
Fundamentals of Statistics (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134508306
Author: Michael Sullivan III
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.2, Problem 27AYU
Male vs. Female Drivers (Refer to Problem 34, Section 4.1.) The following data represent the number of licensed drivers in various age groups and the number of fatal accidents within the age group by gender.
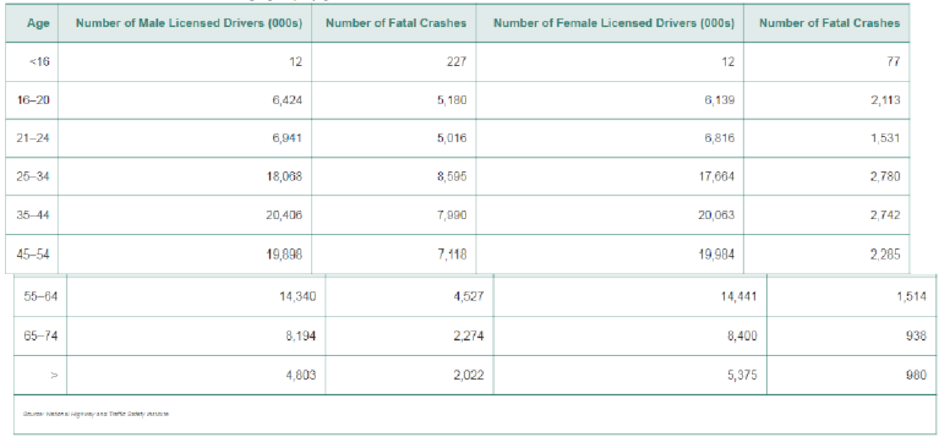
- a. Find the least-squares regression line for males treating number of licensed drivers as the explanatory variable, x, and number of fatal crashes, y, as the response variable. Repeat this procedure for females.
- a. Interpret the slope of the least-squares regression line for each gender. How might an insurance company use this information?
- b. Was the number of fatal accidents for 16- to 20-year-old males above or below average? Was the number of fatal accidents for 21- to 24-year-old-males above or below average? Was the number of fatal accidents for males greater than 74 years old above or below average? How might an insurance company use this information? Does the same relationship hold for females?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Find binomial probability if:
x = 8, n = 10, p = 0.7
x= 3, n=5, p = 0.3
x = 4, n=7, p = 0.6
Quality Control: A factory produces light bulbs with a 2% defect rate. If a random sample of 20 bulbs is tested, what is the probability that exactly 2 bulbs are defective? (hint: p=2% or 0.02; x =2, n=20; use the same logic for the following problems)
Marketing Campaign: A marketing company sends out 1,000 promotional emails. The probability of any email being opened is 0.15. What is the probability that exactly 150 emails will be opened? (hint: total emails or n=1000, x =150)
Customer Satisfaction: A survey shows that 70% of customers are satisfied with a new product. Out of 10 randomly selected customers, what is the probability that at least 8 are satisfied? (hint: One of the keyword in this question is “at least 8”, it is not “exactly 8”, the correct formula for this should be = 1- (binom.dist(7, 10, 0.7, TRUE)). The part in the princess will give you the probability of seven and less than…
please answer these questions
Selon une économiste d’une société financière, les dépenses moyennes pour « meubles et appareils de maison » ont été moins importantes pour les ménages de la région de Montréal, que celles de la région de Québec.
Un échantillon aléatoire de 14 ménages pour la région de Montréal et de 16 ménages pour la région Québec est tiré et donne les données suivantes, en ce qui a trait aux dépenses pour ce secteur d’activité économique.
On suppose que les données de chaque population sont distribuées selon une loi normale.
Nous sommes intéressé à connaitre si les variances des populations sont égales.a) Faites le test d’hypothèse sur deux variances approprié au seuil de signification de 1 %. Inclure les informations suivantes :
i. Hypothèse / Identification des populationsii. Valeur(s) critique(s) de Fiii. Règle de décisioniv. Valeur du rapport Fv. Décision et conclusion
b) A partir des résultats obtenus en a), est-ce que l’hypothèse d’égalité des variances pour cette…
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fundamentals of Statistics (5th Edition)
Ch. 4.1 - What is the difference between univariate data and...Ch. 4.1 - The _____ variable is the variable whose value can...Ch. 4.1 - A _____ _____ is a graph that shows the relation...Ch. 4.1 - What does it mean to say two variables are...Ch. 4.1 - If r = _____, then a perfect negative linear...Ch. 4.1 - True or False: If the linear correlation...Ch. 4.1 - A _____ variable is a variable that is related to...Ch. 4.1 - True or False: Correlation implies causation.Ch. 4.1 - In Problems 912, determine whether the scatter...Ch. 4.1 - In Problems 912, determine whether the scatter...
Ch. 4.1 - In Problems 912, determine whether the scatter...Ch. 4.1 - In Problems 912, determine whether the scatter...Ch. 4.1 - NW Match the linear correlation coefficient to the...Ch. 4.1 - Match the linear correlation coefficient to the...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 15AYUCh. 4.1 - Relation between Education and Birthrate? The...Ch. 4.1 - In Problems 1720, (a) draw a scatter diagram of...Ch. 4.1 - In Problems 1720, (a) draw a scatter diagram of...Ch. 4.1 - In Problems 1720, (a) draw a scatter diagram of...Ch. 4.1 - In Problems 1720, (a) draw a scatter diagram of...Ch. 4.1 - Name the Relation, Part I For each of the...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 22AYUCh. 4.1 - The TIMMS Exam The Trends in International...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 24AYUCh. 4.1 - NW An Unhealthy Commute The Gallup Organization...Ch. 4.1 - Credit Scores Your Fair Isaacs Corporation (FICO)...Ch. 4.1 - Height versus Head Circumference A pediatrician...Ch. 4.1 - American Black Bears The American black bear...Ch. 4.1 - Weight of a Car versus Miles per Gallon An...Ch. 4.1 - Hurricanes The data in the next column represent...Ch. 4.1 - CEO Performance The following data represent the...Ch. 4.1 - Bear Markets A bear market in the stock market is...Ch. 4.1 - Does Size Matter? Researchers wondered whether the...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 34AYUCh. 4.1 - Weight of a Car versus Miles per Gallon Suppose...Ch. 4.1 - American Black Bears The website that contained...Ch. 4.1 - Draw Your Data! Consider the four data sets shown...Ch. 4.1 - Predicting Winning Percentage The ultimate goal in...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 39AYUCh. 4.1 - Lyme Disease versus Drownings Lyme disease is an...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 41AYUCh. 4.1 - Prob. 42AYUCh. 4.1 - Crime Rate and Cell Phones The linear correlation...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 44AYUCh. 4.1 - Influential Consider the following set of data: a....Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 46AYUCh. 4.1 - Prob. 47AYUCh. 4.1 - Prob. 48AYUCh. 4.1 - What does it mean to say that the linear...Ch. 4.1 - What does it mean if r = 0?Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 51AYUCh. 4.1 - Prob. 52AYUCh. 4.1 - Explain the difference between correlation and...Ch. 4.1 - Suppose that two variables, x and y, are...Ch. 4.2 - The difference between the observed and predicted...Ch. 4.2 - If the linear correlation between two variables is...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 3AYUCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4AYUCh. 4.2 - For the data set a. Draw a scatter diagram....Ch. 4.2 - For the data set a. Draw a scatter diagram....Ch. 4.2 - In Problems 712: a. By hand, draw a scatter...Ch. 4.2 - In Problems 712: a. By hand, draw a scatter...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 9AYUCh. 4.2 - In Problems 712: a. By hand, draw a scatter...Ch. 4.2 - In Problems 712: a. By hand, draw a scatter...Ch. 4.2 - In Problems 712: a. By hand, draw a scatter...Ch. 4.2 - NW Income and Education In Problem 15 from Section...Ch. 4.2 - You Explain It! Study Time and Exam Scores After...Ch. 4.2 - Age Gap at Marriage Is there a relation between...Ch. 4.2 - You Explain It! CO2 and Energy Production The...Ch. 4.2 - NW An Unhealthy Commute (Refer to Problem 25,...Ch. 4.2 - Credit Scores (Refer to Problem 26, Section 4.1.)...Ch. 4.2 - Height versus Head Circumference (Refer to Problem...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 20AYUCh. 4.2 - Weight of a Car versus Miles per Gallon (Refer to...Ch. 4.2 - Hurricanes (Refer to Problem 30, Section 4.1) The...Ch. 4.2 - Cola Consumption vs. Bone Density Example 5 in...Ch. 4.2 - Attending Class The following data represent the...Ch. 4.2 - CEO Performance (Refer to Problem 31 in Section...Ch. 4.2 - Bear Markets (Refer to Problem 32, Section 4.1) A...Ch. 4.2 - Male vs. Female Drivers (Refer to Problem 34,...Ch. 4.2 - Graduation Rates Go to...Ch. 4.2 - Putting It Together: Housing Prices One of the...Ch. 4.2 - Putting It Together: Smoking and Birth Weight It...Ch. 4.2 - What is a residual? What does it mean when a...Ch. 4.2 - Explain the phrase outside the scope of the model....Ch. 4.2 - Explain what each point on the least-squares...Ch. 4.3 - The _____ _____ _____, R2, measures the proportion...Ch. 4.3 - Total deviation = _____ deviation + _____...Ch. 4.3 - Match each coefficient of determination to a...Ch. 4.3 - NW The Other Old Faithful Perhaps you are familiar...Ch. 4.3 - Concrete As concrete cures, it gains strength. The...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 7AYUCh. 4.3 - Problems 712 use the results from Problems 2530 in...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 9AYUCh. 4.3 - Problems 712 use the results from Problems 2530 in...Ch. 4.3 - Problems 712 use the results from Problems 2530 in...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 12AYUCh. 4.3 - Weight of a Car versus Miles per Gallon Suppose...Ch. 4.3 - American Black Bears Suppose that we find a bear...Ch. 4.3 - Putting It Together: Exam Scores The data below...Ch. 4.3 - Sullivan Survey II Go to...Ch. 4.4 - What is meant by a marginal distribution? What is...Ch. 4.4 - Refer to Table 8. Is constructing a conditional...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 3AYUCh. 4.4 - Explain the idea behind Simpsons Paradox.Ch. 4.4 - In Problems 5 and 6, a. Construct a frequency...Ch. 4.4 - In Problems 5 and 6, a. Construct a frequency...Ch. 4.4 - Made in America In a recent Harris Poll, a random...Ch. 4.4 - Desirability Traits In a recent Harris Poll, a...Ch. 4.4 - NW Party Affiliation Is there an association...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 10AYUCh. 4.4 - Health and Happiness The General Social Survey...Ch. 4.4 - Happy in Your Marriage? The General Social Survey...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 13AYUCh. 4.4 - Treating Kidney Stones Researchers conducted a...Ch. 4.4 - Sullivan Survey II Go to...Ch. 4 - Basketball Spreads In sports betting, Las Vegas...Ch. 4 - Fat and Calories in Cheeseburgers A nutritionist...Ch. 4 - Prob. 3RECh. 4 - Prob. 4RECh. 4 - Prob. 5RECh. 4 - a. Draw a scatter diagram treating x as the...Ch. 4 - Use the results from Problems 2 and 4 to compute...Ch. 4 - Prob. 8RECh. 4 - Prob. 9RECh. 4 - New versus Used Car Satisfaction Are you more...Ch. 4 - Unemployment Rates Recessions are an economic...Ch. 4 - Prob. 12RECh. 4 - Prob. 13RECh. 4 - Prob. 1CTCh. 4 - Use the data from Problem 1. a. Find the...Ch. 4 - Use the results from Problems 1 and 2 to compute...Ch. 4 - The following data represent the speed of a car...Ch. 4 - Prob. 5CTCh. 4 - Prob. 6CTCh. 4 - Consider the following contingency table, which...Ch. 4 - What would you say about a set of quantitative...Ch. 4 - If the slope of a least-squares regression line is...Ch. 4 - What does it mean if a linear correlation...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- According to an economist from a financial company, the average expenditures on "furniture and household appliances" have been lower for households in the Montreal area than those in the Quebec region. A random sample of 14 households from the Montreal region and 16 households from the Quebec region was taken, providing the following data regarding expenditures in this economic sector. It is assumed that the data from each population are distributed normally. We are interested in knowing if the variances of the populations are equal. a) Perform the appropriate hypothesis test on two variances at a significance level of 1%. Include the following information: i. Hypothesis / Identification of populations ii. Critical F-value(s) iii. Decision rule iv. F-ratio value v. Decision and conclusion b) Based on the results obtained in a), is the hypothesis of equal variances for this socio-economic characteristic measured in these two populations upheld? c) Based on the results obtained in a),…arrow_forwardA major company in the Montreal area, offering a range of engineering services from project preparation to construction execution, and industrial project management, wants to ensure that the individuals who are responsible for project cost estimation and bid preparation demonstrate a certain uniformity in their estimates. The head of civil engineering and municipal services decided to structure an experimental plan to detect if there could be significant differences in project evaluation. Seven projects were selected, each of which had to be evaluated by each of the two estimators, with the order of the projects submitted being random. The obtained estimates are presented in the table below. a) Complete the table above by calculating: i. The differences (A-B) ii. The sum of the differences iii. The mean of the differences iv. The standard deviation of the differences b) What is the value of the t-statistic? c) What is the critical t-value for this test at a significance level of 1%?…arrow_forwardCompute the relative risk of falling for the two groups (did not stop walking vs. did stop). State/interpret your result verbally.arrow_forward
- Microsoft Excel include formulasarrow_forwardQuestion 1 The data shown in Table 1 are and R values for 24 samples of size n = 5 taken from a process producing bearings. The measurements are made on the inside diameter of the bearing, with only the last three decimals recorded (i.e., 34.5 should be 0.50345). Table 1: Bearing Diameter Data Sample Number I R Sample Number I R 1 34.5 3 13 35.4 8 2 34.2 4 14 34.0 6 3 31.6 4 15 37.1 5 4 31.5 4 16 34.9 7 5 35.0 5 17 33.5 4 6 34.1 6 18 31.7 3 7 32.6 4 19 34.0 8 8 33.8 3 20 35.1 9 34.8 7 21 33.7 2 10 33.6 8 22 32.8 1 11 31.9 3 23 33.5 3 12 38.6 9 24 34.2 2 (a) Set up and R charts on this process. Does the process seem to be in statistical control? If necessary, revise the trial control limits. [15 pts] (b) If specifications on this diameter are 0.5030±0.0010, find the percentage of nonconforming bearings pro- duced by this process. Assume that diameter is normally distributed. [10 pts] 1arrow_forward4. (5 pts) Conduct a chi-square contingency test (test of independence) to assess whether there is an association between the behavior of the elderly person (did not stop to talk, did stop to talk) and their likelihood of falling. Below, please state your null and alternative hypotheses, calculate your expected values and write them in the table, compute the test statistic, test the null by comparing your test statistic to the critical value in Table A (p. 713-714) of your textbook and/or estimating the P-value, and provide your conclusions in written form. Make sure to show your work. Did not stop walking to talk Stopped walking to talk Suffered a fall 12 11 Totals 23 Did not suffer a fall | 2 Totals 35 37 14 46 60 Tarrow_forward
- Question 2 Parts manufactured by an injection molding process are subjected to a compressive strength test. Twenty samples of five parts each are collected, and the compressive strengths (in psi) are shown in Table 2. Table 2: Strength Data for Question 2 Sample Number x1 x2 23 x4 x5 R 1 83.0 2 88.6 78.3 78.8 3 85.7 75.8 84.3 81.2 78.7 75.7 77.0 71.0 84.2 81.0 79.1 7.3 80.2 17.6 75.2 80.4 10.4 4 80.8 74.4 82.5 74.1 75.7 77.5 8.4 5 83.4 78.4 82.6 78.2 78.9 80.3 5.2 File Preview 6 75.3 79.9 87.3 89.7 81.8 82.8 14.5 7 74.5 78.0 80.8 73.4 79.7 77.3 7.4 8 79.2 84.4 81.5 86.0 74.5 81.1 11.4 9 80.5 86.2 76.2 64.1 80.2 81.4 9.9 10 75.7 75.2 71.1 82.1 74.3 75.7 10.9 11 80.0 81.5 78.4 73.8 78.1 78.4 7.7 12 80.6 81.8 79.3 73.8 81.7 79.4 8.0 13 82.7 81.3 79.1 82.0 79.5 80.9 3.6 14 79.2 74.9 78.6 77.7 75.3 77.1 4.3 15 85.5 82.1 82.8 73.4 71.7 79.1 13.8 16 78.8 79.6 80.2 79.1 80.8 79.7 2.0 17 82.1 78.2 18 84.5 76.9 75.5 83.5 81.2 19 79.0 77.8 20 84.5 73.1 78.2 82.1 79.2 81.1 7.6 81.2 84.4 81.6 80.8…arrow_forwardName: Lab Time: Quiz 7 & 8 (Take Home) - due Wednesday, Feb. 26 Contingency Analysis (Ch. 9) In lab 5, part 3, you will create a mosaic plot and conducted a chi-square contingency test to evaluate whether elderly patients who did not stop walking to talk (vs. those who did stop) were more likely to suffer a fall in the next six months. I have tabulated the data below. Answer the questions below. Please show your calculations on this or a separate sheet. Did not stop walking to talk Stopped walking to talk Totals Suffered a fall Did not suffer a fall Totals 12 11 23 2 35 37 14 14 46 60 Quiz 7: 1. (2 pts) Compute the odds of falling for each group. Compute the odds ratio for those who did not stop walking vs. those who did stop walking. Interpret your result verbally.arrow_forwardSolve please and thank you!arrow_forward
- 7. In a 2011 article, M. Radelet and G. Pierce reported a logistic prediction equation for the death penalty verdicts in North Carolina. Let Y denote whether a subject convicted of murder received the death penalty (1=yes), for the defendant's race h (h1, black; h = 2, white), victim's race i (i = 1, black; i = 2, white), and number of additional factors j (j = 0, 1, 2). For the model logit[P(Y = 1)] = a + ß₁₂ + By + B²², they reported = -5.26, D â BD = 0, BD = 0.17, BY = 0, BY = 0.91, B = 0, B = 2.02, B = 3.98. (a) Estimate the probability of receiving the death penalty for the group most likely to receive it. [4 pts] (b) If, instead, parameters used constraints 3D = BY = 35 = 0, report the esti- mates. [3 pts] h (c) If, instead, parameters used constraints Σ₁ = Σ₁ BY = Σ; B = 0, report the estimates. [3 pts] Hint the probabilities, odds and odds ratios do not change with constraints.arrow_forwardSolve please and thank you!arrow_forwardSolve please and thank you!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
 College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...
Algebra
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...
Algebra
ISBN:9781680331141
Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt


College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...
Algebra
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:McGraw Hill
Time Series Analysis Theory & Uni-variate Forecasting Techniques; Author: Analytics University;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_X5q9FYLGxM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Operations management 101: Time-series, forecasting introduction; Author: Brandoz Foltz;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EaqZP36ool8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY