
Concept explainers
(Appendix 4B) Support Department Cost Allocation
MedServices Inc. is divided into two operating departments: Laboratory and Tissue Pathology. The company allocates delivery and accounting costs to each operating department. Delivery costs include the costs of a fleet of vans and drivers that drive throughout the state each day to clinics and doctors’ offices to pick up samples and deliver them to the centrally located laboratory and tissue pathology offices. Delivery costs are allocated on the basis of number of samples. Accounting costs are allocated on the basis of the number of transactions processed. No effort is made to separate fixed and variable costs; however, only budgeted costs are allocated. Allocations for the coming year are based on the following data:
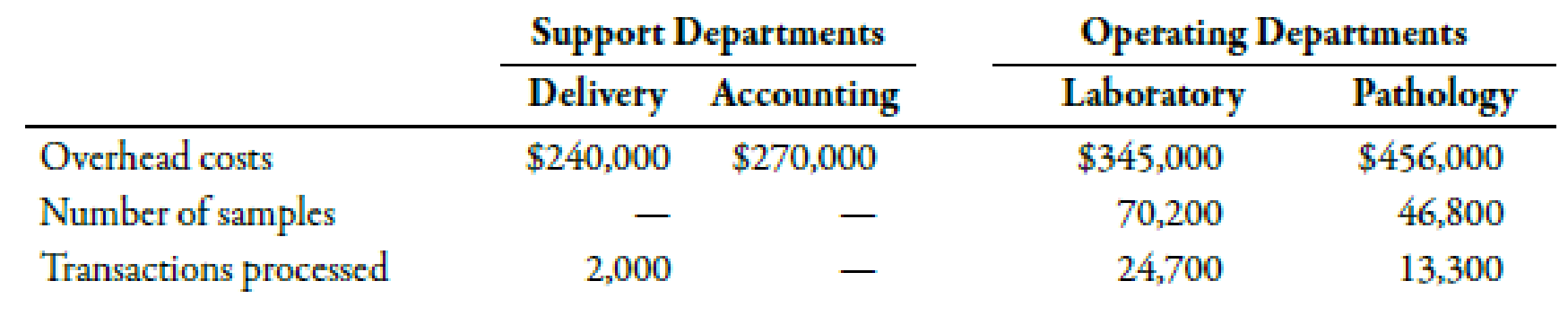
Required:
- 1. Assign the support department costs by using the direct method. (Note: Round allocation ratios to four decimal places.)
- 2. Assign the support department costs by using the sequential method, allocating accounting costs first. (Note: Round allocation ratios to four decimal places.)
1.
Calculate the assigned cost of support departments by using direct method.
Explanation of Solution
Direct Method:
Direct method implies that the unit cost must include all the factory costs. It states that the cost of support departments should not be added in the unit cost if it is not included in operating departments’ cost because they do not play any role in selling the unit or product.
Use the following formula to calculate assignment ratios on the basis of number of samples:
Laboratory department:
Substitute 70,200 for number of samples in laboratory and 117,000 for total samples in operating department in the above formula.
Therefore, the assignment ratio for laboratory department is 0.60.
Pathology department:
Substitute 46,800 for number of samples in laboratory and 117,000 for total samples in operating department in the above formula.
Therefore, the assignment ratio for pathology department is 0.40.
Use the following formula to calculate assignment ratios on the basis of transactions processed:
Laboratory department:
Substitute 24,700 for transactions processed in laboratory and 38,000 for total transactions processed in operating department in the above formula.
Therefore, the assignment ratio for laboratory department is 0.65.
Pathology department:
Substitute 13,300 for transactions processed in laboratory and 38,000 for total transactions processed in operating department in the above formula.
Therefore, the assignment ratio for pathology department is 0.35.
Assign cost of support departments to the operating departments:
| Support departments | Operating departments | |||
| Delivery($) | Accounting($) | Laboratory($) | Pathology($) | |
| Direct costs | 240,000 | 270,000 | 345,000 | 456,000 |
| Delivery1 | -240,000 | 144,000 | 96,000 | |
| Accounting1 | -270,000 | 175,500 | 94,500 | |
| Total | 0 | 0 | 664,500 | 646,500 |
Table (1)
Working Note:
1. Calculation of assigned cost of support department to operating department:
| Account Title |
Assignment ratio A |
Support department cost($) B |
Assigned cost($) |
| Delivery cost: | |||
| Laboratory | 0.6000 | 240,000 | 144,000 |
| Pathology | 0.4000 | 240,000 | 96,000 |
| Accounting: | |||
| Laboratory | 0.65 | 270,000 | 175,500 |
| Pathology | 0.35 | 270,000 | 94,500 |
Table (2)
2.
Calculate the assigned cost of support departments by using sequential method and allocate accounting costs first.
Explanation of Solution
Sequential Method:
Sequential method recognizes that there is possible interaction between the support departments. However, it does not account for such interaction in full which makes it more accurate as compared to the direct method.
Use the following formula to calculate cost assignment ratios on the basis of number of transactions processed:
Delivery:
Substitute 2,000 for transactions processed in delivery and 40,000 for total transactions processed in the above formula.
Therefore, the cost assignment ratio for delivery is 0.0500.
Laboratory department:
Substitute 24,700 for transactions processed in laboratory and 40,000 for total transactions processed in the above formula.
Therefore, the cost assignment ratio for laboratory department is 0. 6175.
Pathology department:
Substitute 13,300 for transactions processed in pathology and 40,000 for total transactions processed in the above formula.
Therefore, the cost assignment ratio for pathology department is 0.3325.
Use the following formula to calculate assignment ratios on the basis of number of samples:
Laboratory department:
Substitute 70,200 for number of samples in laboratory and 117,000 for total samples in operating department in the above formula.
Therefore, the assignment ratio for laboratory department is 0.60.
Pathology department:
Substitute 46,800 for number of samples in laboratory and 117,000 for total samples in operating department in the above formula.
Therefore, the assignment ratio for pathology department is 0.40.
Assign cost of support departments to the operating departments:
| Support departments | Operating departments | |||
| Delivery($) | Accounting($) | Laboratory($) | Pathology($) | |
| Direct costs | 240,000 | 270,000 | 345,000 | 456,000 |
| Accounting2 | 13,500 | 166,725 | 89,775 | |
| Delivery2 | -253,500 | -270,000 | 152,100 | 101,400 |
| Total | 0 | 0 | 663,825 | 647,175 |
Table (3)
Working Note:
2. Calculation of assigned cost of support department:
| Account Title |
Assignment ratio A |
Support department cost($) B |
Assigned cost($) |
| Accounting: | |||
| Delivery | 0.0500 | 270,000 | 13,500 |
| Laboratory | 0.6175 | 270,000 | 166,725 |
| Pathology | 0.3325 | 270,000 | 89,775 |
| Delivery cost: | |||
| Laboratory | 0.60 | 253,500 | 152,100 |
| Pathology | 0.40 | 253,500 | 101,400 |
Table (4)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Bundle: Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making, Loose-Leaf Version, 7th + CengageNOWv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- financial accountiongarrow_forwardHello tutor please solve this questionarrow_forwardUsing the following data: Actual direct labor-hours worked Standard direct labor rate Labor efficiency variance 6,100 hours $10 per hour $2,000 Unfavorable The standard hours allowed for December's production isarrow_forward
- No WRONG ANSWERarrow_forwardSchumacher Company uses the perpetual inventory system, and it engaged in the following transactions during 2009: 1) Started the business by issuing common stock for $7,500 cash. 2) Paid cash to purchase $5,000 of inventory. 3) Sold inventory that cost $3,000 for $7,250 cash. 4) Incurred and paid operating expenses, $250. Schumacher Company engaged in the following transactions during 2010: 1) Paid cash to purchase $5,800 of inventory. 2) Sold inventory that cost $7,000 for $15,150 cash. 3) Incurred and paid operating expenses, $500. a. The gross margin for the year 2009 is b. The amount of Retained Earnings at December 31, 2009, isarrow_forwardcan you please solve this financial accountingarrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning


