
Concept explainers
On April 1, Jiro Nozomi created a new travel agency, Adventure Travel. The following transactions occurred during the company’s first month.

The company’s chart of accounts follows.
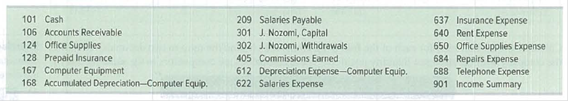
Required
- 1. Use the balance column format to set up each ledger account listed in its chart of accounts.
- 2. Prepare
journal entries to record the transactions for April and post them to the ledger accounts. The company records prepaid and unearned items inbalance sheet accounts. - 3. Prepare an unadjusted
trial balance as of April 30. - 4. Use the following information to journalize and post
adjusting entries for the month:- a. Prepaid insurance of $133 has expired this month.
- b. At the end of the month. $600 of office supplies are still available.
- c. This month’s
depreciation on the computer equipment is $500. - d. Employees earned $420 of unpaid and unrecorded salaries as of month-end.
- e. The company earned $1,750 of commissions that are not yet billed at month-end.
- 5. Prepare the adjusted trial balance as of April 30. Prepare the income statement and the statement of owner’s equity for the month of April and the balance sheet at April 30.
- 6. Prepare journal entries to close the temporary accounts and post these entries to the ledger.
- 7. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.
Requirement 2:
Prepare journal entries to record the transactions for April.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
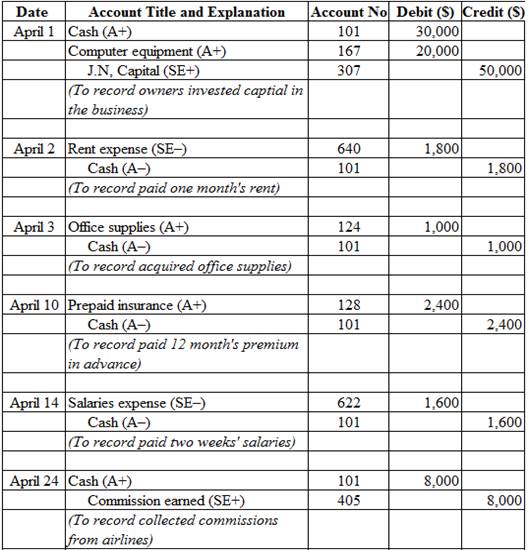
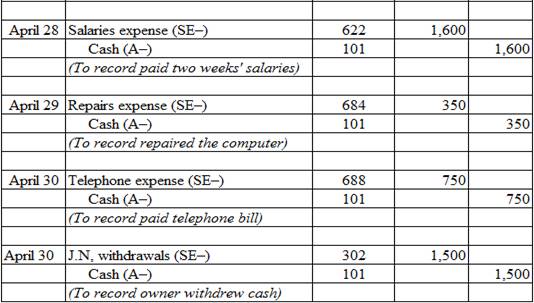
Table (1)
Requirement 3:
Prepare an unadjusted trial balance as of April 30.
Explanation of Solution
Unadjusted trial balance:
The unadjusted trial balance is the summary of all the ledger accounts that appears on the ledger accounts before making adjusting journal entries.
Prepare an unadjusted trial balance as of April 30:
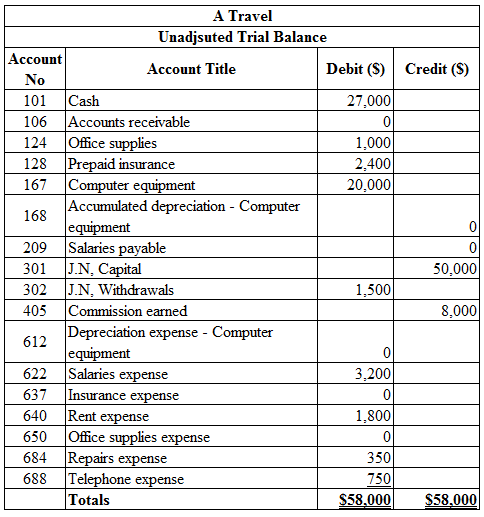
Table (2)
Requirement 4:
Journalize the adjusting entries.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle.
Journalize the adjusting entries:
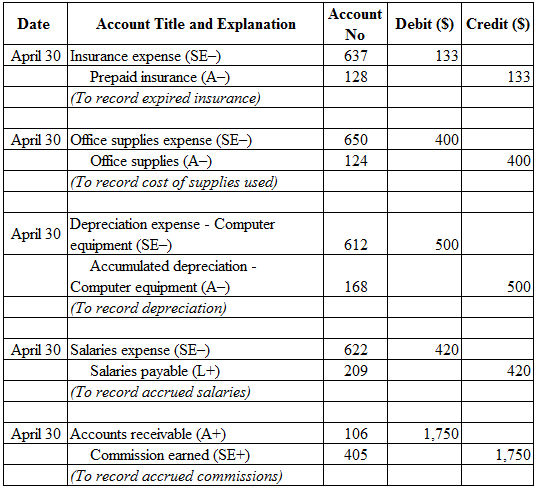
Table (3)
Working note:
Calculate the amount of office supplies used:
Requirement 5:
Prepare the followings:
- Adjusted trial balance as of April 30.
- Income statement for the month ended April 30.
- Statement of owner’s equity for the month ended April 30.
- Balance sheet at April 30.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusted Trial Balance: Adjusted trial balance is that statement which contains complete list of accounts with their adjusted balances, after all relevant adjustments have been made. This statement is prepared at the end of every financial period.
Prepare the adjusted trial balance as of April 30:
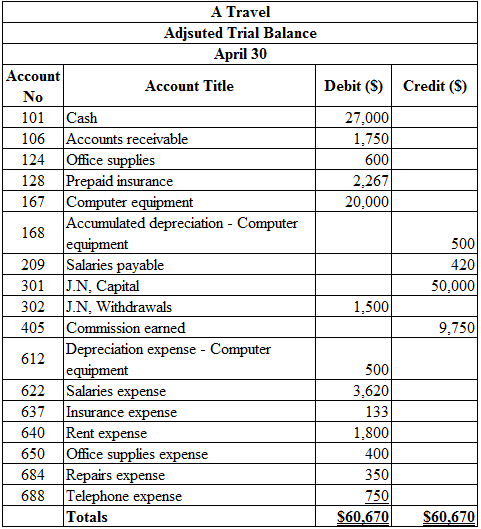
Table (4)
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare an income statement for the month ended April 30:
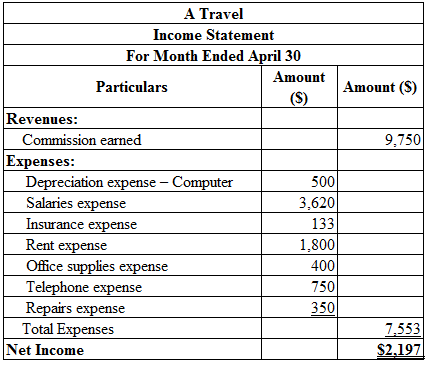
Table (5)
Statement of owners’ equity: This statement reports the beginning owner’s equity and all the changes, which led to ending owners’ equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to and a drawing is deducted from beginning owner’s equity to arrive at the result, ending owner’s equity.
Prepare the statement of owners’ equity for the month ended April 30:
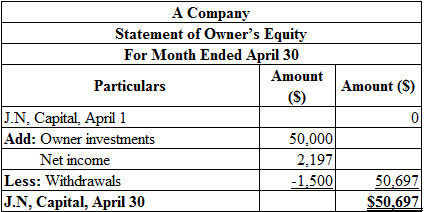
Table (6)
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
Prepare the balance sheet as of April 30:
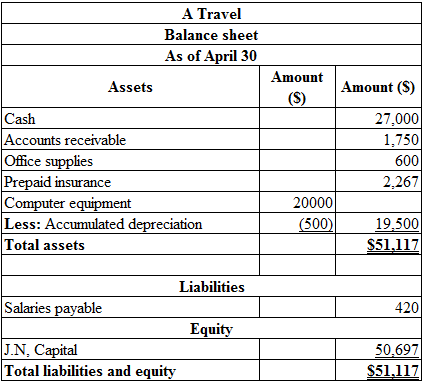
Table (7)
Requirement 5:
Prepare journal entries to close the temporary accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to permanent account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and dividends accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Prepare the closing entries:
| Date | Accounts and Explanation |
Account Number |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| April 30 | Commission earned (SE–) | 405 | 9,750 | |
| Income Summary (SE+) | 901 | 9750 | ||
| (To close the revenue account) | ||||
| April 30 | Income summary (SE–) | 901 | 7,553 | |
| Depreciation expense - Equipment (SE+) | 612 | 500 | ||
| Salaries expense (SE+) | 622 | 3,620 | ||
| Insurance expense (SE+) | 637 | 133 | ||
| Rent expense (SE+) | 640 | 1,800 | ||
| Office supplies expense (SE+) | 650 | 400 | ||
| Repairs expense (SE+) | 684 | 350 | ||
| Telephone expense (SE+) | 688 | 750 | ||
| (To close the expense accounts) | ||||
| April 30 | Income Summary (SE–) | 901 | 2,197 | |
| J.N’s Capital (SE+) | 301 | 2,197 | ||
| (To close the income summary accounts) | ||||
| April 30 | J.N’s Capital (SE–) | 301 | 1,500 | |
| J.N’s Withdrawals (SE+) | 302 | 1,500 | ||
| (To close withdrawals account.) |
Table (8)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of J.N’s capital (transferred):
Requirement 1,2,4, and 6:
Post the journal entries, adjusting entries and closing entries to the ledger account:
Explanation of Solution
Ledger:
Ledger is the book, where the debit and credit entries recorded in the journal book are transferred to their relevant accounts. The entire accounts of the company are collectively called the ledger.
Posting the journal entries, adjusting entries and closing entries to the ledger account:
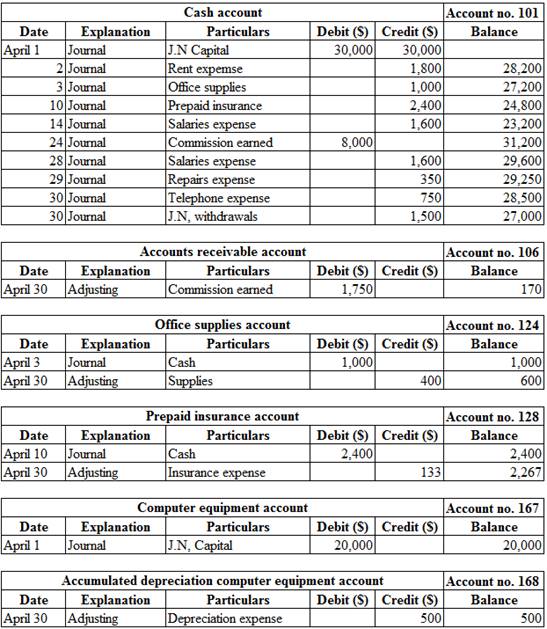
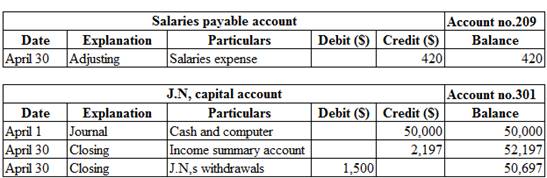
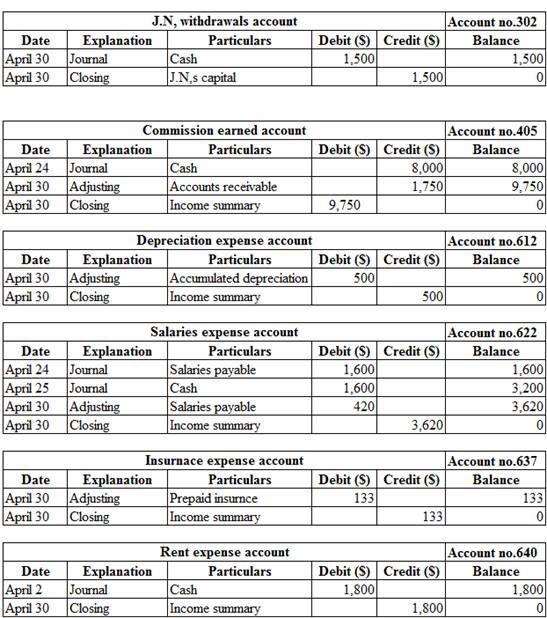
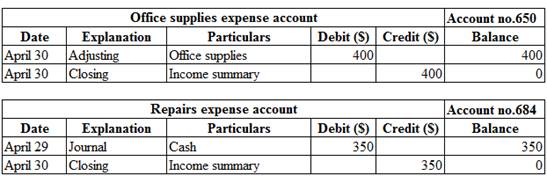
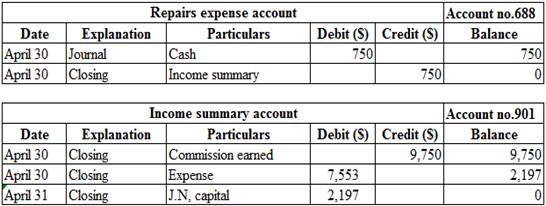
Table (9)
Requirement 7:
Prepare a post-closing trial balance.
Explanation of Solution
Post-closing trial balance:
The post-closing trial balance is a summary of all ledger accounts, and it shows the debit and the credit balances after the closing entries are journalized and posted. The post-closing trial balance contains only permanent (balance sheet) accounts, and the debit and the credit balances of permanent accounts should agree.
Prepare a post-closing trial balance:
| A Company | ||
| Post-Closing Trial Balance | ||
| April 30 | ||
| Particulars | Debit($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 27,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 1,750 | |
| Office supplies | 600 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 2,267 | |
| Computer equipment | 20,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation – Computer equipment | 500 | |
| Salaries payable | 420 | |
| J.N’s Capital | 50,697 | |
| Totals | $51,617 | $51,617 |
Table (10)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- I need help solving this financial accounting question with the proper methodology.arrow_forward18. Inventory shrinkage is recorded as:A. Increase in revenueB. Decrease in liabilitiesC. Inventory loss expenseD. Owner withdrawalarrow_forward19. What does a classified balance sheet show?A. Net cash from operationsB. Revenue by categoryC. Assets and liabilities in current and long-term sectionsD. Owners' drawings helparrow_forward
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this financial accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forward19. What does a classified balance sheet show?A. Net cash from operationsB. Revenue by categoryC. Assets and liabilities in current and long-term sectionsD. Owners' drawingsarrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this financial accounting question.arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College PubCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College PubCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage





