
Organic Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781118452288
Author: David R. Klein
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 4, Problem 49PP
(a)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The compound is needed to found which has more heat of combustion value between the given set of compounds.
Concept introduction:
- Heat of combustion: heat of combustion is the numeric value, which represents the energy required to burn a hydrocarbon completely in presence of oxygen. For more stable molecule heat of combustion value will be high when compare with least stable molecule.
- Chair conformer: chair conformer is a stable conformer for cyclohexane compound. In this chair conformer two positions are important for substitutions one is equatorial and other one axial position. Axial positions are parallel to the axis of ring while equatorial positions are perpendicular to the axis of the ring.
Example:
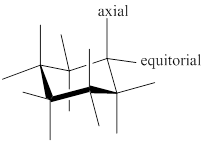
- Equatorial position is more stable than axial position; therefore a compound with equatorial substituents has high heat of combustion value than a compound with axial substituents.
(b)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The compound is needed to found which has more heat of combustion value between the given set of compounds.
Concept introduction:
- Heat of combustion: heat of combustion is the numeric value, which represents the energy required to burn a hydrocarbon completely in presence of oxygen. For more stable molecule heat of combustion value will be high when compare with least stable molecule.
- Chair conformer: chair conformer is a stable conformer for cyclohexane compound. In this chair conformer two positions are important for substitutions one is equatorial and other one axial position. Axial positions are parallel to the axis of ring while equatorial positions are perpendicular to the axis of the ring.
Example:

- Equatorial position is more stable than axial position; therefore a compound with equatorial substituents has high heat of combustion value than a compound with axial substituents.
(c)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The compound is needed to found which has more heat of combustion value between the given set of compounds.
Concept introduction:
- Heat of combustion: heat of combustion is the numeric value, which represents the energy required to burn a hydrocarbon completely in presence of oxygen. For more stable molecule heat of combustion value will be high when compare with least stable molecule.
- Chair conformer: chair conformer is a stable conformer for cyclohexane compound. In this chair conformer two positions are important for substitutions one is equatorial and other one axial position. Axial positions are parallel to the axis of ring while equatorial positions are perpendicular to the axis of the ring.
Example:

- Equatorial position is more stable than axial position; therefore a compound with equatorial substituents has high heat of combustion value than a compound with axial substituents.
(d)
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The compound is needed to found which has more heat of combustion value between the given set of compounds.
Concept introduction:
- Heat of combustion: heat of combustion is the numeric value, which represents the energy required to burn a hydrocarbon completely in presence of oxygen. For more stable molecule heat of combustion value will be high when compare with least stable molecule.
- Chair conformer: chair conformer is a stable conformer for cyclohexane compound. In this chair conformer two positions are important for substitutions one is equatorial and other one axial position. Axial positions are parallel to the axis of ring while equatorial positions are perpendicular to the axis of the ring.
Example:

- Equatorial position is more stable than axial position; therefore a compound with equatorial substituents has high heat of combustion value than a compound with axial substituents.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely:
(a) 0.200 M HCl
Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely:
(a) 0.000259 M HClO4
What is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 1LTSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 1PTSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 2ATSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 3ATSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4ATSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 2LTSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 5PTSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 6ATSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 3LTSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 7PTS
Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 8ATSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 9ATSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4LTSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 10PTSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 11ATSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 5LTSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 12PTSCh. 4.2 - Prob. 13ATSCh. 4.3 - Prob. 6LTSCh. 4.3 - Prob. 14PTSCh. 4.3 - Prob. 15ATSCh. 4.6 - Prob. 7LTSCh. 4.6 - Prob. 16PTSCh. 4.6 - Prob. 17ATSCh. 4.6 - Prob. 18ATSCh. 4.7 - Prob. 19CCCh. 4.8 - Prob. 8LTSCh. 4.8 - Prob. 20PTSCh. 4.8 - Prob. 21ATSCh. 4.11 - Prob. 9LTSCh. 4.11 - Prob. 22PTSCh. 4.11 - Prob. 23ATSCh. 4.11 - Prob. 10LTSCh. 4.11 - Prob. 24PTSCh. 4.11 - Prob. 25PTSCh. 4.11 - Prob. 26PTSCh. 4.11 - Prob. 27ATSCh. 4.12 - Prob. 11LTSCh. 4.12 - Prob. 28PTSCh. 4.12 - Prob. 29ATSCh. 4.12 - Prob. 30CCCh. 4.12 - Prob. 12LTSCh. 4.12 - Prob. 31PTSCh. 4.12 - Prob. 32ATSCh. 4.12 - Prob. 13LTSCh. 4.12 - Prob. 33PTSCh. 4.12 - Prob. 34ATSCh. 4.12 - Prob. 35ATSCh. 4.14 - Prob. 36CCCh. 4.14 - Prob. 37CCCh. 4.14 - Prob. 38CCCh. 4 - Prob. 39PPCh. 4 - Prob. 40PPCh. 4 - Prob. 41PPCh. 4 - Prob. 42PPCh. 4 - Prob. 43PPCh. 4 - Prob. 44PPCh. 4 - Prob. 45PPCh. 4 - Prob. 46PPCh. 4 - Prob. 47PPCh. 4 - Prob. 48PPCh. 4 - Prob. 49PPCh. 4 - Prob. 50PPCh. 4 - Prob. 51PPCh. 4 - Prob. 52PPCh. 4 - Prob. 53PPCh. 4 - Prob. 54PPCh. 4 - Prob. 55PPCh. 4 - Prob. 56PPCh. 4 - Prob. 57PPCh. 4 - Prob. 58PPCh. 4 - Prob. 59PPCh. 4 - Prob. 60PPCh. 4 - Prob. 61PPCh. 4 - Prob. 62PPCh. 4 - Prob. 63PPCh. 4 - Prob. 64IPCh. 4 - Prob. 65IPCh. 4 - Prob. 67IPCh. 4 - Prob. 68IPCh. 4 - Prob. 69IP
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY