
Concept explainers
The adjusted
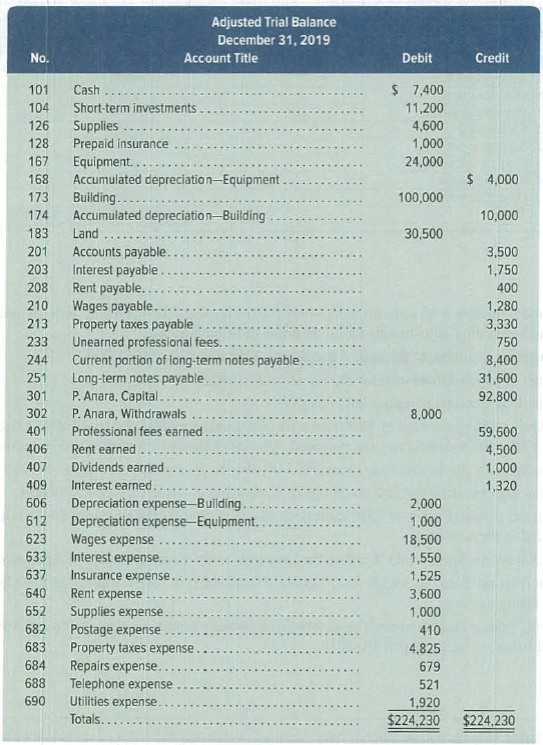
Required
- 1. Prepare the income statement and the statement of owner’s equity for calendar-year 2019 and the classified
balance sheet at December 31, 2019. - 2. Prepare the necessary closing entries at December 31, 2019.
- 3. Use the information in the financial statements to calculate these ratios: (a) return on assets (total assets at December 31, 2018, were $160,000), (b) debt ratio, (c) profit margin ratio (use total revenues as the denominator), and (d)
current ratio . Round ratios to three decimals for parts a and c and to two decimals for parts b and d.
Requirement 1:
Prepare the following:
- Income statement for the year ended December 31, 2019.
- Statement of owner’s equity for the year ended December 31, 2019.
- Balance sheet at December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare an income statement for the year ended December 31, 2019:
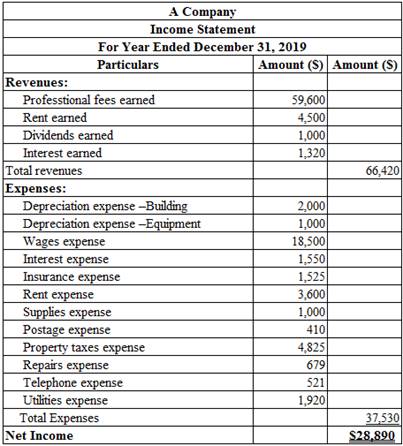
Table (1)
Statement of owners’ equity: This statement reports the beginning owner’s equity and all the changes, which led to ending owners’ equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to and a drawing is deducted from beginning owner’s equity to arrive at the result, ending owner’s equity.
Prepare the statement of owners’ equity for the year ended December 31, 2019:
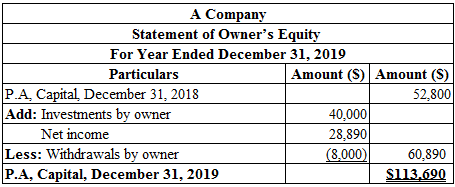
Table (2)
Classified balance sheet: The main elements of balance sheet assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity are categorized or classified further into sections, and sub-sections in a classified balance sheet. Assets are further classified as current assets, long-term investments, property, plant, and equipment (PPE), and intangible assets. Liabilities are classified into two sections current and long-term. Stockholders’ equity comprises of common stock and retained earnings. Thus, the classified balance sheet includes all the elements under different sections.
Prepare the classified balance sheet at December 31, 2019:
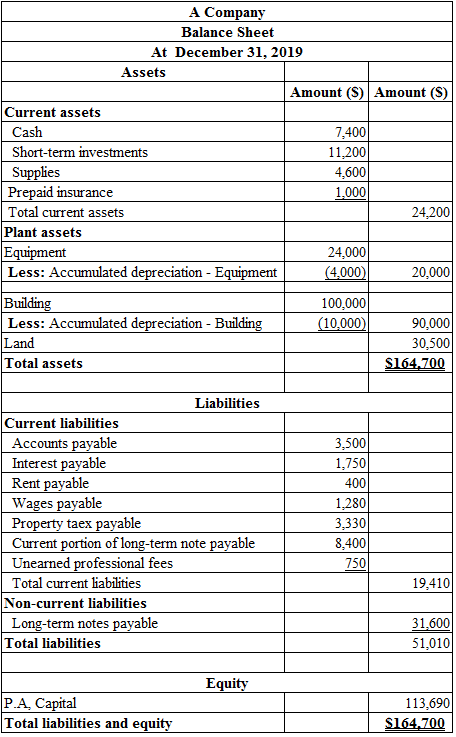
Table (3)
Requirement 2:
Prepare the closing entries at December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to permanent account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and dividends accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Prepare the closing entries at December 31, 2019:
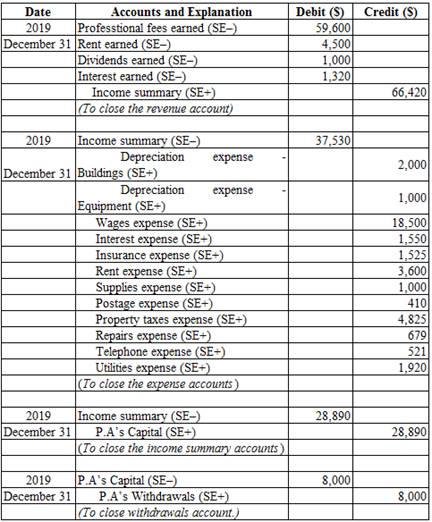
Table (4)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of P. A’s capital (transferred):
Revenue account:
In this closing entry, the professional fees earned account is closed by transferring the amount of professional fees earned account to Income summary account in order to bring the revenue account balance to zero. Hence, debit professional fees earned account and credit Income summary account.
Expense account:
In this closing entry, all expense accounts are closed by transferring the amount of total expense to the Income summary account in order to bring the expense account balance to zero. Hence, debit the Income summary account and credit all expenses account.
Income summary account:
Income summary account is a temporary account. This account is debited to close the net income value to P.A’s capital account.
P.A’s capital is a component of stockholders’ equity account. The value of P.A’s capital increased because net income is transferred. Therefore, it is credited.
Withdrawals account:
P.A’s capital is a component of owner’s equity. Thus, owners ‘equity is debited since the capital is decreased on owners’ drawings.
P.A’s withdrawals are a component of owner’s equity. It is credited because the balance of owners’ withdrawals account is transferred to owners ‘capital account.
Requirement 3:
Compute the following ratios:
- (a) Return on assets.
- (b) Debt ratio.
- (c) Profit margin ratio.
- (d) Current ratio.
Explanation of Solution
Return on Assets (ROA): This financial ratio evaluates a company’s efficiency in operating the assets to generate net income. So, ROA is a tool used to measure the performance of a company.
The following formula is used to calculate return on assets:
(a)
Compute the return on assets ratio:
Debt Ratio:
Debt ratio is the ratio that measures the relationship between total assets and total liabilities of the company. Debt ratio reflects the finance strategy of the company. It is used to evaluate company’s ability to pay its debts. Higher debt ratio implies the higher financial risk.
The following formula is used to calculate debt ratio:
(b)
Compute the debt ratio:
Profit margin ratio:
Profit margin ratio is used to determine the percentage of net income that is being generated per dollar of revenue or sales.
The following formula is used to calculate profit margin ratio:
(c)
Compute the profit margin ratio:
Current ratio: The financial ratio which evaluates the ability of a company to pay off the debt obligations which mature within one year or within completion of operating cycle is referred to as current ratio. This ratio assesses the liquidity of a company.
The following formula is used to calculate current ratio:
(d)
Compute the current ratio:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- I am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes owner’s equity?A. Assets minus liabilitiesB. Total assetsC. Revenues minus expensesD. Retained earnings onlyarrow_forward
- Please provide the solution to this financial accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forwardRustic Table Restaurant had a 12% return on a $90,000 investment in new dining facilities. The investment resulted in increased sales and an increase in income that was 5% of the increase in sales. What was the increase in sales? Provide answerarrow_forwardno chatgpt Which of these is considered a permanent account?A. Salaries ExpenseB. RevenueC. Retained EarningsD. Dividendsarrow_forward
- Can you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this financial accounting problem using the correct accounting process?arrow_forwardWhich of these is considered a permanent account?A. Salaries ExpenseB. RevenueC. Retained EarningsD. Dividendsarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage


