
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Chair conformations of structure (1) and (2) have to be drawn for six-membered rings; the lowest energy conformations for the compound have to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Conformations: Rotation about C-C single bonds allows a compound to adopt a variety of possible three-dimensional shapes.
Drawing Axial and Equatorial substituents:
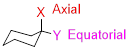
Each carbon in cyclohexane can bear two substituents. One group is said to occupy an axial position, which is parallel to a vertical axis passing through the center of the ring. the other group is said to occupy an equatorial position, which is positioned approximately along the equator of the ring.
Conformations: Rotation about C-C single bonds allows a compound to adopt a variety of possible three-dimensional shapes.
Newman projections: The new conformations of compounds can be drawn and analyzed by Newman projections. A Newman projection visualizes different conformations of Carbon-carbon
The angle between two hydrogens of a Newman projection is called as dihedral angle or torsional angle. This dihedral angle changes as the C-C bond rotates. Two conformations with special attentions are staggered and eclipsed conformation. Staggered conformation is the lowest in energy and the eclipsed conformation is the highest in energy.
For example,

Anti-conformation: The conformation with a dihedral angle of

The two methyl groups achieve maximum separation from each other. In other, methyl groups are closer to each other; their electron clouds are repelling each other, causing an increase in energy. This unfavorable interaction is called gauche interaction.
Conversion of chair conformation into Newman projection:
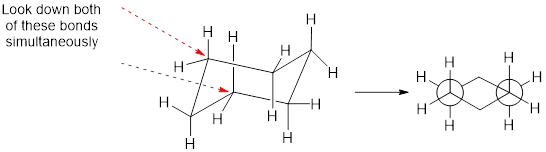
Ring flipping between Newman projections:
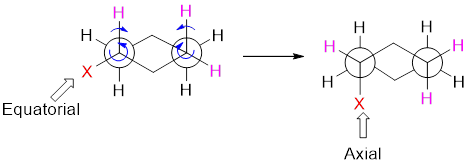
Ring flipping is a conformational change that is accomplished only through a rotation of all C-C single bonds. On ring flipping between two chair conformation equatorial changes into axial and vice-versa.
(b)
Interpretation:
The larger heat of combustion out of the given compounds has to be identified and explained.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
Conformations: Rotation about C-C single bonds allows a compound to adopt a variety of possible three-dimensional shapes.
Drawing Axial and Equatorial substituents:
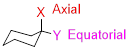
Each carbon in cyclohexane can bear two substituents. One group is said to occupy an axial position, which is parallel to a vertical axis passing through the center of the ring. the other group is said to occupy an equatorial position, which is positioned approximately along the equator of the ring.
Conformations: Rotation about C-C single bonds allows a compound to adopt a variety of possible three-dimensional shapes.
Newman projections: The new conformations of compounds can be drawn and analyzed by Newman projections. A Newman projection visualizes different conformations of Carbon-carbon chemical bond from front to back with the front carbon represented as a black dot and the back represented as a circle.
The angle between two hydrogens of a Newman projection is called as dihedral angle or torsional angle. This dihedral angle changes as the C-C bond rotates. Two conformations with special attentions are staggered and eclipsed conformation. Staggered conformation is the lowest in energy and the eclipsed conformation is the highest in energy.
For example,

Anti-conformation: The conformation with a dihedral angle of

The two methyl groups achieve maximum separation from each other. In other, methyl groups are closer to each other; their electron clouds are repelling each other, causing an increase in energy. This unfavorable interaction is called gauche interaction.
Conversion of chair conformation into Newman projection:

Ring flipping between Newman projections:

Ring flipping is a conformational change that is accomplished only through a rotation of all C-C single bonds. On ring flipping between two chair conformation equatorial changes into axial and vice-versa.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY AS A SECOND LANGU
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





