
Trigonometry (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134217437
Author: Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.1, Problem 47E
Average Annual Temperature Scientists believe that the average annual temperature in a given location is periodic. The average temperature at a given place during a given season fluctuates as time goes on, from colder to warmer, and back to colder. The graph shows an idealized description of the temperature (in °F) for approximately the last 150 thousand years of a particular location.
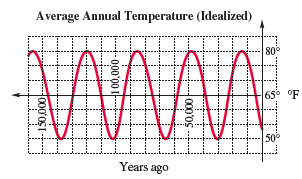
(a) Find the highest and lowest temperatures recorded.
(b) Use these two numbers to find the amplitude.
(c) Find the period of the
(d) What is the trend of the temperature now?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Use a calculator to find a decimal approximation for the following trigonometric function.
cot 226°54'
cot 226°54'
(Simplify your answer. Type an integer or a decimal. Round to eight decimal places as needed.)
X
Acellus | Student
admin192c.acellus.com
go
0:0
Hannah wants to have concrete stairs for
her backdoor. How much concrete will be
needed to build the stairs?
20 cm
70 cm
30 cm
15 cm
10 cm
45 cm
cm
70 cm
GIF
自
لا
1
Hannah wants to have concrete stairs for
her backdoor. How much concrete will be
needed to build the stairs?
70 cm
30 cm
15 cm
10 cm
10 cm
20 cm
45 cm
cm³
GIF
GIF/
2
3
4
qwe
asdf
5
6
自
yu
ty u
8
ghjk
9
P
Z X
C
cv b
vbnm ×
Chapter 4 Solutions
Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Ch. 4.1 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.1 -
CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.1 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.1 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.1 -
5. The least positive number x for which cos x =...Ch. 4.1 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.1 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.1 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.1 -
Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.1 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...
Ch. 4.1 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.1 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over the interval [ –2π, 2π]....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over the interval [ 2, 2]....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over the interval [2, 2]. Give...Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over the interval [–2π, 2π]....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over the interval [2,2]. Give...Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over the interval [–2π,2π]....Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over the interval [–2 π,2π]....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over the interval [–2π,2π]....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over the interval [2,2 ]. Give...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 22ECh. 4.1 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.1 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Determine an...Ch. 4.1 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Determine an...Ch. 4.1 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Determine an...Ch. 4.1 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Determine an...Ch. 4.1 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Determine an...Ch. 4.1 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Determine an...Ch. 4.1 - Average Annual Temperature Scientists believe that...Ch. 4.1 - Blood Pressure Variation The graph gives the...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 49ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 50ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 51ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 52ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 53ECh. 4.1 - Activity of a Nocturnal Animal Many activities of...Ch. 4.1 -
55. Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide At Mauna Loa....Ch. 4.1 - Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Refer to Exercise 55....Ch. 4.1 -
57. Average Daily Temperature The temperature in...Ch. 4.1 - 58. Fluctuation in the Solar Constant The solar...Ch. 4.1 -
Musical Sound Waves Pure sounds produce single...Ch. 4.1 - Musical Sound Waves Pure sounds produce single...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 61ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 62ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 63ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 64ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 65ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 66ECh. 4.2 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.2 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.2 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blanks to correctly...Ch. 4.2 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blanks to correctly...Ch. 4.2 -
CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.2 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.2 -
CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.2 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blanks to correctly...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Match each function w ith its graph...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Match each function w ith its graph...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.2 - The graphs of y = sin x + 1 and y = sin(x + 1) are...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Refer to Exercise 17. Which one of...Ch. 4.2 -
Concept Check Match each function in Column I...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Match each function in Column I with...Ch. 4.2 -
Concept Check Match each function in Column I...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Match each function in Column I with...Ch. 4.2 - Concept Check Fill in each blank with the word...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 24ECh. 4.2 - Connecting Graphs with equations Each function...Ch. 4.2 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Each function...Ch. 4.2 -
Connecting Graphs with Equations Each function...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 28ECh. 4.2 -
Find the amplitude, the period, any vertical...Ch. 4.2 -
Find the amplitude, the period, any vertical...Ch. 4.2 -
Find the amplitude, the period, any vertical...Ch. 4.2 -
Find the amplitude, the period, any vertical...Ch. 4.2 - Find the amplitude, the period, any vertical...Ch. 4.2 -
Find the amplitude, the period, any vertical...Ch. 4.2 - Find the amplitude, the period, any vertical...Ch. 4.2 - Find the amplitude, the period, any vertical...Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 -
Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.2 -
Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.2 -
Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.2 -
Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 60ECh. 4.2 - Average Monthly Temperature The average monthly...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 62ECh. 4.2 - Prob. 63ECh. 4.2 - Prob. 64ECh. 4.2 - Prob. 65ECh. 4.2 - Prob. 66ECh. 4.2 - Prob. 1QCh. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 3QCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4QCh. 4.2 - Prob. 5QCh. 4.2 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 7QCh. 4.2 - Prob. 8QCh. 4.2 - Prob. 9QCh. 4.2 - Prob. 10QCh. 4.2 - Prob. 11QCh. 4.2 - Prob. 12QCh. 4.3 - 1. The least positive value x for which tan x = 0...Ch. 4.3 - The least positive value x for which cot x = 0 is...Ch. 4.3 - Concept Check Fill in each blank with the word...Ch. 4.3 - Concept Check Fill in each blank with the word...Ch. 4.3 - The negative value k with the greatest value for...Ch. 4.3 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly...Ch. 4.3 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.3 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.3 -
Concept Check Match each function with its...Ch. 4.3 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.3 - Concept CheckMatch each function with its graph...Ch. 4.3 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 -
Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 -
Graph each function over a one-period...Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 -
Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.3 -
Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.3 -
Graph each function over a two-period...Ch. 4.3 -
Graph each function over a two-period...Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 31ECh. 4.3 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 34ECh. 4.3 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 36ECh. 4.3 - Graph each function over a two-period interval....Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 38ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 39ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 40ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 41ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 42ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 43ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 44ECh. 4.3 - Concept Check Decide whether each statement is...Ch. 4.3 - Concept CheckDecide whether each statement is true...Ch. 4.3 -
Concept Check Decide whether each statement is...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 48ECh. 4.3 - Concept Check If c is any number, then how many...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 50ECh. 4.3 - 51. Show that tan(–x) = –tan x by writing tan(–x)...Ch. 4.3 - 52. Show that cot (–x) = –cot x by writing cot...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 53ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 54ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 55ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 56ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 57ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 58ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 59ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 60ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 61ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 62ECh. 4.4 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Match each description in Column I...Ch. 4.4 -
CONCEPT PREVIEW Match each description in...Ch. 4.4 -
CONCEPT PREVIEW Match each description in Column...Ch. 4.4 -
CONCEPT PREVIEW Match each description in Column...Ch. 4.4 -
CONCEPT PREVIEW Match each description in Column...Ch. 4.4 -
CONCEPT PREVIEW Match each description in Column...Ch. 4.4 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.4 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.4 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.4 - Concept Check Match each function with its graph...Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 -
Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Graph each function over a one-period interval....Ch. 4.4 - Connecting Graphs with EquationsDetermine an...Ch. 4.4 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Determine an...Ch. 4.4 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Determine an...Ch. 4.4 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Determine an...Ch. 4.4 - Connecting Graphs with Equations Determine an...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 30ECh. 4.4 - Concept CheckDecide whether each statement is true...Ch. 4.4 - Concept Check Decide whether each statement is...Ch. 4.4 - Concept CheckDecide whether each statement is true...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 34ECh. 4.4 - 35. Concept Check If c is any number such that -1...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 36ECh. 4.4 - 37. Show that sec (–x) = sec x by writing sec (–x)...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 38ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 39ECh. 4.4 - (Modeling) Distance of a Rotating Beacon The...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 41ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 42ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 43ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 44ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 45ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 46ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 1SECh. 4.4 - Prob. 2SECh. 4.4 - These summary exercises provide practice with the...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 4SECh. 4.4 - Prob. 5SECh. 4.4 - Prob. 6SECh. 4.4 - Prob. 7SECh. 4.4 -
Graph each function over a two-period...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 9SECh. 4.4 - Graph each function over a two-period...Ch. 4.5 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Refer to the equations in the...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 2ECh. 4.5 - CONCEPT PREVIEW Refer to the equations in the...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4ECh. 4.5 - Prob. 5ECh. 4.5 - Prob. 6ECh. 4.5 - Spring Motion An object is attached to a coiled...Ch. 4.5 - Spring Motion Repeat Exercise 7, but assume that...Ch. 4.5 - 9. Voltage of an Electrical Circuit The voltage E...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 10ECh. 4.5 - Particle Movement Write the equation and then...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 12ECh. 4.5 -
13. Pendulum Motion What are the period P and...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 14ECh. 4.5 - Spring Motion The formula for the up and down...Ch. 4.5 - Spring Motion (See Exercise 15.) A spring with...Ch. 4.5 - Spring Motion The position of a weight attached to...Ch. 4.5 - Spring Motion The position of a weight attached to...Ch. 4.5 - Spring Motion A weight attached to a spring is...Ch. 4.5 -
20. Spring Motion A weight attached to a spring...Ch. 4.5 -
(Modeling) Springs A weight on a spring has...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 22ECh. 4.5 -
(Modeling) Springs A weight on a spring has...Ch. 4.5 -
(Modeling) Springs A weight on a spring has...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 25ECh. 4.5 - Prob. 26ECh. 4.5 - Prob. 27ECh. 4.5 - Prob. 28ECh. 4.5 -
(Modeling) Spring Motion Consider the spring in...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 30ECh. 4.5 - Prob. 31ECh. 4.5 - (Modeling) Spring Motion Consider the spring in...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 33ECh. 4.5 - Prob. 34ECh. 4 - Concept Check Which one of the following...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2RECh. 4 - Prob. 3RECh. 4 - Prob. 4RECh. 4 - Prob. 5RECh. 4 - Prob. 6RECh. 4 - Prob. 7RECh. 4 - Prob. 8RECh. 4 -
For each function, give the amplitude, period,...Ch. 4 - Prob. 10RECh. 4 - Prob. 11RECh. 4 - Prob. 12RECh. 4 - Prob. 13RECh. 4 -
For each function, give the amplitude, period,...Ch. 4 - Prob. 15RECh. 4 - Prob. 16RECh. 4 - Prob. 17RECh. 4 - Prob. 18RECh. 4 - Prob. 19RECh. 4 - Prob. 20RECh. 4 - Prob. 21RECh. 4 - Prob. 22RECh. 4 - Prob. 23RECh. 4 - Prob. 24RECh. 4 - Prob. 25RECh. 4 - Prob. 26RECh. 4 - Prob. 27RECh. 4 - Prob. 28RECh. 4 - Prob. 29RECh. 4 - Prob. 30RECh. 4 - Prob. 31RECh. 4 - Prob. 32RECh. 4 - Graph each function over a one-period...Ch. 4 -
Graph each function over a one-period...Ch. 4 -
Graph each function over a one-period...Ch. 4 - Prob. 36RECh. 4 -
Graph each function over a one-period...Ch. 4 - Prob. 38RECh. 4 - Prob. 39RECh. 4 - Prob. 40RECh. 4 - Prob. 41RECh. 4 - Prob. 42RECh. 4 - (Modeling) Monthly Temperatures A set of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 44RECh. 4 - Prob. 45RECh. 4 - Prob. 46RECh. 4 - Prob. 47RECh. 4 - Prob. 48RECh. 4 - Prob. 49RECh. 4 - Prob. 50RECh. 4 - Prob. 51RECh. 4 - Prob. 52RECh. 4 - Prob. 53RECh. 4 - Prob. 54RECh. 4 - Prob. 55RECh. 4 - Prob. 56RECh. 4 - Prob. 57RECh. 4 - Prob. 58RECh. 4 - Prob. 1TCh. 4 - Prob. 2TCh. 4 - Prob. 3TCh. 4 - Prob. 4TCh. 4 - Prob. 5TCh. 4 - Prob. 6TCh. 4 - Prob. 7TCh. 4 - Prob. 8TCh. 4 - Prob. 9TCh. 4 - Prob. 10TCh. 4 - Prob. 11TCh. 4 - Prob. 12TCh. 4 - Average Monthly Temperature The average monthly...Ch. 4 -
14. Spring Motion The position of a weight...Ch. 4 - Prob. 15T
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, trigonometry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- skip A swimming pool plan has concrete stairs leading down into the shallow end How much concrete will be needed to build the stairs? Bift 9 ft 2 ft 1 ft 9 ft 2 ft 5 ft [ ? ] ft³arrow_forwardFor the given right triangle, the longer leg is 8 units long and the shorter leg is 6 units long. sina=arrow_forwardWrite the equation of the trigonometric function shown in the graph. LO 5 4 3 2 1 y -5 -5 4 8 8 500 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 x 5 15л 5л 25л 15л 35π 5л 4 8 2 8 4 8arrow_forward
- 2. If log2 (sin x) + log₂ (cos x) = -2 and log2 (sin x + cos x) = (-2 + log2 n), find n.arrow_forwardIf cscx- cotx = -4, find cscx + cotx.arrow_forwardQuestion 10 (5 points) (07.04 MC) Vectors u and v are shown in the graph. -12-11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 What is proju? a -6.5i - 4.55j b -5.2i+2.6j с -4.7631 3.334j d -3.81i+1.905j < + 10 6 5 4 3 2 -3 -2 -10 1 -1 -2 -3 u -4 -5 -6 -7arrow_forward
- Find the lengths of PR and OR in terms of the angles α and β. Find the angles ∠ONQ and ∠NPQ. Find the lengths of ON and PN in terms of the angle β. Find the length of PQ. Find the length of QR. Find the length of OM. Find the length of RM. What formula can you write down by noting that PR = QR + PQ? What formula can you write down by noting that OR = OM - RM?arrow_forward5) Solve the triangle. 2 95° 4 B с A) c=3.63, A=59.5°, B = 25.5° C) c = 4.63, A = 59.5°, B = 25.5° A B) c 4.63, A 25.5°, B = 59.5° = = D) c 5.63, A = 25.5°, B = 59.5°arrow_forwardFind zw. Leave your answer in polar form. = လ 3π 2 z = 6 cos 6 cos 37 3π + i sin 2 57 W = 12 cos + i sin 6 6 ༠།ལྦ་arrow_forward
- 10 Write the expression (1 – i) i)in the standard form a + bi.arrow_forward11) The letters r and 0 represent polar coordinates. Write the equation r sine = 10 using rectangular coordinates (x, y). A) x = 10y B) y = 10 C) x = 10 D) y = 10xarrow_forward18) Find all the complex cube roots of - 8i. Leave your answers in polar form with the argument in degrees.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage
Sine, Cosine and Tangent graphs explained + how to sketch | Math Hacks; Author: Math Hacks;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z9mqGopdUQk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY