
Concept explainers
A “Lob” Pass Versus a “Bullet” A quarterback can throw a receiver a high, lazy “lob” pass or a low, quick “bullet” pass. These passes are indicated by curves 1 and 2, respectively, in Figure 4-30. (a) The lob pass is thrown with an initial speed of 21.5 m/s and its time of flight is 3.97 s. What is its launch angle? (b) The bullet pass is thrown with a launch angle of 25.0°. What is the initial speed of this pass? (c) What is the time of flight of the bullet pass?
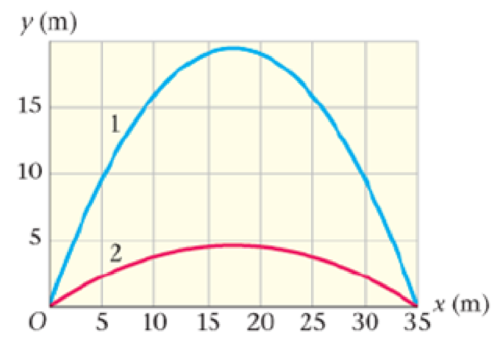
Figure 4-30
Problem 78
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
University Physics Volume 1
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Physics: Principles with Applications
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
- Asap plzzzzarrow_forwardA ball rolls off the edge of a table top 1m high and strikes the floor at a point 15m horizontally away from the edge of the table. a)find the time of flight, b) initial velocity, c)the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the ball just before it strikes the floor.arrow_forwardA golfer hits a golfball off a cliff from 8.5 metres above flat ground. The golfball is hit with an initial velocity of 43m/s [33 degrees above the horizontal]. a) Calculate the time of flight of the golfball. b) Calculate the horizontal range of the golfball. c) Calculate the maximum height of the golfball above the ground. d) Calculate the velocity of the golfball at its maximum height.arrow_forward
- For a projectile lunched with an initial velocity of v0 at an angle of θ (between 0 and 90o) , a) derive the general expression for maximum height hmax and the horizontal range R. b) For what value of θ gives the highest maximum height? Please see images for full problem.arrow_forwardFor all questions, assume concepts such as friction or air resistance are negligible, unless stated otherwise in the question. A ball is launched from ground level at an angle of 60˚ and with a speed of 15 m/s. a)What is the maximum height the ball will reach? b)How far horizontally will the ball travel before returning to ground level?arrow_forwardAn object is launched at a velocity of 20m/s in a direction making an angle of 25° upward with the horizontal. a) What is the maximum height reached by the object? b) What is the total flight time ( between launch and touching the ground) of the object? C) What is the horizontal range (maximum x above ground) of the object? d) What is the magnitude of the velocity of the object just before it hits the ground?arrow_forward
- A cannon ball is fired with an initial velocity vo at a wall that is 100. meters tall and located 450. meters away. The initial angle of launch of the cannon ball is 0. We want to determine if the cannon ball will clear the wall. If not how high-up will the ball strike the wall from the ground. (A) Sketch a graph showing position of the cannonball during its flight (y versus x) showing and labeling the initial velocity vector. Identify and write knowns and unknowns (B) Without using numerical values, determine which physics equations of motion will help solve this problem. Simplify as useful for this particular case. (C) If the initial horizontal component of the balls velocity is 90.0 m/s and its initial angle is 0-24 degrees, does the cannonball clear the wall? If not, how high above the ground is the ball when it hits the wall?arrow_forwardThe initial speed of a tennis ball is 57.5 m/s and the launch angle is ?i = 16°. Neglect air resistance.Question 1) What is the maximum height, h, of the tennis ball? in mQuestione 2) What is the range, R, of the tennis ball? in m info given: what angle results in the greatest height=90 For this 90° angle, the horizontal component of velocity is zero, so the initial velocity is completely in the vertical direction, resulting in greatest height Kato tries substituting ty,max for t, 0 for yi, and h for yf, and gets h = vi2 sin2 ?i 2g When ?i = 90°, sin2 ?i is maximum, so h is maximum what angle results in the maximum horizontal range=45° I substituted 2vi sin ?i g into the expression for the horizontal component of velocity, (vi cos ?i)t, and got R = 2vi2 sin ?i cos ?i g when ?i = 45°, 2?i = 90°, and sin 90° = 1, which is its maximum value.arrow_forwardA ball is kicked from the ground with an initial speed of 10 m/s at a 50 degree angle with the horizontal. a) Calculate the magnitude of the ball’s velocity just before it hits the ground. b) Suppose a house is in the path of the ball and instead of landing on the ground, it lands on the roof (12m high). How long after the kick will the ball collide with the roof? I’ve found that: Horizontal range= 10.05 m Total flight time of ball= 1.56 s Maximum height= 3 marrow_forward
- For a projectile lunched with an initial velocity of vo at an angle of 0 (between 0 and 90°), a) derive the general expression for maximum height hmax and the horizontal range R. b) For what value of 0 gives the highest maximum height? Solution The components of vo are expressed as follows: Vinitial-x = Vocos(e) Vinitial-y = vosin(e) a) Let us first find the time it takes for the projectile to reach the maximum height. Using: Vfinal-y = Vinitial-y * ayt since the y-axis velocity of the projectile at the maximum height is Vfinal-y= Then, = Vinitial-y + ayt Substituting the expression of Vịnitial-y and ay = -g, results to the following: Thus, the time to reach the maximum height is tmax-height= We will use this time to the equation Yfinal - Yinitial = Vinitial-yt + (1/2)ayt2 if we use the time reach the maximum height, therefore, the displacement will yield the hum height, so hmax = Vinitial-yt + (1/2)ayt2 substituting, the vinitial-y expression above, results to the following hmax = t+…arrow_forwardA long jumper leaves the ground with an initial velocity of 16 m/s at an angle of 45° from the horizontal. a) How long was the jumper in the air? b) What is the range of his jump?arrow_forwardEngineering dynamics. Don't use Artificial intelligence tools.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





