
Concept explainers
For the boom and loading shown, determine (a) the tension in cord BD, (b) the reaction at C.
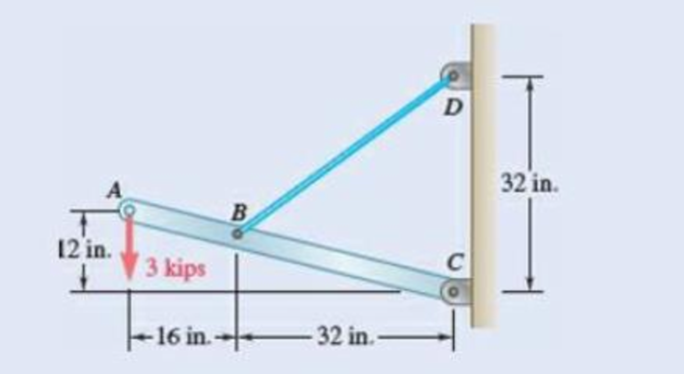
Fig.P4.71
(a)
The tension in the cord
Answer to Problem 4.71P
The tension in the cord
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
If the rigid body subjected to three forces, such a body is commonly called a three-force body. If a two force body is in equilibrium the lines of action of the three forces must be either concurrent or parallel.
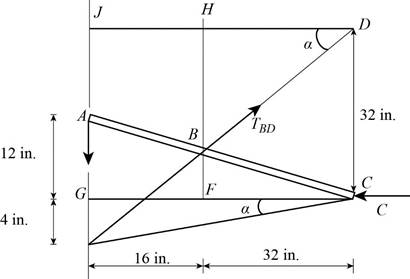
The figure 1 represents the free body diagram of the system.
Write the expression for the angle
Here,
Write the expression for the angle
Write the relations connecting the sides of the triangle.
Figure 2 represents a force triangle as shown in the above figure with its interior angles computed from the known directions of the forces. Then use the law of sines to find the unknown forces.
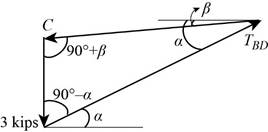
Write the expression for the law of sines from the force triangle.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
On rearranging the above equation to find
Therefore, the tension in the cord
(b)
The reaction at
Answer to Problem 4.71P
The reaction at
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
If the rigid body subjected to three forces, such a body is commonly called a three-force body. If a two force body is in equilibrium the lines of action of the three forces must be either concurrent or parallel.
Write the expression for the angle
Here,
Write the expression for the angle
Write the relations connecting the sides of the triangle.
Figure 2 represents a force triangle as shown in the above figure with its interior angles computed from the known directions of the forces. Then use the law of sines to find the unknown forces.
Write the expression for the law of sines from the force triangle.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
On rearranging the above equation to find
Therefore, reaction at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Qu 3 Nickel (Ni) single crystal turbine blades burn less fuel at higher temperatures because blades are grown on [110] closed packed direction. Nickel (Ni) at 20°C is FCC, and has an atomic radius, R, of 0.125 nm. Draw a reduced-sphere unit cell for this crystal and draw and label the vector [I 10], starting from the origin (0, 0, 0). a) Calculate the length of the vector [| 10] in nanometers. Express your answer in nanometers to one significant figure. b) Calculate the linear density of Nickel in the [| 1 0] direction in [atom/nm]. Express your answer in atoms/nm to one significant figure. show all work problemsarrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- Required information An eccentric force P is applied as shown to a steel bar of 25 × 90-mm cross section. The strains at A and B have been measured and found to be εΑ = +490 μ εB=-70 μ Know that E = 200 GPa. 25 mm 30 mm 90 mm 45 mm B Determine the distance d. The distance dis 15 mm mm.arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- ! Required information Assume that the couple shown acts in a vertical plane. Take M = 25 kip.in. r = 0.75 in. A B 4.8 in. M 1.2 in. [1.2 in. Determine the stress at point B. The stress at point B is ksi.arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- No use chatgptarrow_forwardProblem 6 (Optional, extra 6 points) 150 mm 150 mm 120 mm 80 mm 60 mm PROBLEM 18.103 A 2.5 kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates with an angular velocity ₁ with respect to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE rotating as shown at the constant rate w212 rad/s. Friction in the bearing at A causes ₁ to decrease at the rate of 15 rad/s². Determine the dynamic reactions at D and E at a time when ₁ has decreased to 50 rad/s. Answer: 5=-22.01 +26.8} N E=-21.2-5.20Ĵ Narrow_forwardProblem 1. Two uniform rods AB and CE, each of weight 3 lb and length 2 ft, are welded to each other at their midpoints. Knowing that this assembly has an angular velocity of constant magnitude c = 12 rad/s, determine: (1). the magnitude and direction of the angular momentum HD of the assembly about D. (2). the dynamic reactions (ignore mg) at the bearings at A and B. 9 in. 3 in. 03 9 in. 3 in. Answers: HD = 0.162 i +0.184 j slug-ft²/s HG = 2.21 k Ay =-1.1 lb; Az = 0; By = 1.1 lb; B₂ = 0.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





