
Concept explainers
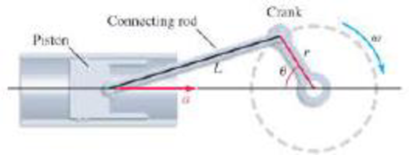
Crankshaft A crank of radius r rotates with an angular frequency ω. It is connected to a piston by a connecting rod of length L (see figure). The acceleration of the piston varies with the position of the crank according to the function
For fixed ω, L, and r, find the values of θ, with 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π, for which the acceleration of the piston is a maximum and minimum.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Single Variable Calculus: Early Transcendentals, Books a la Carte, and MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Title-Specific Access Card Package (3rd Edition)
- 2 prove that Dxy #Dx Dyarrow_forwardEXAMPLE 3 Find S X √√2-2x2 dx. SOLUTION Let u = 2 - 2x². Then du = Χ dx = 2- 2x² = 信 du dx, so x dx = du and u-1/2 du (2√u) + C + C (in terms of x).arrow_forwardLet g(z) = z-i z+i' (a) Evaluate g(i) and g(1). (b) Evaluate the limits lim g(z), and lim g(z). 2-12 (c) Find the image of the real axis under g. (d) Find the image of the upper half plane {z: Iz > 0} under the function g.arrow_forward
- k (i) Evaluate k=7 k=0 [Hint: geometric series + De Moivre] (ii) Find an upper bound for the expression 1 +2x+2 where z lies on the circle || z|| = R with R > 10. [Hint: Use Cauchy-Schwarz]arrow_forward21. Determine for which values of m the function (x) = x™ is a solution to the given equation. a. 3x2 d²y dx² b. x2 d²y +11x dy - 3y = 0 dx dy dx2 x dx 5y = 0arrow_forwardhelp me solve thisarrow_forward
- help me solve thisarrow_forwardHint: You may use the following derivative rules: ddxsin(x)=cos(x) ddxcos(x)=−sin(x) ddxln(x)=1x Find the equation of the tangent line to the curve y=4sinx at the point (π6,2).The equation of this tangent line isarrow_forwardQuestion Find the following limit. Select the correct answer below: 1 2 0 4 5x lim sin (2x)+tan 2 x→arrow_forward
- 12. [0/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 5.5.022. Evaluate the indefinite integral. (Use C for the constant of integration.) sin(In 33x) dxarrow_forward2. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 5.5.003.MI. Evaluate the integral by making the given substitution. (Use C for the constant of integration.) x³ + 3 dx, u = x² + 3 Need Help? Read It Watch It Master It SUBMIT ANSWER 3. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 5.5.006.MI. Evaluate the integral by making the given substitution. (Use C for the constant of integration.) | +8 sec² (1/x³) dx, u = 1/x7 Need Help? Read It Master It SUBMIT ANSWER 4. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 5.5.007.MI. Evaluate the indefinite integral. (Use C for the constant of integration.) √x27 sin(x28) dxarrow_forward53,85÷1,5=arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning




