
Concept explainers
Use the following information for Brief Exercises 4-34 and 4-35:
Sanjay Company manufactures a product in a factory that has two producing departments, Assembly and Painting, and two support departments, S1 and S2. The activity driver for S1 is square footage, and the activity driver for S2 is number of machine hours. The following data pertain to Sanjay:
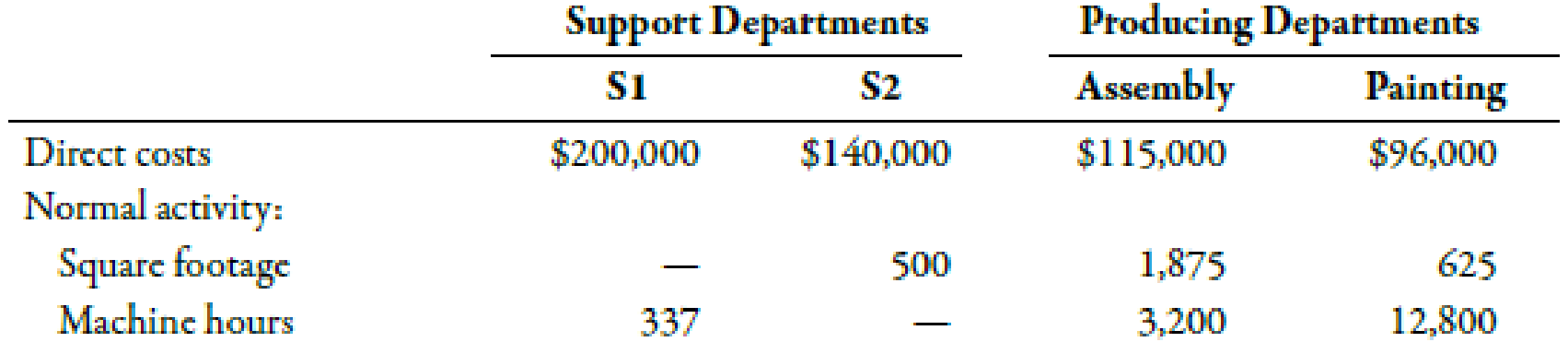
Brief Exercises 4-35 (Appendix 4B) Sequential Method
Refer to the information for Sanjay Company on the previous page. Now assume that Sanjay uses the sequential method to allocate support department costs. S1 is allocated first, then S2.
Required:
- 1. Calculate the cost assignment ratios to be used under the sequential method for S2, Assembly, and Painting. Carry out your answers to four decimal places.
- 2. Allocate the
overhead costs to the producing departments by using the sequential method.
1.
Computecost assignment ratios for S2 under sequential method.
Explanation of Solution
Sequential Method:
Sequential method recognizes that there is possible interaction between the support departments. However, it does notaccount for such interaction in full which makes it more accurate as compared to the direct method.
Use the following formula to calculatecost assignment ratios for S1 on the basis of number of square footage:
S2:
Substitute 500 for number of square footage in S2 and 3,000 for total square footage in the above formula.
Therefore, the cost assignment ratio for S2 is 0.1667.
Assembly department:
Substitute 1,875 for number ofsquare footage in assembly and 3,000 for total square footage in the above formula.
Therefore, the cost assignment ratio for assembly department is 0.6250.
Painting department:
Substitute 625 for number ofsquare footage in assembly and 3,000 for total square footage in the above formula.
Therefore, the cost assignment ratio for painting department is 0.2083.
Use the following formula to calculate cost assignment ratios for Department S2 on the basis of number of machine hours:
Assembly department:
Substitute 3,200 for number of machine hoursofassembly and 16,000 for total machine hours of producing department in the above formula.
Therefore, the assignment ratio for assembly department is 0.20.
Painting department:
Substitute 12,800 for number of machine hours of painting and 16,000 for total machine hours of producing department in the above formula.
Therefore, the assignment ratio for painting department is 0.80.
Working Note:
1.
Calculation of total number of square footage in producing departments:
2.
Calculation of total number of machine hoursof producing departments:
2.
Allocate the support department costs to the producing departments by using the sequential method:
Explanation of Solution
Allocation:
Allocation can be defined as the process of assigning the indirect costs to the cost object with the help of a convenient and reasonable method. It is essential to allocate indirect costs to the cost objects.
| Support departments | Producing departments | |||
| Allocate | S1($) | S2($) | Assembly($) | Painting($) |
| Direct costs | 200,000 | 140,000 | 115,000 | 96,000 |
| S1 | (200,000) | 33,340 | 125,000 | 41,660 |
| S2 | (173,340) | 34,668 | 138,672 | |
| Total | 0 | 0 | 274,668 | 276,332 |
Table (1)
Working Note:
1.
Allocation of support departments cost to S2:
For S1 cost:
2.
Allocation of support departments cost to assembly department:
For S1 cost:
For S2 cost:
3.
Allocation of support departments to painting department:
For S1 cost:
For S2 cost:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Bundle: Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making, Loose-Leaf Version, 7th + CengageNOWv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- Mead Incorporated began operations in Year 1. Following is a series of transactions and events involving its long-term debt investments in available-for-sale securities. Year 1 January 20 Purchased Johnson & Johnson bonds for $20,500. February 9 Purchased Sony notes for $55,440. June 12 Purchased Mattel bonds for $40,500. December 31 Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Johnson & Johnson, $21,500; Sony, $52,500; and Mattel, $46,350. Year 2 April 15 Sold all of the Johnson & Johnson bonds for $23,500. July 5 Sold all of the Mattel bonds for $35,850. July 22 Purchased Sara Lee notes for $13,500. August 19 Purchased Kodak bonds for $15,300. December 31 Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Kodak, $17,325; Sara Lee, $12,000; and Sony, $60,000. Year 3 February 27 Purchased Microsoft bonds for $160,800. June 21 Sold all of the Sony notes for $57,600. June 30 Purchased Black & Decker bonds for $50,400. August 3 Sold all of the Sara…arrow_forwardWhat is the ending inventory?arrow_forwardMaple industries uses the straight line method solution general accounting questionarrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





