
Concept explainers
This serial problem began in Chapter 1 and continues through most of the book. If previous chapter segments were not completed, the serial problem can begin at this point.
SP 4 The December 31, 2019, adjusted

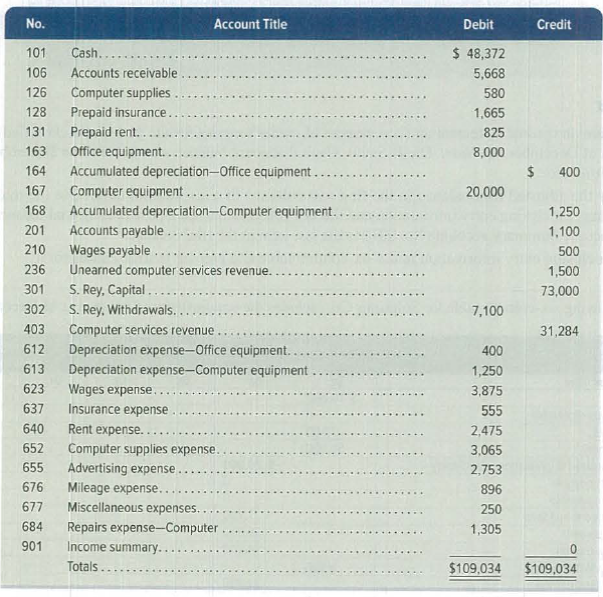
Required
- 1. Record and post the necessary closing entries as of December 31, 2019.
- 2. Prepare a post-closing trial balance as of December 31, 2019.
1.
Record and post the necessary closing entries as of December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to permanent account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and dividends accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Record the closing entries as of December 31, 2019:
| Date | Accounts and Explanation |
Account Number |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| 2019 | Computer service revenue (SE–) | 401 | 31,284 | |
| December 31 | Income Summary (SE+) | 901 | 31,284 | |
| (To close the revenue account) | ||||
| 2019 | ||||
| December 31 | Income summary (SE–) | 901 | 16,824 | |
| Depreciation expense – Office equipment(SE+) | 612 | 400 | ||
| Depreciation expense – Computer equipment(SE+) | 613 | 1,250 | ||
| Wages expense (SE+) | 623 | 3,875 | ||
| Insurance expense (SE+) | 637 | 555 | ||
| Rent expense (SE+) | 640 | 2,475 | ||
| Computer supplies expense (SE+) | 652 | 3,065 | ||
| Advertising expense (SE+) | 655 | 2,753 | ||
| Mileage expense (SE+) | 676 | 896 | ||
| Miscellaneous expense (SE+) | 677 | 250 | ||
| Repairs expense (SE+) | 684 | 1,305 | ||
| (To close the expense accounts) | ||||
| 2019 | Income Summary (SE–) | 901 | 14,460 | |
| December 31 | S.R’s Capital (SE+) | 301 | 14,460 | |
| (To close the income summary accounts) | ||||
| 2019 | S.R’s Capital (SE–) | 301 | 7,100 | |
| December 31 | S.R’s Withdrawals (SE+) | 302 | 7,100 | |
| (To close withdrawals account.) |
Table (1)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of S.R’s capital (transferred):
Revenue account:
In this closing entry, the computer service revenue earned account is closed by transferring the amount of computer service revenue account to Income summary account in order to bring the revenue account balance to zero. Hence, debit computer service revenue account and credit Income summary account.
Expense account:
In this closing entry, all expense accounts are closed by transferring the amount of total expense to the Income summary account in order to bring the expense account balance to zero. Hence, debit the Income summary account and credit all expenses account.
Income summary account:
Income summary account is a temporary account. This account is debited to close the net income value to S.R’s capital account.
S.R’s capital is a component of stockholders’ equity account. The value of S.R’s capital increased because net income is transferred. Therefore, it is credited.
Withdrawals account:
S.R’s capital is a component of owner’s equity. Thus, owners ‘equity is debited since the capital is decreased on owners’ drawings.
S.R’s withdrawals are a component of owner’s equity. It is credited because the balance of owners’ withdrawals account is transferred to owners ‘capital account.
Ledger:
Ledger is the book, where the debit and credit entries are recorded in the journal book are transferred to their relevant accounts. The entire accounts of the company are collectively called the ledger.
Posting the closing entries to the ledger account:
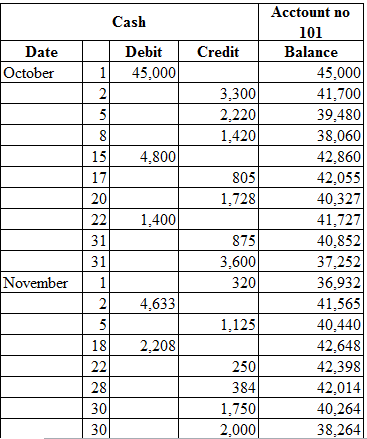
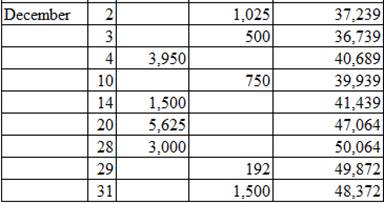
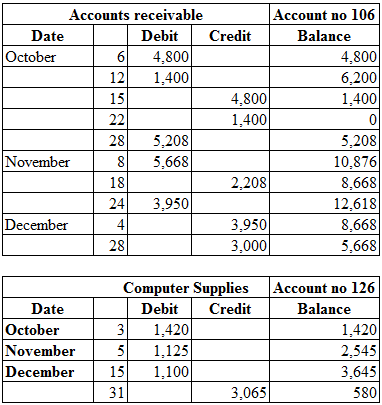
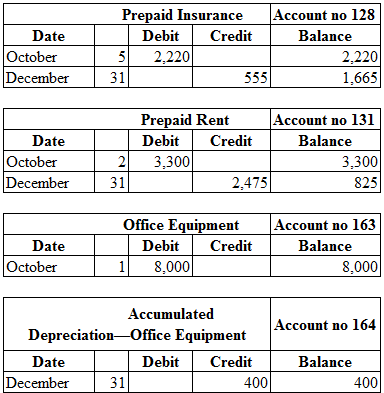
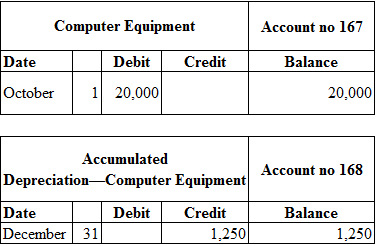
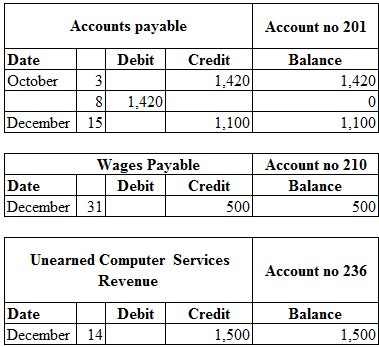
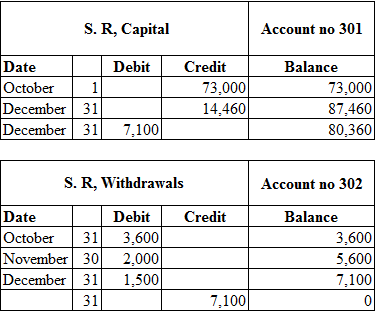
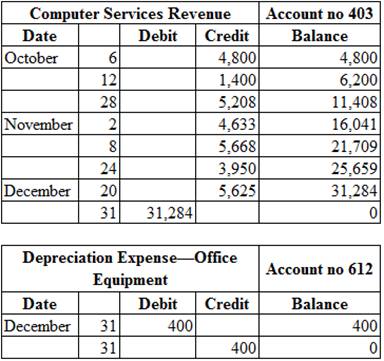
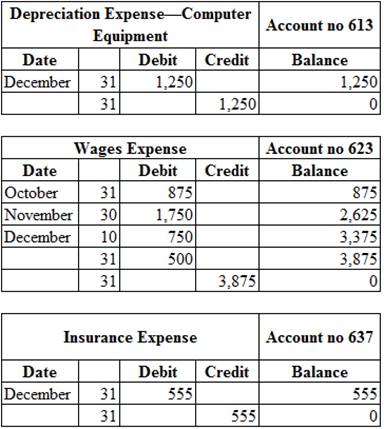
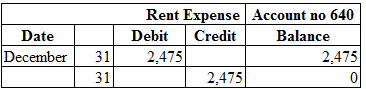
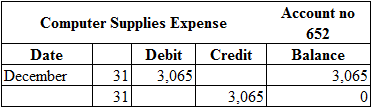
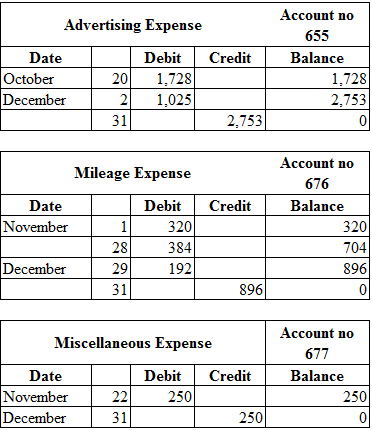
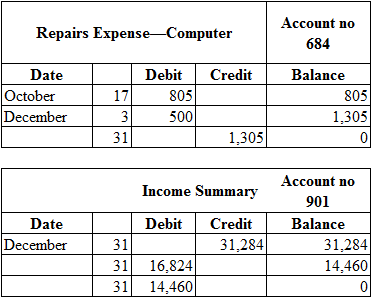
Table (2)
2.
Prepare a post-closing trial balance.
Explanation of Solution
Post-closing trial balance:
The post-closing trial balance is a summary of all ledger accounts, and it shows the debit and the credit balances after the closing entries are journalized and posted. The post-closing trial balance contains only permanent (balance sheet) accounts, and the debit and the credit balances of permanent accounts should agree.
Prepare a post-closing trial balance:
| B Solutions | ||
| Post-Closing Trial Balance | ||
| December 31, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Debit($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 48,372 | |
| Accounts receivable | 5,668 | |
| Computer supplies | 580 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 1,665 | |
| Prepaid rent | 825 | |
| Office equipment | 8,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation – Office equipment | 400 | |
| Computer equipment | 20,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation – Computer equipment | 1,250 | |
| Accounts payable | 1,100 | |
| Wages payable | 500 | |
| Unearned computer service revenue | 1,500 | |
| S.R’s Capital | 80,360 | |
| Totals | $85,110 | $85,110 |
Table (3)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- Please provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct financial process.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forward
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning  College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub




