
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be named.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of bicyclic compounds:
The organic compound naming is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Identify and the parent: The term ‘Bicylo-’ is introduced in the name of the parent. Count the number of carbons excluding the bridge heads. In the compound below, each of the three paths has two carbons. These three numbers are ordered from largest to smallest, as [2.2.2] and placed in the middle of the parent.
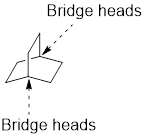
Identify and name substituents: If substituent is present, the parent must be numbered properly in order to assign the locants to the substituent. To number the parent, start at one of the bridgeheads and begin numbering along the longest path, then go to the second longest path, and finally go along the shortest path.
Arrange the substituents alphabetically.
In the complex substituent in compounds, the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(b)
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be named.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of bicyclic compounds:
The organic compound naming is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Identify and the parent: The term ‘Bicylo-’ is introduced in the name of the parent. Count the number of carbons excluding the bridge heads. In the compound below, each of the three paths has two carbons. These three numbers are ordered from largest to smallest, as [2.2.2] (each number represent number of carbon atoms) and placed in the middle of the parent.
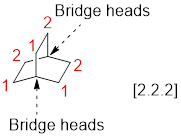
Identify and name substituents: If substituent is present, the parent must be numbered properly in order to assign the locants to the substituent. To number the parent, start at one of the bridgeheads and begin numbering along the longest path, then go to the second longest path, and finally go along the shortest path.
Arrange the substituents alphabetically.
In the complex substituent in compounds, the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(c)
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be named.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of bicyclic compounds:
The organic compound naming is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Identify and the parent: The term ‘Bicylo-’ is introduced in the name of the parent. Count the number of carbons excluding the bridge heads. In the compound below, each of the three paths has two carbons. These three numbers are ordered from largest to smallest, as [2.2.2] and placed in the middle of the parent.

Identify and name substituents: If substituent is present, the parent must be numbered properly in order to assign the locants to the substituent. To number the parent, start at one of the bridgeheads and begin numbering along the longest path, then go to the second longest path, and finally go along the shortest path.
Arrange the substituents alphabetically.
In the complex substituent in compounds, the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(d)
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be named.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of bicyclic compounds:
The organic compound naming is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Identify and the parent: The term ‘Bicylo-’ is introduced in the name of the parent. Count the number of carbons excluding the bridge heads. In the compound below, each of the three paths has two carbons. These three numbers are ordered from largest to smallest, as [2.2.2] and placed in the middle of the parent.

Identify and name substituents: If substituent is present, the parent must be numbered properly in order to assign the locants to the substituent. To number the parent, start at one of the bridgeheads and begin numbering along the longest path, then go to the second longest path, and finally go along the shortest path.
Arrange the substituents alphabetically.
In the complex substituent in compounds, the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
(e)
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be named.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of bicyclic compounds:
The organic compound naming is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Identify and the parent: The term ‘Bicylo-’ is introduced in the name of the parent. Count the number of carbons excluding the bridge heads. In the compound below, each of the three paths has two carbons. These three numbers are ordered from largest to smallest, as [2.2.2] and placed in the middle of the parent.

Identify and name substituents: If substituent is present, the parent must be numbered properly in order to assign the locants to the substituent. To number the parent, start at one of the bridgeheads and begin numbering along the longest path, then go to the second longest path, and finally go along the shortest path.
Arrange the substituents alphabetically.
In the complex substituent in compounds, the substituent name is assigned by a name each of them based on numbers going away from the parent.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY AS A SECOND LANGU
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





