
BIOLOGY
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781260169614
Author: Raven
Publisher: RENT MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 42, Problem 1DA
Data analysis Draw the resulting potentials for all possible combinations of E1, E2, and I.
Expert Solution & Answer
Summary Introduction
To draw: The illustration for resulting potentials for all possible combination of E1, E2 and I
Introduction: The graded potential arises during resting, depolarization, and action potential. The gated channels help in the movement of ions from the extracellular region to the intracellular region.
Explanation of Solution
The graded potential (mV) in the axonal membrane is shown below:
- 1-represents the weak excitation (E1)
- indicates the stronger stimulus (E2)
- represents the inhibitory stimulus (I) produced by the hyperpolarization.
- represents the sum of all resulting graded potential
Pictorial representation: Fig 1 represents resulting potentials for all possible combinations.
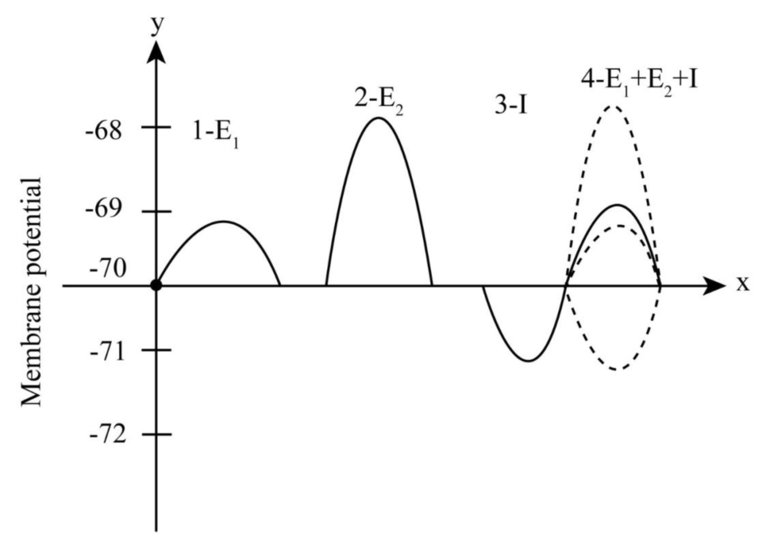
Fig 1: represents resulting potentials for all possible combinations.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
Joden Koepp
olor in chickens is due to incomplete dominance. BB = Black chicken, WW = White
BLOOD TYPES
Arhite chicken is
In humans, Rh positive blood is dominant (R) over Rh negative blood (r). A man with type 0, Rh positive
blood (whose mother had Rh negative blood), marries a woman with type AB, Rh negative blood. Several
children were born.
is?
R
R
Genotypes
Phenotypes
RRR
RR Rr
Rr
4/16 RR
R RR RK Rr
Rr
4/16 rr
3/4 Rh posi
1/4 Rh negu
1/2 Rr
rr
rr
rrrr
88
888
75
e genotype of the man?
the genotype of the woman?
The mother of the man had type AB blood.
Please indentify the unknown organism
Please indentify the unknown organism
Chapter 42 Solutions
BIOLOGY
Ch. 42.1 - Differentiate between subdivisions of the...Ch. 42.1 - Prob. 2LOCh. 42.1 - Explain the roles of the different nervous system...Ch. 42.2 - Contrast the relative concentrations of important...Ch. 42.2 - Prob. 2LOCh. 42.2 - Prob. 3LOCh. 42.3 - Prob. 1LOCh. 42.3 - Prob. 2LOCh. 42.3 - Prob. 3LOCh. 42.4 - Prob. 1LO
Ch. 42.4 - Prob. 2LOCh. 42.4 - Prob. 3LOCh. 42.5 - Describe the organization of the peripheral...Ch. 42.5 - Prob. 2LOCh. 42.5 - Prob. 3LOCh. 42.5 - Prob. 4LOCh. 42 - Data analysis Draw the resulting potentials for...Ch. 42 - Prob. 2DACh. 42 - Which of the following best describes the...Ch. 42 - The ____ cannot be controlled by conscious...Ch. 42 - Prob. 3UCh. 42 - Inhibitory neurotransmitters a. hyperpolarize...Ch. 42 - White matter is ______, and gray matter is...Ch. 42 - During an action potential a. the rising phase is...Ch. 42 - Prob. 7UCh. 42 - Imagine that you are doing an experiment on the...Ch. 42 - The Na+/K+ ATPase pump is a. not required for...Ch. 42 - Prob. 3ACh. 42 - The following is a list of the components of a...Ch. 42 - Prob. 5ACh. 42 - As you sit quietly reading this sentence, the part...Ch. 42 - G proteincoupled receptors are involved in the...Ch. 42 - Tetraethylammonium (TEA) is a drug that blocks...Ch. 42 - Describe the status of the Na+ and K+ channels at...Ch. 42 - Describe the steps required to produce an...Ch. 42 - Prob. 4S
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please indentify the unknown organismarrow_forwardPlease indentify the unknown organismarrow_forward5G JA ATTC 3 3 CTIA A1G5 5 GAAT I I3 3 CTIA AA5 Fig. 5-3: The Eco restriction site (left) would be cleaved at the locations indicated by the arrows. However, a SNP in the position shown in gray (right) would prevent cleavage at this site by EcoRI One of the SNPs in B. rapa is found within the Park14 locus and can be detected by RFLP analysis. The CT polymorphism is found in the intron of the Bra013780 gene found on Chromosome 1. The Park14 allele with the "C" in the SNP has two EcoRI sites and thus is cleaved twice by EcoRI If there is a "T" in that SNP, one of the EcoRI sites is altered, so the Park14 allele with the T in the SNP has only one EcoRI site (Fig. 5-3). Park14 allele with SNP(C) Park14 allele with SNPT) 839 EcoRI 1101 EcoRI 839 EcoRI Fig. 5.4: Schematic restriction maps of the two different Park14 alleles (1316 bp long) of B. rapa. Where on these maps is the CT SNP located? 90 The primers used to amplify the DNA at the Park14 locus (see Fig. 5 and Table 3 of Slankster et…arrow_forward
- From your previous experiment, you found that this enhancer activates stripe 2 of eve expression. When you sequence this enhancer you find several binding sites for the gap gene, Giant. To test how Giant interacts with eve, you decide to remove all of the Giant binding sites from the eve enhancer. What results do you expect to see with respect to eve expression?arrow_forwardWhat experiment could you do to see if the maternal gene, bicoid, is sufficient to form anterior fates?arrow_forwardYou’re curious about the effect that gap genes have on the pair-rule gene, evenskipped (eve), so you isolate and sequence each of the eve enhancers. You’re particularly interested in one of the enhancers, which is just upstream of the eve gene. Describe an experimental technique you would use to find out where this particular eve enhancer is active.arrow_forward
- For short answer questions, write your answers on the line provided. To the right is the mRNA codon table to use as needed throughout the exam. First letter U บบบ U CA UUCPhe UUA UCU Phe UCC UUG Leu CUU UAU. G U UAC TV UGCys UAA Stop UGA Stop A UAG Stop UGG Trp Ser UCA UCG CCU] 0 CUC CUA CCC CAC CAU His CGU CGC Leu Pro CCA CAA Gin CGA Arg CUG CCG CAG CGG AUU ACU AAU T AUC lle A 1 ACC Thr AUA ACA AUG Mot ACG AGG Arg GUU GCU GUC GCC G Val Ala GAC Asp GGU GGC GUA GUG GCA GCG GAA GGA Gly Glu GAGJ GGG AACASH AGU Ser AAA1 AAG Lys GAU AGA CAL CALUCAO CAO G Third letter 1. (+7) Use the table below to answer the questions; use the codon table above to assist you. The promoter sequence of DNA is on the LEFT. You do not need to fill in the entire table. Assume we are in the middle of a gene sequence (no need to find a start codon). DNA 1 DNA 2 mRNA tRNA Polypeptide C Val G C. T A C a. On which strand of DNA is the template strand (DNA 1 or 2)?_ b. On which side of the mRNA is the 5' end (left or…arrow_forward3. (6 pts) Fill in the boxes according to the directions on the right. Structure R-C R-COOH OH R-OH i R-CO-R' R R-PO4 R-CH3 C. 0 R' R-O-P-OH 1 OH H R-C-H R-N' I- H H R-NH₂ \H Name Propertiesarrow_forward4. (6 pts) Use the molecule below to answer these questions and identify the side chains and ends. Please use tidy boxes to indicate parts and write the letter labels within that box. a. How many monomer subunits are shown? b. Box a Polar but non-ionizable side chain and label P c. Box a Basic Polar side chain and label BP d. Box the carboxyl group at the end of the polypeptide and label with letter C (C-terminus) H H OHHO H H 0 HHO H-N-CC-N-C-C N-C-C-N-GC-OH I H-C-H CH2 CH2 CH2 H3C-C+H CH2 CH2 OH CH CH₂ C=O OH CH2 NH2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College- Case Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College

Case Studies In Health Information Management
Biology
ISBN:9781337676908
Author:SCHNERING
Publisher:Cengage

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax
What is cancer? What causes cancer and how is it treated? *UPDATE*; Author: Cancer Treatment Centers of America - CTCA;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_N1Sk3aiSCE;License: Standard Youtube License