
Concept explainers
(a)
The value of
Answer to Problem 74QAP
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
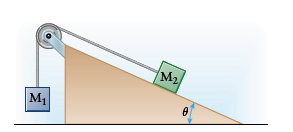
We'll use two different but related coordinate systems for the two blocks. For block
We can draw free-body diagrams and apply Newton's second law in component form for both blocks.
The tension acting on each block will be identical in magnitude.
Since block
Since, both blocks are at rest, which means the acceleration of each block is zero and we can calculate
.
Free-body diagram of
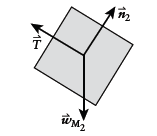
Newton's second law for
Free-body diagram of
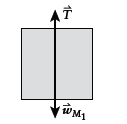
Conclusion:
For two blocks to be in equilibrium the value of
(b)
The magnitude of acceleration of two blocks if the system can move.
Answer to Problem 74QAP
The magnitude of acceleration of two blocks
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
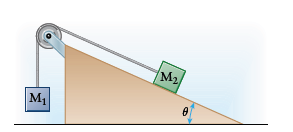
We'll use two different but related coordinate systems for the two blocks. For block
We can draw free-body diagrams and apply Newton's second law in component form for both blocks.
The tension acting on each block will be identical in magnitude.
Since block
Since,
The magnitude of the acceleration will be the same for each block because they are joined together with a string.
Free-body diagram of
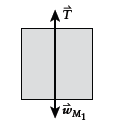
Free-body diagram of
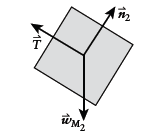
Newton's second law for
Conclusion:
If the system can move the magnitude of acceleration of two blocks is
(c)
The direction of
Answer to Problem 74QAP
The direction of
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
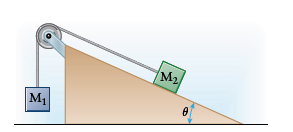
We'll use two different but related coordinate systems for the two blocks. For block
We can draw free-body diagrams and apply Newton's second law in component form for both blocks.
The tension acting on each block will be identical in magnitude.
Since block
Since,
Free-body diagram of
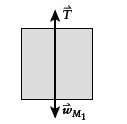
Free-body diagram of
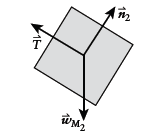
Newton's second law for
Since
Conclusion:
As we have value of
(d)
The distance to which block
Answer to Problem 74QAP
The distance to which block
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
And
Calculation:
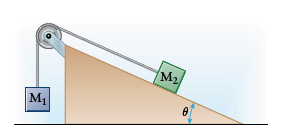
We'll use two different but related coordinate systems for the two blocks. For block
We can draw free-body diagrams and apply Newton's second law in component form for both blocks.
The tension acting on each block will be identical in magnitude.
Since block
Since,
If the acceleration is constant, we can use the constant acceleration equations to calculate how far
Free-body diagram of
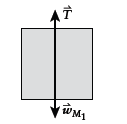
Free-body diagram of
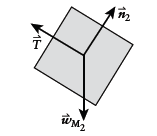
Newton's second law for
By using the constant acceleration equations to calculate how far
Conclusion:
Thus in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS LL W/ 6 MONTH ACCESS
- A man slides two boxes up a slope. The two boxes A and B have a mass of 75 kg and 50 kg, respectively. (a) Draw the free body diagram (FBD) of the two crates. (b) Determine the tension in the cable that the man must exert to cause imminent movement from rest of the two boxes. Static friction coefficient USA = 0.25 HSB = 0.35 Kinetic friction coefficient HkA = 0.20 HkB = 0.25 M₁ = 75 kg MB = 50 kg P 35° Figure 3 B 200arrow_forwardA golf ball is struck with a velocity of 20 m/s at point A as shown below (Figure 4). (a) Determine the distance "d" and the time of flight from A to B; (b) Determine the magnitude and the direction of the speed at which the ball strikes the ground at B. 10° V₁ = 20m/s 35º Figure 4 d Barrow_forwardThe rectangular loop of wire shown in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 0.18 g per centimeter of length and is pivoted about side ab on a frictionless axis. The current in the wire is 8.5 A in the direction shown. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane. Find the direction of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane.arrow_forward
- A particle with a charge of − 5.20 nC is moving in a uniform magnetic field of (B→=−( 1.22 T )k^. The magnetic force on the particle is measured to be (F→=−( 3.50×10−7 N )i^+( 7.60×10−7 N )j^. Calculate the y and z component of the velocity of the particle.arrow_forwardneed answer asap please thank youarrow_forward3. a. Determine the potential difference between points A and B. b. Why does point A have a higher potential energy? Q = +1.0 C 3.2 cm 4.8 cm Aarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





