
Concept explainers
Unter Components
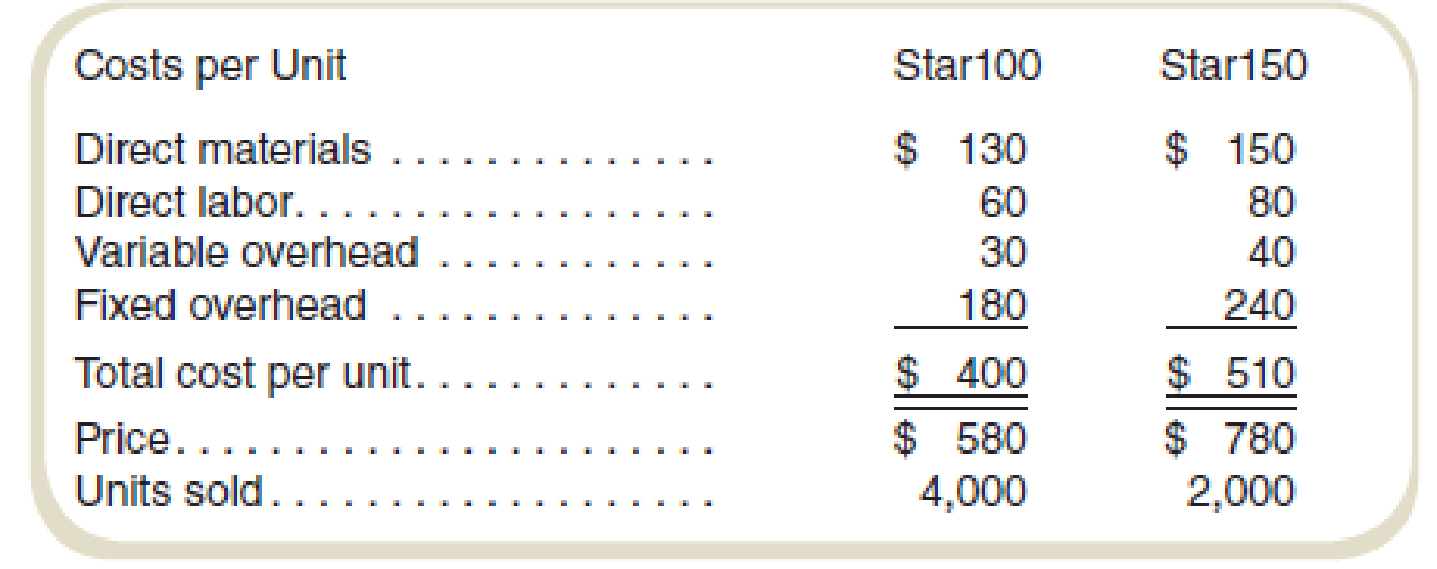
The average wage rate is $40 per hour. Variable
Required
- a. A nationwide car-sharing service has offered to buy 2,500 Star100 systems and 2,500 Star150 systems if the price is lowered to $400 and $500, respectively, per unit. If Unter accepts the offer, how many direct labor-hours will be required to produce the additional systems? How much will the profit increase (or decrease) if Unter accepts this proposal? Prices on regular sales will remain the same.
- b. Suppose that the car-sharing has offered instead to buy 3,500 each of the two models at $400 and $500, respectively. This customer will purchase the 3,500 units of each model only in an all-or-nothing deal. That is, Unter must provide all 3,500 units of each model or none. Unter’s management has decided to fill the entire special order for both models. In view of its capacity constraints, Unter will reduce sales to regular customers as needed to fill the special order. How much will the profits change if the order is accepted? Assume that the company cannot increase its production capacity to meet the extra demand.
- c. Answer the question in requirement (b), assuming instead that the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $60 per hour. Variable overhead costs for overtime production are $10 per hour more than for normal production.
a.
Identify, if Company U accepts the offer, how many direct labors will be required to produce the additional systems, and calculate the change in profit in case of company accepts the offer.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate direct labor hours per unit:
| Particulars | Star 100 | Star 150 |
| Labor cost per unit (A) | $60 | $80 |
| Wage rate per labor hour (B) | $40 | $40 |
| Labor hours per unit (A) ÷ (B) | 1.5 hours | 2 hours |
Table (1)
Calculate total direct labor hours required for the additional business.
The current production uses 10,000 direct labor hours and capcity is 20,000 direct labor hours. Thus capacity will not have to expanded to accept the order.
Calculate the change in profit:
| Particulars | Star 100 | Star 150 | Total |
| Units (A) | $2,500 | $2,500 | |
| Sales price (B) | $400 | $500 | |
| Variable costs (C) | $220 | $270 | |
| Differential revenue (A × B) | $1,000,000 | $1,250,000 | $2,250,000 |
| Less: Differential variable cost (A × C) | $550,000 | $675,000 | $1,225,000 |
| Differential Profit | $450,000 | $575,000 | $1,025,000 |
Table (2)
Thus, the differential operating profit is $1,025,000, so Company U should accept the offer.
Working note 1:
Calculate the variable costs:
| Particulars | Star 100 | Star 150 |
| Direct materials | $130 | $150 |
| Add: Direct labor | $60 | $80 |
| Variable overheads | $30 | $40 |
| Total variable costs | $220 | $270 |
Table (3)
b.
Calculate the change in profit in case of acceptance of the offer.
Answer to Problem 53P
The increase in profit is $895,000 if it accepts the offer. So the company should accept the offer.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate total direct labor hours required for the additional business.
The total production time required is 10,000 hours for normal business and 12,250 direct labor hours for the special order, but the direct labor hours capacity is limited to 20,000 hours. In this case, company need to reduce the production of the units sold to the regular customers.
Due to direct labor time is the constraing resource, the companyhaving two alternatives, one is company need to reduce the number of star 100 machines sold to the regular customers, and the second is company need to reduce the number of start 150 machines sold to the regular customers.
Calculate the contribution margin per direct labor hour for each product on the basis of regular customers:
| Particulars | Star 100 | Star 150 |
| Revenue per unit | $580 | $780 |
| Less: Variable cost per unit | $220 | $270 |
| Contribution margin per unit (A) | $360 | $510 |
| Direct labor hours per unit (B) | 1.5 | 2 |
| Contribution margin per hour (A ÷ B) | $240 | $255 |
Table (4)
Star 100 model has the lower contribution margin per hour compared with the star 150 model. The company should reduce the production of this product to sell the special order.
After producing the special order, the company will have 7,750 direct labor hours (20,000 direct labor hours – 12,250 direct labor hours). Company will produce first 2,000 units of srtar 150 model (4,000 direct labor hours = 2,000 units × 2 direct labor hours). The balance direct labor hours ( 3,750 direct labor hours = 7,750 direct labor hours – 4,000 direct labor hours) to produce 2,500 units of the star 100 model.
Calculate the change in operating profit:
Thus, the changes in profit are $895,000, if it accepts the offer. So the company should accept the offer.
Working note 2:
Calculate the contribution margin in case of special order and normal production:
| Particulars | Star 100 | Star 150 | Total |
| Special order: | |||
| Sales price | $400 | $500 | |
| Less: Variable cost | $220 | $270 | |
| Contribution margin per unit (A) | $180 | $230 | |
| Number of units (B) | 3,500 | 3,500 | |
| Total contribution margin ( 1 =A × B) | $630,000 | $805,000 | $1,435,000 |
| Regular production: | |||
| Sales price | $580 | $780 | |
| Less: Variable cost | $220 | $270 | |
| Contribution margin per unit (A) | $360 | $510 | |
| Number of units (B) | 2,500 | 2,000 | |
| Total contribution margin ( 2 =A × B) | $900,000 | $1,020,000 | $1,920,000 |
| Total contribution margin (1 + 2) | $1,530,000 | $1,825,000 | $3,355,000 |
| Less: Fixed Costs | $720,000 | $480,000 | $1,200,000 |
| Net Operating Income (3) | $810,000 | $1,345,000 | $2,155,000 |
Table (5)
Working note 3:
Total contribution margin in case of normal course of business:
| Particulars | Star 100 | Star 150 | Total |
| Regular production: | |||
| Sales price | $580 | $780 | |
| Less: Variable cost | $220 | $270 | |
| Contribution margin per unit (A) | $360 | $510 | |
| Number of units (B) | 4,000 | 2,000 | |
| Total contribution margin ( C =A × B) | $1,440,000 | $1,020,000 | $2,460,000 |
| Less: Fixed costs | $720,000 | $480,000 | $1,200,000 |
| Net operating Income (4) | $720,000 | $540,000 | $1,260,000 |
Table (6)
c.
Calculate the change in profit in case of acceptance of the offer with the given change.
Answer to Problem 53P
The change in profit is $1,367,500 if it accepts the offer. So the company should accept the offer.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution margin:
The excess of sales price over the variable expenses is referred to as the contribution margin. It is computed by deducting the variable expenses from the sales revenue. A contribution margin income statement is prepared in order to record the contribution margin.
Calculate the change in operating profit:
Thus, the change in profit is $1,367,500 if, it accepts the offer. So the company should accept the offer.
Working note 4:
Calculate the contribution margin in case of special order:
| Particulars | Star 100 | Star 150 | Total |
| Special order: | |||
| Sales price | $400 | $500 | |
| Less: Variable cost | $220 | $270 | |
| Contribution margin per unit (A) | $180 | $230 | |
| Number of units (B) | 3,500 | 3,500 | |
| Total contribution margin ( 1 =A × B) | $630,000 | $805,000 | $1,435,000 |
| Regular production: | |||
| Sales price | $580 | $780 | |
| Less: Variable cost | $220 | $270 | |
| Contribution margin per unit (A) | $360 | $510 | |
| Number of units (B) | 4,000 | 2,000 | |
| Total contribution margin ( 2 =A × B) | $1,440,000 | $1,020,000 | $2,460,000 |
| Gross contribution margin (1 + 2) | $2,070,000 | $1,825,000 | $3,895,000 |
| Less: Additional direct labor costs | $45,000 | ||
| Additional variable overhead | $22,500 | ||
| Total contribution margin | $3,827,500 | ||
| Less: Fixed costs | $720,000 | $480,000 | $1,200,000 |
| Net operating Income | $2,627,500 |
Table (7)
Working note 5:
Calculate the additional labor costs:
Calculate the additional variable costs:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING BUNDLE
- 1: Armand Giroux (single; 0 federal withholding allowances) earned weekly gross pay of $1,500. For each period, he makes a 401(k) retirement plan contribution of 8% of gross pay. The city in which he works (he lives elsewhere) levies a tax of 1% of an employee's taxable pay (which is the same for federal and local income tax withholding) on residents and 0.60% of an employee's taxable pay on nonresidents. Federal income tax withholding = $ State income tax withholding = $ Local income tax withholding = $ 144.10 69.00 8.28 2: Peter Quigley (married; 8 federal withholding allowances) earned weekly gross pay of $2,350. He contributed $100 to a flexible spending account during the period. The city in which he lives and works levies a tax of 2.7% of an employee's taxable pay (which is the same for federal and local income tax withholding) on residents and 1.9% of an employee's taxable pay on nonresidents. Federal income tax withholding = $ State income tax withholding = $ Local income tax…arrow_forwardCheck my work mode: This sh so hat is correct or incorrect for the work you have compl it does not indicate completion. Return to questi 1.5 9 points You've collected the following information about Fender, Incorporated: Sales Net income Dividends Total debt Total equity $ 170,000 $ 12,800 $ 8,400 $ 68,000 $ 56,000 a. What is the sustainable growth rate for the company? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b. If it does grow at this rate, how much new borrowing will take place in the coming year, assuming a constant debt-equity ratio? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. c. What growth rate could be supported with no outside financing at all? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. × Answer is complete but not entirely correct. a. Sustainable growth rate b.…arrow_forwardOn December 31, 2018, Blackpink Company, a financing institution lent ₱15,000,000 to YG Corp. due 3 years after. The loan is supported by an 12% note receivable. Based on the company’s initial estimates the present value of the 12 months expected credit loss (ECL) discounted at 10% is at 2,000,000. The probability of default (PD) is at 7%. Blackpink Company was able to collect interest as it became due at the end of 2019. There was no evidence of significant increase in credit risk by the end 2019 and that the receivable is determined to have “low credit risk”. There were no changes in its initial estimate of the 12 months expected credit loss either. By the end of 2020, Blackpink Company was able to collect interest as it became due. Based on available forward-looking information (determinable without undue cost or effort), however, there is evidence that there was a significant increase in credit risk by the end of 2020. Blackpink Company therefore had to change its basis…arrow_forward
- On December 31, 2018, Blackpink Company, a financing institution lent ₱15,000,000 to YG Corp. due 3 years after. The loan is supported by an 12% note receivable. Based on the company’s initial estimates the present value of the 12 months expected credit loss (ECL) discounted at 10% is at 2,000,000. The probability of default (PD) is at 7%. Blackpink Company was able to collect interest as it became due at the end of 2019. There was no evidence of significant increase in credit risk by the end 2019 and that the receivable is determined to have “low credit risk”. There were no changes in its initial estimate of the 12 months expected credit loss either. By the end of 2020, Blackpink Company was able to collect interest as it became due. Based on available forward-looking information (determinable without undue cost or effort), however, there is evidence that there was a significant increase in credit risk by the end of 2020. Blackpink Company therefore had to change its basis…arrow_forwardNeed correct answer general accounting questionarrow_forwardCalculate Federal Income Tax Withholding Using the Percentage Method (Pre-2020 Form W-4) Publication 15-T. round to two decimal places at each calculationarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
