A light-sensing circuit is in Fig. 4.90, including a resistor that changes value under illumination (photoresistor Rlight) and a variable resistor (potentiometer Rpot). The circuit is in the Wheatstone bridge configuration such that a “balanced” condition results in Vout = 0 for a defined value of incident light and a corresponding value for Rlight. (a) Derive an algebraic expression for Vout in terms of RS, R1, R2, Rlight, and Rpot. (b) Using the numerical values given in the circuit, calculate the value of Rpot required to balance the circuit at 500 lux, where Rlight = 200 Ω. (c) If the resistance of the photoresistor decreases by 2% for a light increase to 600 lux (and assuming the resistance change with light is linear), what will the light level be if you measure Vout = 150 mV?
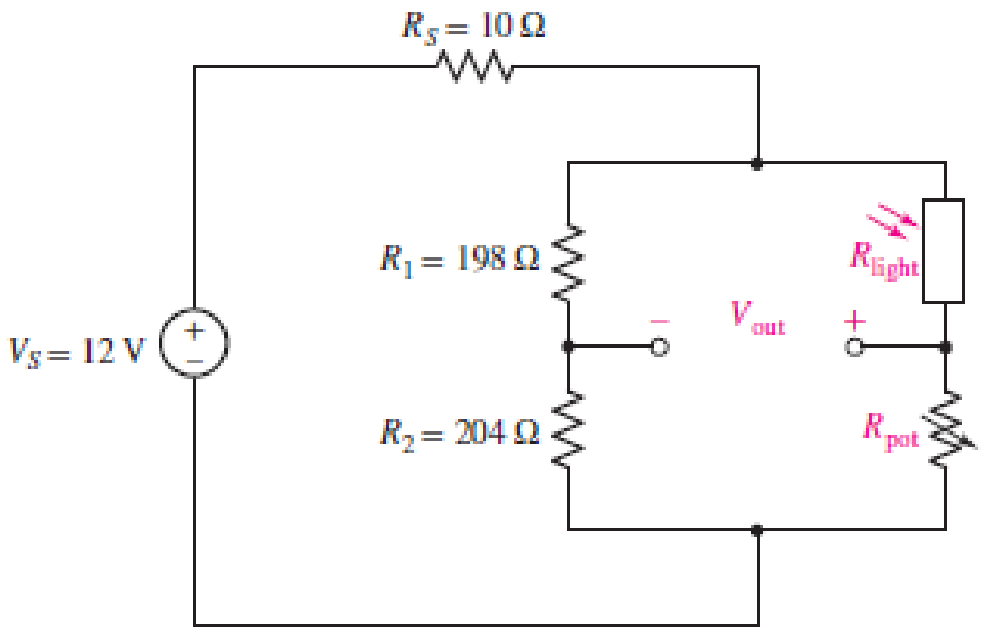
■ FIGURE 4.90
(a)
Write an algebraic expression for the output voltage
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 4.90 in the textbook.
Calculation:
The given circuit of Figure 4.90 is redrawn as shown in Figure 1.
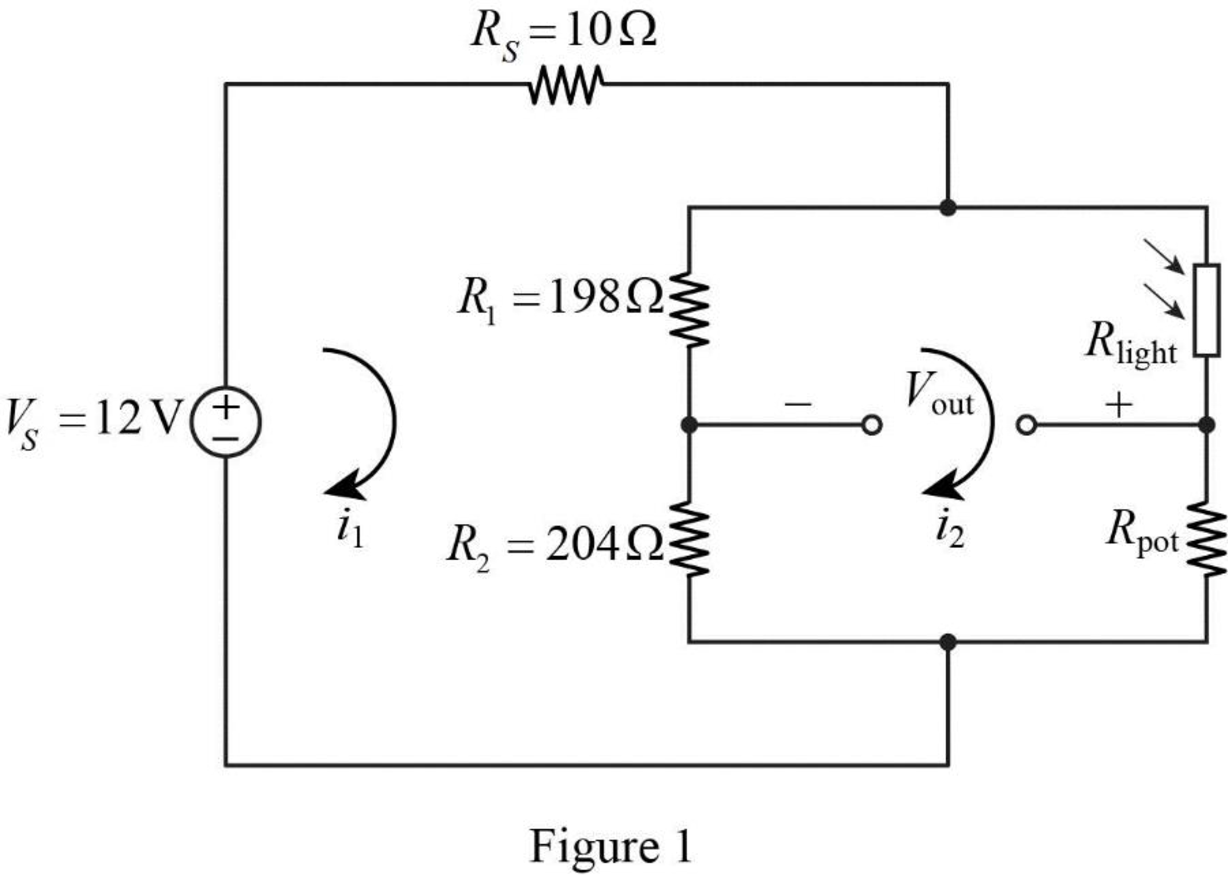
Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law for the loop current
Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law for the loop current
Rearrange the equation as follows,
Substitute equation (2) in equation (1).
Rearrange the equation as follows,
Substitute equation (3) in equation (2).
In Figure 1, the output voltage
Substitute equation (3) and (4) in equation (5).
Conclusion:
Thus, the output voltage
(b)
Calculate the value of variable resistor
Answer to Problem 74E
The value of variable resistor
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Part (a).
The resistance
For balanced condition,
Calculation:
Refer to Part (a).
Substitute 0 for
Simplify the equation as follows,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the value of variable resistor
(c)
Find the light level if the resistance of the photoresistor decreases by 2% for a light increase to 600 lux with the measure of output voltage
Answer to Problem 74E
The light level is 760 lux if the resistance of the photoresistor decreases by 2% for a light increase to 600 lux with the measure of output voltage
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Part (b).
The variable resistor
The output voltage
Calculation:
When the photoresistor resistance decreases by 2% with a light increase to 600 lux, then
Refer to Part (a), reduce the equation (6) as follows,
Substitute 12 V for
Reduce the equation as follows,
For a linear change, the light level is calculated as follows.
Conclusion:
Thus, the light level is 760 lux if the resistance of the photoresistor decreases by 2% for a light increase to 600 lux with the measure of output voltage
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Engineering Circuit Analysis
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Modern Database Management
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
- A left-sided signal x(t)=-e¯bt u(-t): 0 == X(s) -e-bu(t)e-st dt =- -Le-c 1 -(b+o+jw)t dt = = -00 -∞ (a + b) + jw 1 s+b For this integral to converge, it is necessary that b +σ <0; i.e., ROC: Re[s]=σ < −b. 2 How ?arrow_forwardA left-sided signal x(t)=-ebt u(-t): A right-sided signal x(t)=e¯at u(t) Find Laplace transform of x(t)=u(t)arrow_forwardFind Laplace transform of x(t) = −e¯btu(−t) + e¯atu(t) Find Laplace transform of x(t) = u(t)arrow_forward
- Expert only, don't use artificial intelligence ,or screenshot of an AI solving stepsarrow_forwardfind inverse LT for the following functions 1- [0.2s+1.4] s2+1.96. 2. L-1 5s+1 Ls2-25. 4s+32 3. L- L(s2-16).arrow_forwardQ Figurel shows the creation of the Frequency Reuse Pattern Using the Cluster Size K (A) illustrates how i and j can be used to locate a co-channel cell. Juster Cluster CB Cluster 2 X=7(i=2,j=1)arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





