794909Author:Des Jardins, Terry.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





