
Concept explainers
(a)
To find:
(a)
Answer to Problem 2E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Definition used:
Let
Calculation:
The graph of the given function f is shown below:
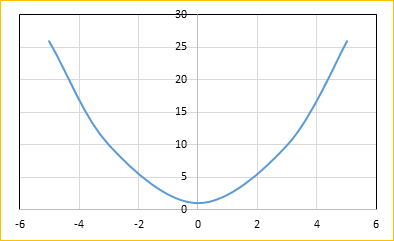
From the graph, it is clear that on the subset
The minimum value of function f will be:
The maximum value of function f will be:
Since
∴
(b)
To find:
(b)
Answer to Problem 2E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Theorem used:
Let
Then,
Calculation:
From the graph, it is clear that on the subset
The minimum value of function f will be:
The maximum value of function f will be:
On the subset
The minimum value of function f will be:
The maximum value of function f will be:
(c)
To find:
(c)
Answer to Problem 2E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Definition used:Let
Calculation:
Since
That is
(d)
To find:
(d)
Answer to Problem 2E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Definition used: Let
Calculation:
Since
That is, for
∴The possible values of x are
∴
(e)
To find:
(e)
Answer to Problem 2E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Formulas used:Let
Calculation:
For,
∴The possible values of x are
∴
(f)
To find:
(f)
Answer to Problem 2E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Formulas used:
Let
Calculation:
To calculate
Since
That is, for
∴
To calculate
∴The possible values of x are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
A Transition to Advanced Mathematics
- Page < 2 of 2 - ZOOM + The set of all 3 x 3 upper triangular matrices 6) Determine whether each of the following sets, together with the standard operations, is a vector space. If it is, then simply write 'Vector space'. You do not have to prove all ten vector space axioms. If it is not, then identify one of the ten vector space axioms with its number in the attached sheet that fails and also show that how it fails. a) The set of all polynomials of degree four or less. b) The set of all 2 x 2 singular matrices. c) The set {(x, y) : x ≥ 0, y is a real number}. d) C[0,1], the set of all continuous functions defined on the interval [0,1]. 7) Given u = (-2,1,1) and v = (4,2,0) are two vectors in R³-space. Find u xv and show that it is orthogonal to both u and v. 8) a) Find the equation of the least squares regression line for the data points below. (-2,0), (0,2), (2,2) b) Graph the points and the line that you found from a) on the same Cartesian coordinate plane.arrow_forwardPage < 1 of 2 - ZOOM + 1) a) Find a matrix P such that PT AP orthogonally diagonalizes the following matrix A. = [{² 1] A = b) Verify that PT AP gives the correct diagonal form. 2 01 -2 3 2) Given the following matrices A = -1 0 1] an and B = 0 1 -3 2 find the following matrices: a) (AB) b) (BA)T 3) Find the inverse of the following matrix A using Gauss-Jordan elimination or adjoint of the matrix and check the correctness of your answer (Hint: AA¯¹ = I). [1 1 1 A = 3 5 4 L3 6 5 4) Solve the following system of linear equations using any one of Cramer's Rule, Gaussian Elimination, Gauss-Jordan Elimination or Inverse Matrix methods and check the correctness of your answer. 4x-y-z=1 2x + 2y + 3z = 10 5x-2y-2z = -1 5) a) Describe the zero vector and the additive inverse of a vector in the vector space, M3,3. b) Determine if the following set S is a subspace of M3,3 with the standard operations. Show all appropriate supporting work.arrow_forwardPlease help solve the following whilst showing all working out. Is part of exam revision questions but no solution is givenarrow_forward
- please help me with this question with working out thanksarrow_forwardPage < 1 of 2 - ZOOM + 1) a) Find a matrix P such that PT AP orthogonally diagonalizes the following matrix A. = [{² 1] A = b) Verify that PT AP gives the correct diagonal form. 2 01 -2 3 2) Given the following matrices A = -1 0 1] an and B = 0 1 -3 2 find the following matrices: a) (AB) b) (BA)T 3) Find the inverse of the following matrix A using Gauss-Jordan elimination or adjoint of the matrix and check the correctness of your answer (Hint: AA¯¹ = I). [1 1 1 A = 3 5 4 L3 6 5 4) Solve the following system of linear equations using any one of Cramer's Rule, Gaussian Elimination, Gauss-Jordan Elimination or Inverse Matrix methods and check the correctness of your answer. 4x-y-z=1 2x + 2y + 3z = 10 5x-2y-2z = -1 5) a) Describe the zero vector and the additive inverse of a vector in the vector space, M3,3. b) Determine if the following set S is a subspace of M3,3 with the standard operations. Show all appropriate supporting work.arrow_forwardUsing Karnaugh maps and Gray coding, reduce the following circuit represented as a table and write the final circuit in simplest form (first in terms of number of gates then in terms of fan-in of those gates).arrow_forward
- Consider the alphabet {a, b, c}.• Design a regular expression that recognizes all strings over {a, b, c} that have at least three nonconsec-utive c characters (two characters are non-consecutive if there is at least one character between them)and at least one a character.• Explain how your regular expression recognizes the string cbbcccac by clearly identifying which partsof the string match to the components of your regular expressionarrow_forwardComplex Analysis 2 z3+3 Q1: Evaluate cz(z-i)² the Figure. First exam 2024-2025 dz, where C is the figure-eight contour shown inarrow_forwardConstruct a state-level description (i.e., a state diagram with transitions) for aTuring machine that decides the language {a^(n)b^(2n)c^(n) | n ∈ N}.arrow_forward
- Find the sum of products expansion of the function F (x, y, z) = ̄x · y + x · z in two ways: (i) using a table; and (ii) using Boolean identitiesarrow_forwardThe NOR operator, denoted as ↓, behaves as 0 ↓ 0 = 1, 0 ↓ 1 = 0, 1 ↓ 0 = 0,1 ↓ 1 = 0. Show that the any Boolean function over any number of variables can be expressed using onlyNOR operators (in addition to those variables and constants). HINT: Recall that any Boolean function hasa representation as a sum of products expansionarrow_forwardConsider the Turing machine given in lecture which decides the languageB = {w#w | w is a binary string}.Simulate the Turing machine to show that the string 1001#1001 will be accepted by the Turing machine. Show all steps.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Elements Of Modern AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285463230Author:Gilbert, Linda, JimmiePublisher:Cengage Learning,
Elements Of Modern AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285463230Author:Gilbert, Linda, JimmiePublisher:Cengage Learning, Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning



