
Concept explainers
Presidents and first ladies: The presents the ages of the last 10 U.S. presidents and their wives on the first day of their presidencies.
- Compute the least-squares regression line for predicting the president’s age from the first lady’s age.
- Compute the coefficient of determination-
- Construct a
scatterplot of the presidents' ages (y) versus the first ladies' ages (x). - Which point is an outlier?
- Remove die outlier and compute the least-squares regression line for predicting the president’s age from the first lady: s age.
- Is the outlier influential? Explain.
- Compute the coefficient of determination for the data set with the outlier removed. Is due proportion of variation explained by due least-squares regression he greater, less. or about the same without due outlier? Explain.
a.
To Calculate: The least-squares regression line for predicting the president’s age from lady’s age.
Answer to Problem 24E
The least-squares regression line is,
Explanation of Solution
Given: The following table presents the age of the president’s and their wives on the first day of their presidencies.
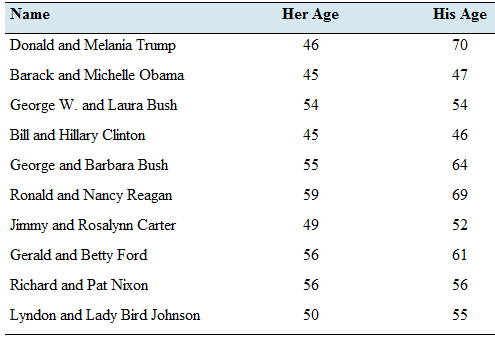
| Name | Her Age | His Age |
| Donald and Melania Trump | 46 | 70 |
| Barak and Mechelle Obama | 45 | 47 |
| George W. and Laura Bush | 54 | 54 |
| Bill and Hillary Clinton | 45 | 46 |
| George and Babara Bush | 55 | 64 |
| Ronald and Nancy Reagan | 59 | 69 |
| Jimmy and Rosalyn Carter | 49 | 52 |
| Gerald and Betty Ford | 56 | 61 |
| Richard and Pat Nixon | 56 | 56 |
| Lyndon and Lady Bird Johnson | 50 | 55 |
Calculation:
Here,
From below formula we can find least regression line.
where
We can find these constants from below formulas.
Where,
| Descriptive Statistics | |||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| His age | 10 | 57.40 | 8.409 |
| Her age | 10 | 51.50 | 5.148 |
| Valid N (listwise) | 10 | ||
To find constants,
And,
By substituting above formula,
Conclusion:
The least-squares regression line for predicting the president’s age from lady’s age is,
b.
To find: The correlation coefficient of the two variables.
Answer to Problem 24E
The correlation coefficient is found to be,
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The correlation coefficient
Where
The means and the standard deviations of the both variables can be obtained by using the Excel.
| Descriptive Statistics | |||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| His age | 10 | 57.40 | 8.409 |
| Her age | 10 | 51.50 | 5.148 |
| Valid N (listwise) | 10 | ||
Then,
Then, a table should be constructed to calculate
The correlation coefficient can be calculated as,
Conclusion:
The correlation coefficient between the interest rates for two mortgage plans is found tobe,
c.
To graph: The scatter plot of the given two quantitative variables.
Explanation of Solution
Graph:
Let
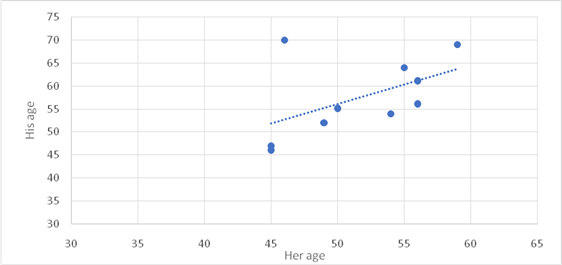
Interpretation:
Out of all these
d.
To Identify: The outliers within the given data.
Answer to Problem 24E
There is one outlier which is age
Explanation of Solution
Explain:
Here, Excel is used to calculate below statistics.
The interquartile range is equal to
To calculate upper bound,
To calculate lower bound,
An outlier is a data point that lies outside the upper bound and lower bound.
Out of all
e.
To find: The least-squares regression line for predicting the president’s age from lady’s age with removing outlier.
Answer to Problem 24E
The least-squares regression is,
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Here,
From below formula we can find least regression line.
where
We can find constants from below formulas.
Where,
When the outlier is removed, the number of ordered pairs is
| Descriptive Statistics | |||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| His age | 9 | 56.00 | 7.583 |
| Her age | 9 | 52.11 | 5.061 |
| Valid N (listwise) | 9 | ||
To find constants,
And,
By substituting into the above formula,
Conclusion:
The least-squares regression line for predicting the president’s age from lady’s age is,
f.
To Check: The influence of outlier.
Answer to Problem 24E
Yes. It is influenced.
Explanation of Solution
Explain:
| Descriptive Statistics | |||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| His age | 10 | 57.40 | 8.409 |
| Her age | 10 | 51.50 | 5.148 |
| Valid N (listwise) | 10 | ||
| Descriptive Statistics | |||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| His age | 9 | 56.00 | 7.583 |
| Her age | 9 | 52.11 | 5.061 |
| Valid N (listwise) | 9 | ||
To calculate above statistics, Excel is used. Here we can see statistics with outlier and without outlier. Second table shows statistics without outlier. Total number of observations, mean and standard deviation of dependent and independent variables are changed. So, it influences to least squares regression line for predicting the president’s age from lady’s age.
g.
To find: The correlation coefficient of the two variables without outlier.
Answer to Problem 24E
The correlation coefficient is found to be,
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The correlation coefficient
Where
The means and the standard deviations of the both variables can be obtained by using the Excel.
For the remaining
| Descriptive Statistics | |||
| N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| His age | 9 | 56.00 | 7.583 |
| Her age | 9 | 52.11 | 5.061 |
| Valid N (listwise) | 9 | ||
Then,
Then, a table should be constructed to calculate
The correlation coefficient can be calculated as,
Conclusion:
The correlation coefficient between the interest rates for two mortgage plans is found to be,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
ELEMENTARY STATISTICS(LL)(FD)
- 1. (i) Explain the difference in application between the Mann-Whitney U test and the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test, i.e. in which scenarios would each test be used? (ii) What is the main procedure underlying these nonparametric tests? [3 Marks]arrow_forwardYou may need to use the appropriate appendix table or technology to answer this question. You are given the following information obtained from a random sample of 4 observations. 24 48 31 57 You want to determine whether or not the mean of the population from which this sample was taken is significantly different from 49. (Assume the population is normally distributed.) (a) State the null and the alternative hypotheses. (Enter != for ≠ as needed.) H0: Ha: (b) Determine the test statistic. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) (c) Determine the p-value, and at the 5% level of significance, test to determine whether or not the mean of the population is significantly different from 49. Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) p-value = State your conclusion. Reject H0. There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the mean of the population is different from 49.Do not reject H0. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the…arrow_forward65% of all violent felons in the prison system are repeat offenders. If 43 violent felons are randomly selected, find the probability that a. Exactly 28 of them are repeat offenders. b. At most 28 of them are repeat offenders. c. At least 28 of them are repeat offenders. d. Between 22 and 26 (including 22 and 26) of them are repeat offenders.arrow_forward
- 08:34 ◄ Classroom 07:59 Probs. 5-32/33 D ا. 89 5-34. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at the pin A and the normal force at the smooth peg B on the member. A 0,4 m 0.4 m Prob. 5-34 F=600 N fr th ar 0. 163586 5-37. The wooden plank resting between the buildings deflects slightly when it supports the 50-kg boy. This deflection causes a triangular distribution of load at its ends. having maximum intensities of w, and wg. Determine w and wg. each measured in N/m. when the boy is standing 3 m from one end as shown. Neglect the mass of the plank. 0.45 m 3 marrow_forwardExamine the Variables: Carefully review and note the names of all variables in the dataset. Examples of these variables include: Mileage (mpg) Number of Cylinders (cyl) Displacement (disp) Horsepower (hp) Research: Google to understand these variables. Statistical Analysis: Select mpg variable, and perform the following statistical tests. Once you are done with these tests using mpg variable, repeat the same with hp Mean Median First Quartile (Q1) Second Quartile (Q2) Third Quartile (Q3) Fourth Quartile (Q4) 10th Percentile 70th Percentile Skewness Kurtosis Document Your Results: In RStudio: Before running each statistical test, provide a heading in the format shown at the bottom. “# Mean of mileage – Your name’s command” In Microsoft Word: Once you've completed all tests, take a screenshot of your results in RStudio and paste it into a Microsoft Word document. Make sure that snapshots are very clear. You will need multiple snapshots. Also transfer these results to the…arrow_forwardExamine the Variables: Carefully review and note the names of all variables in the dataset. Examples of these variables include: Mileage (mpg) Number of Cylinders (cyl) Displacement (disp) Horsepower (hp) Research: Google to understand these variables. Statistical Analysis: Select mpg variable, and perform the following statistical tests. Once you are done with these tests using mpg variable, repeat the same with hp Mean Median First Quartile (Q1) Second Quartile (Q2) Third Quartile (Q3) Fourth Quartile (Q4) 10th Percentile 70th Percentile Skewness Kurtosis Document Your Results: In RStudio: Before running each statistical test, provide a heading in the format shown at the bottom. “# Mean of mileage – Your name’s command” In Microsoft Word: Once you've completed all tests, take a screenshot of your results in RStudio and paste it into a Microsoft Word document. Make sure that snapshots are very clear. You will need multiple snapshots. Also transfer these results to the…arrow_forward
- Examine the Variables: Carefully review and note the names of all variables in the dataset. Examples of these variables include: Mileage (mpg) Number of Cylinders (cyl) Displacement (disp) Horsepower (hp) Research: Google to understand these variables. Statistical Analysis: Select mpg variable, and perform the following statistical tests. Once you are done with these tests using mpg variable, repeat the same with hp Mean Median First Quartile (Q1) Second Quartile (Q2) Third Quartile (Q3) Fourth Quartile (Q4) 10th Percentile 70th Percentile Skewness Kurtosis Document Your Results: In RStudio: Before running each statistical test, provide a heading in the format shown at the bottom. “# Mean of mileage – Your name’s command” In Microsoft Word: Once you've completed all tests, take a screenshot of your results in RStudio and paste it into a Microsoft Word document. Make sure that snapshots are very clear. You will need multiple snapshots. Also transfer these results to the…arrow_forward2 (VaR and ES) Suppose X1 are independent. Prove that ~ Unif[-0.5, 0.5] and X2 VaRa (X1X2) < VaRa(X1) + VaRa (X2). ~ Unif[-0.5, 0.5]arrow_forward8 (Correlation and Diversification) Assume we have two stocks, A and B, show that a particular combination of the two stocks produce a risk-free portfolio when the correlation between the return of A and B is -1.arrow_forward
- 9 (Portfolio allocation) Suppose R₁ and R2 are returns of 2 assets and with expected return and variance respectively r₁ and 72 and variance-covariance σ2, 0%½ and σ12. Find −∞ ≤ w ≤ ∞ such that the portfolio wR₁ + (1 - w) R₂ has the smallest risk.arrow_forward7 (Multivariate random variable) Suppose X, €1, €2, €3 are IID N(0, 1) and Y2 Y₁ = 0.2 0.8X + €1, Y₂ = 0.3 +0.7X+ €2, Y3 = 0.2 + 0.9X + €3. = (In models like this, X is called the common factors of Y₁, Y₂, Y3.) Y = (Y1, Y2, Y3). (a) Find E(Y) and cov(Y). (b) What can you observe from cov(Y). Writearrow_forward1 (VaR and ES) Suppose X ~ f(x) with 1+x, if 0> x > −1 f(x) = 1−x if 1 x > 0 Find VaRo.05 (X) and ES0.05 (X).arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning




