
Biology (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781337392938
Author: Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 42, Problem 8TYU
Test Your Understanding
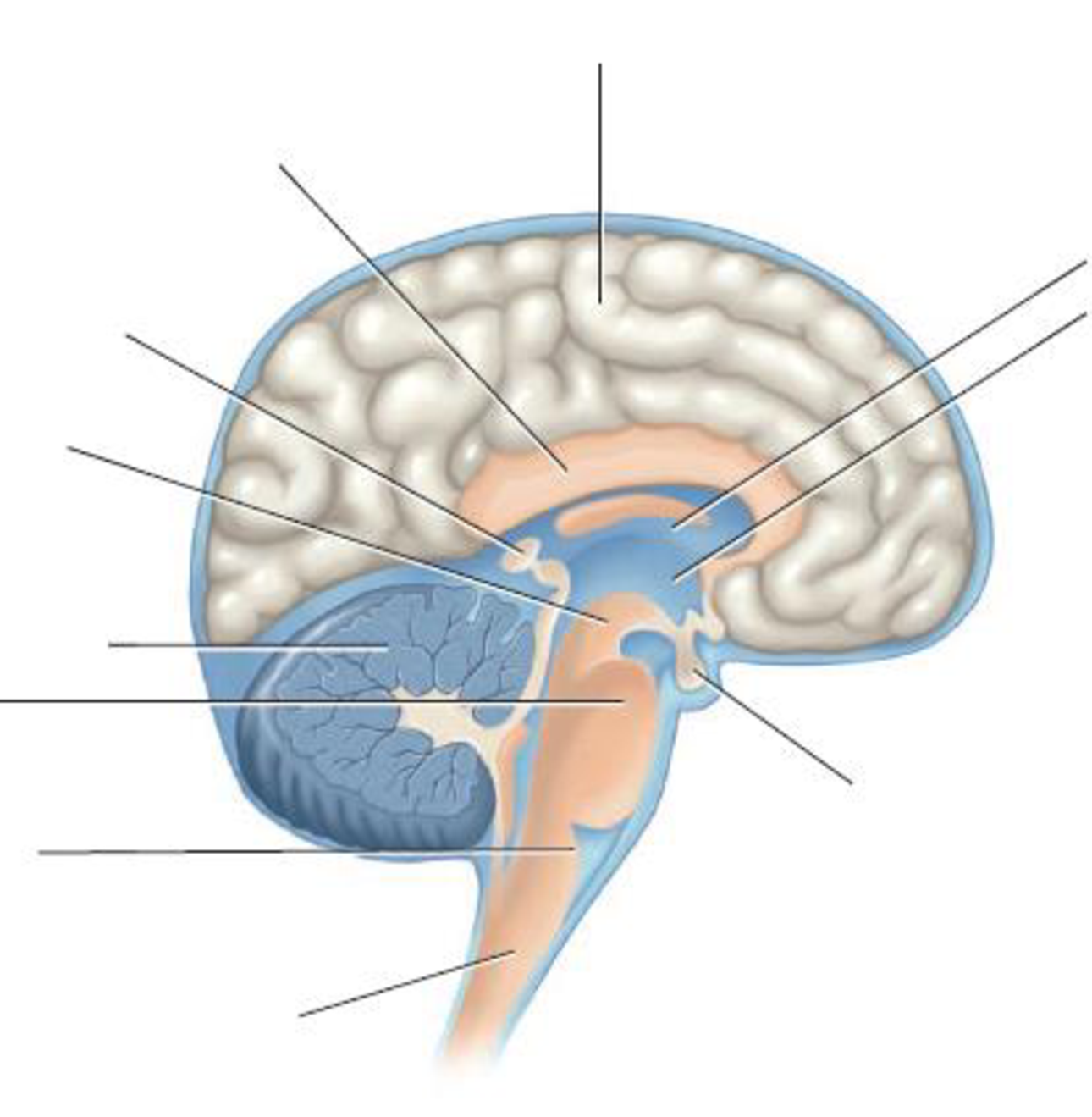
8. VISUALIZE Label the diagram of the human brain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Explain down bellow what happens to the cell in pictures not in words:
Decreased pH in mitochondria
Increased ATP
Decreased pH in cytosol
Increased hydrolysis
Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides
Increased MAP kinase activity
Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?
1.) Community Diversity:
The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities.
a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness?
b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness?
Relative abundance
0.1
0.04
0.001
2 4 6
8
10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
Rank abundance
c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's
index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)?
d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of
species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?
1.) Community Diversity:
The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities.
a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness?
b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness?
Relative abundance
0.1
0.04
0.001
2 4 6
8
10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
Rank abundance
c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's
index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)?
d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of
species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?
Chapter 42 Solutions
Biology (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 42.1 - Prob. 1LOCh. 42.1 - Identify trends in the evolution of invertebrate...Ch. 42.1 - Prob. 1CCh. 42.1 - Prob. 2CCh. 42.1 - What are some advantages of cephalization?Ch. 42.2 - Prob. 3LOCh. 42.2 - Prob. 1CCh. 42.2 - Describe the functions of each component of the...Ch. 42.3 - Prob. 4LOCh. 42.3 - Prob. 1C
Ch. 42.3 - Prob. 2CCh. 42.4 - Prob. 5LOCh. 42.4 - Prob. 6LOCh. 42.4 - Prob. 7LOCh. 42.4 - Prob. 8LOCh. 42.4 - Prob. 9LOCh. 42.4 - Prob. 1CCh. 42.4 - What are two main functions of the vertebrate...Ch. 42.4 - Prob. 3CCh. 42.4 - What role does the limbic system play in emotions?...Ch. 42.4 - In what ways does your success on a biology exam...Ch. 42.5 - Describe the organization of the peripheral...Ch. 42.5 - Prob. 11LOCh. 42.5 - Prob. 1CCh. 42.5 - Prob. 2CCh. 42.6 - Prob. 12LOCh. 42.6 - Prob. 1CCh. 42 - Test your Understanding Know and Comprehend A...Ch. 42 - Which part of the vertebrate brain maintains...Ch. 42 - The main association area in the amphibian brain...Ch. 42 - Prob. 4TYUCh. 42 - Prob. 5TYUCh. 42 - Prob. 6TYUCh. 42 - Prob. 7TYUCh. 42 - Test Your Understanding 8. VISUALIZE Label the...Ch. 42 - Prob. 9TYUCh. 42 - Prob. 10TYUCh. 42 - Prob. 11TYUCh. 42 - EVOLUTION LINK CREB has been shown to be a...Ch. 42 - Prob. 13TYU
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- what measures can a mother to take to improve the produce of her to milk to her newborn baby ?arrow_forward1. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Eastern white pine tree green (but only the ancestral line NOT shared with other organisms) 2. Oncle the last common ancestor of the Colorado blue spruce tree and Eastern white pine tree. 3. Put a box around the last common ancestor of the sugar maple tree and the dogwood tree. 4. Put a triangle around the last common ancestor of the red pine tree and the american holly bush. 5. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Ponderosa pine tree red (including all shared ancestors). 6. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the American elm tree blue (including all shared ancestors). 7 Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Sabal palm tree purple (including all shared ancestors) 8. Using a yellow highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all pine trees. 9. Using a orange highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all gymnosperms 10. Can you tell…arrow_forwardYou have been hired as a public relations specialist to give invertebrates a good name. After all, they are much more than just creepy crawly bugs! Your first task though is to convince yourself that is true. The best way to do that is to start close to home. Find something in your house that is a product obtained directly from an invertebrate or only due to an invertebrate’s actions. Describe the product, its function and utility, as well as any human manufactured alternatives. Be sure to highlight the advantages of obtaining this directly from nature. Keep in mind, a product can be something you use, wear, eat, or enjoy for its visual appeal.arrow_forward
- Use the following tree diagram to answer Questions #8-10. 8) Which of the following two animals are the most closely related based on the tree to the left? a) Pig and camel b) Hippo and pig c) Deer and cow 9) CIRCLE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a hippo and a cow is. 10) Put a SQUARE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a pig and a peccary is.arrow_forwardExplain: Healthy Cell Function Overview→ Briefly describe how a healthy cell usually works: metabolism (ATP production), pH balance, glycogen storage, ion transport, enzymes, etc. Gene Mutation and Genetics Part→ Focus on the autosomal recessive mutation and explain: How gene mutation affects the cell. How autosomal inheritance works. Compare the normal and mutated gene sequences simply. → Talk about possible consequences of a faulty hydrolytic enzyme.arrow_forwardCan you fill out those termsarrow_forward
- Explain down bellow what happens to the cell: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forwardAn 1100 pound equine patient was given 20 mg/kg sucralfate 3 times a day, 2.8 mg/kg famotidine twice a day, and 10mg/kg doxycycline twice a day. Sucralfate comes as a 1 gm tablet, famotidine as 20 mg tablets, and doxycycline as 100mg tablets. All are in bottles of 100 tablets.How many total mg are needed for the patient and how many tablets of each would be needed to provide each dose?How many bottles of each would be needed to have available if this patient were to be on this drug regimen for 5 days?arrow_forwardThe patient needs a solution of 2.5% dextrose in Lactated Ringer’s solution to run at 75 ml/hr for at least the next 12hours. LRS comes in fluid bags of 500 ml, 1 Liter, 3 Liters and 5 Liters. How can a 2.5% solution be made by adding50% dextrose to the LRS?arrow_forward
- “Gretchen” was a 68-pound canine who came to the VMTH as small animal surgery patient. She receivedacepromazine, 0.2 mg/kg from a 10 mg/ml solution and oxymorphone, 0.08 mg/kg from a 1 mg/ml solution before surgery.What are the mechanisms of action of acepromazine and oxymorphone? Why would they be given together?How many mg provide each dose and how many ml of each of these solutions were given?arrow_forwardAfter surgery, “Gretchen” was put on carprofen, 1 mg/pound bid (twice a day). The tablets come in 25, 75 and 100 mgsizes. Which size tablet would be appropriate?What is the mechanism of action of carprofen?An outpatient prescription was written for her so she would have enough for 10 days. How many tablets did she need?What information needs to be on her out-patient prescription?arrow_forwardJoden Koepp olor in chickens is due to incomplete dominance. BB = Black chicken, WW = White BLOOD TYPES Arhite chicken is In humans, Rh positive blood is dominant (R) over Rh negative blood (r). A man with type 0, Rh positive blood (whose mother had Rh negative blood), marries a woman with type AB, Rh negative blood. Several children were born. is? R R Genotypes Phenotypes RRR RR Rr Rr 4/16 RR R RR RK Rr Rr 4/16 rr 3/4 Rh posi 1/4 Rh negu 1/2 Rr rr rr rrrr 88 888 75 e genotype of the man? the genotype of the woman? The mother of the man had type AB blood.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781337794909Author:Des Jardins, Terry.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781337794909Author:Des Jardins, Terry.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College

Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781337794909
Author:Des Jardins, Terry.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781337408332
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Nervous System - Get to know our nervous system a bit closer, how does it works? | Neurology; Author: FreeMedEducation;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6O-0CVAgaEM;License: Standard youtube license