
Concept explainers
A mass of 3 kg of saturated liquid–vapor mixture of water is contained in a piston–cylinder device at 160 kPa. Initially, 1 kg of the water is in the liquid phase and the rest is in the vapor phase. Heat is now transferred to the water, and the piston, which is resting on a set of stops, starts moving when the pressure inside reaches 500 kPa. Heat transfer continues until the total volume increases by 20 percent. Determine (a) the initial and final temperatures, (b) the mass of liquid water when the piston first starts moving, and (c) the work done during this process. Also, show the process on a P-v diagram.
FIGURE P4–120
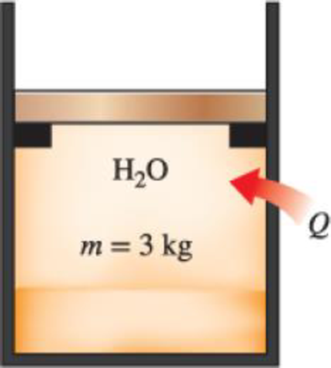
(a)
The initial temperature of the piston cylinder device.
The final temperature of the piston cylinder device.
Answer to Problem 120RP
The initial temperature of the piston cylinder device is
The final temperature of the piston cylinder device is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the total initial volume of piston cylinder device.
Here, the mass of the liquid phase is
Determine the total volume of the piston cylinder device at final state.
Determine the specific volume of the piston cylinder device at final state.
Here, the mass of the saturated liquid vapour mixture of water is contained in a piston cylinder device is
Conclusion:
Write the formula of interpolation method of two variables.
Here, the variables denote by x and y is saturated pressure and saturated temperature.
For initial temperature of the piston cylinder device.
Show the temperature at pressure of 150 kPa, 160 kPa, and 175 kPa as in Table (1).
|
Pressure, kPa |
Temperature, C |
| 150 kPa | 111.35 |
| 160 kPa | |
| 175 kPa | 116.04 |
Substitute the value of x and y from Table (1) in Equation (IV) to calculate the value of initial temperature
Thus, the initial temperature of the piston cylinder device is
For specific volume of saturated liquid of the piston cylinder device.
Show the specific volume of saturated liquid at pressure of 150 kPa, 160 kPa, and 175 kPa as in Table (2).
|
Pressure, kPa |
Specific volume of saturated liquid, |
| 150 kPa | 0.001053 |
| 160 kPa | |
| 175 kPa | 0.001057 |
Substitute the value of x and y from Table (2) in Equation (IV) to calculate the value of specific volume of saturated liquid
For specific volume of saturated vapour of the piston cylinder device.
Show the specific volume of saturated vapour at pressure of 150 kPa, 160 kPa, and 175 kPa as in Table (3).
|
Pressure, kPa |
Specific volume of saturated vapour, |
| 150 kPa | 1.1594 |
| 160 kPa | |
| 175 kPa | 1.0037 |
Substitute the value of x and y from Table (3) in Equation (IV) to calculate the value of specific volume of saturated vapour
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The unit conversion of pressure from kPa to MPa.
For temperature of the piston cylinder device at final state.
Show the temperature at specific volume of the piston cylinder device at final state at
|
specific volume of the piston cylinder device at final state, |
Temperature, |
| 600 | |
| 700 |
Substitute the value of x and y from Table (4) in Equation (IV) to calculate the value of temperature of the piston cylinder device at final state
Thus, the final temperature of the piston cylinder device is
(b)
The mass of liquid water when the piston first starts moving.
Answer to Problem 120RP
The mass of liquid water when the piston first starts moving is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the specific volume of the piston cylinder device at this state.
Here, the mass of the saturated liquid vapour mixture of water is contained in a piston cylinder device is
Conclusion:
Since,
Substitute
Therefore, the value of specific volume of the piston cylinder device at this state is greater than
Thus, the mass of liquid water when the piston first starts moving is
(c)
The work done during the process state 2 and 3.
Answer to Problem 120RP
The work done during the process state 2 and 3 is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the work done in constant pressure process.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the work done during the process state 2 and 3 is
Show the P-v diagram of this process.
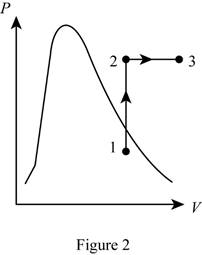
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS: ENG APPROACH LOOSELEAF
- Which of the following sequences converge and which diverge? 1/n 1) a₁ = 2+(0.1)" 3 16) a = n 1-2n 2) a = In n 1+2n 17) an = 1/n n 1-5n4 3) an = n² +8n³ 18) an = √4" n n! n² -2n+1 20) a = 4) an = 106 5) n-1 a₁ =1+(-1)" n+1 a-(+) (1-4) 6) = 7) a = 2n (-1)"+1 2n-1 21) an = n -A" 1/(Inn) 3n+1 22) a = 3n-1 1/n x" 23) a = , x>0 2n+1 3" x 6" 24) a = 2™" xn! 2n 8) a = n+1 πT 1 9) a„ = sin +- 2 n sin n 10) an = n 25) a = tanh(n) 26) a = 2n-1 27) a = tan(n) 1 -sin n n 11) a = 2" 28) an == " 1 + 2" In(n+1) 12) a = n (In n) 200 29) a = n 13) a = 8/n 14) a 1+ =(1+²)" 15) an 7 n = 10n 30) an-√√n²-n 1"1 31) adx nixarrow_forwardCalculate the angle of incidence of beam radiation on a collector located at (Latitude 17.40S) on June 15 at 1030hrs solar time. The collector is tilted at an angle of 200, with a surface azimuth angle of 150.arrow_forwardMechanical engineering, please don't use chatgpt. Strict warningarrow_forward
- Compute the mass fraction of eutectoid cementite in an iron-carbon alloy that contains 1.00 wt% C.arrow_forwardCompute the mass fraction of eutectoid cementite in an iron-carbon alloy that contains 1.00 wt% C.arrow_forward! Required information Mechanical engineering, don't use chatgpt. Thanks A 60-kip-in. torque T is applied to each of the cylinders shown. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. 3 in. 4 in. (a) (b) Determine the inner diameter of the 4-in. diameter hollow cylinder shown, for which the maximum stress is the same as in part a. The inner diameter is in.arrow_forward
- Mechanical engineering, Don't use chatgpt. Strict warning.arrow_forward10:38 PM P 4136 54 A man Homework was due west for and 4km. He then changes directies walks on a bearing south-wes IS How far Point? of 1970 until he of his Starting Port Is he then from his stating What do you think about ... ||| Մ כarrow_forwardA simply supported T-shaped beam of 6m in length has to be designed to carry an inclined central point load W. Find the max- imum value of this load such that the maximum tensile and com- pression stresses on the beam do not exceed 30 and 60 respectively. N mm² N mm², 90 mm 80 mm Y W 60 mm 30° 10 mm 10 mm Xarrow_forward
- Problem 9.5 9.5 A 1080-kg car is parked on a sloped street. The figure shows its wheels and the position of its center of mass. The street is icy, and as a result the coefficient of static friction between the car's tires and the street surface is μs = 0.2. Determine the steepest slope (in degrees relative to the horizontal) at which the car could remain in equilibrium if a. the brakes are applied to both its front and rear wheels; b. the brakes are applied to the front (lower) wheels only. Problem 9.5 1380 mm 532 mm 2370 mmarrow_forwardCan someone explain please with conversionsarrow_forwardCorrect Answer is written below. Detailed and complete fbd only please. I will upvote, thank you. 1: The assembly shown is composed of a rigid plank ABC, supported by hinge at A, spring at B and cable at C.The cable is attached to a frictionless pulley at D and rigidly supported at E. The cable is made of steel with E = 200,000MPa and cross-sectional area of 500 mm2. The details of pulley at D is shown. The pulley is supported by a pin, passingthough the pulley and attached to both cheeks. Note that E is directly above B.Given: H = 3 m; L1 = 2 m; L2 = 4 m; w = 12 kN/m; x:y = 3:4Spring Parameters:Wire diameter = 30 mmMean Radius = 90 mmNumber of turns = 12Modulus of Rigidity = 80 GPaAllowable stresses:Allowable shear stress of Pin at D = 85 MPaAllowable normal stress of cheek at D = 90MPaAllowable bearing stress of cheek at D = 110MPa1. Calculate the reaction of spring Band tension in cable at C.2. Calculate the vertical displacementat C and the required diameter ofpin at D.3.…arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





