
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes, 5th edition
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780073525310
Author: Leland H. Hartwell, Michael L. Goldberg, Janice A. Fischer, Leroy Hood, Charles F. Aquadro
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 45P
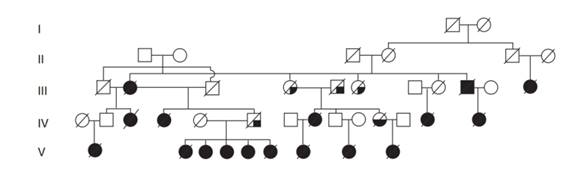
The pedigree at the bottom of the page shows the inheritance of various types of cancer in a particular family. Molecular analyses (described in subsequent chapters) indicate that with one exception, the cancers occurring in the patients in this pedigree as associ- ated with a rare mutation in a gene called BRCA2.
| a. | Which individual is the exceptional cancer patient whose disease is not associated with a BRCA2 mutation? |
| b. | Is the BRCA2 mutation dominant or recessive to the normal BRCA2 allele in terms of its cancer-causing effects? |
| c. | Is the BRCA2 gene likely to reside on the X chromosome, the Y chromosome, or an autosome? How definitive is your assignment of the chromosome carrying BRCA2?  |
| d. | Is the penetrance of the cancer phenotype complete or incomplete? |
| e. | Is the expressivity of the cancer phenotype unvarying or variable? |
| f. | Are any of the cancer |
| g. | How can you explain the absence of individuals diagnosed with cancer in generations I and II? |
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Preoperative Diagnosis: Torn medial meniscus, left knee
Postoperative Diagnosis: Combination horizontal cleavage tear/flap tear, posterior horn, medial meniscus, left knee.
Operation: Arthroscopic subtotal medial meniscectomy, left knee
Anesthetic: General endotracheal
Description of Procedure: The patient was placed on the operating table in the supine position and general endotracheal anesthesia was administered. After an adequate level of anesthesia was achieved, the patient's left lower extremity was prepped with Betadine scrubbing solution, then draped in a sterile manner. Several sites were then infiltrated with 1% Xylocaine solution with Epinephrine to help control bleeding from stab wounds to be made at these sites. These stab wounds were made anterolaterally at the level of the superior pole of the patella for insertion of an irrigation catheter into the suprapatellar pouch area, anterolaterally at the level of the joint line for insertion of the scope and anteromedially at…
UARDIAN
SIGNA
Life Sciences/ Baseline Test
Grade 10
ry must be written in point form.
pot
in full sentences using NO MORE than 70 words
sentences from 1 to 7.
only ONE point per sentence.
words as far as possible.
number of words you have used in brackets at the end
GDE/2024
QUESTION 3
The table below shows the results of an investigation in which the effect of
temperature and light on the yield of tomatoes in two greenhouses on a farm
was investigated.
TEMPERATURE
(°C)
AVERAGE YIELD OF TOMATOES PER
3.1
PLANT
(kg)
LOW LIGHT LEVELS
HIGH LIGHT LEVELS
5
0,5
0,5
10
1,5
2,5
15
3,0
5,0
20
3,6
8,5
25
3,5
7,8
30
2,5
6,2
State TWO steps the investigator may have taken into
consideration during the planning stage of the investigation.
(2)
3.2
Identify the:
a) Independent variables
(2)
b) Dependent variable
(1)
3.3
Plot a line graph showing the results of the average yield of the
tomatoes from 5°C to 30°C for low light levels.
(6)
3.4
State ONE way in which the scientists could have improved the…
Explain why you chose this mutation. Begin by transcribing and translating BOTH the
normal and abnormal DNA sequences. The genetic code below is for your reference.
SECOND BASE OF CODON
כ
FIRST BASE OF CODON
O
THIRD BASE OF CODON
SCAGUCAGUGAGUCAG
UUU
UUC
UCU
UAU
UGU
Phenylalanine
(F)
Tyrosine (Y)
Cysteine (C)
UCC
UAC
UGC
Serine (S)
UUA
UUG
Leucine (L)
UCA
UCG_
UAA
UGA
Stop codon
-Stop codon
UAG
UGG -Tryptophan (W)
CUU
CUC
CCU
CAU
CGU
Histidine (H)
CCC
CAC
CGC
-Leucine (L)
Proline (P)
CUA
CCA
CAA
CUG
CCG
CAG-Glutamine (Q)
-Arginine (R)
CGA
CGG
AUU
ACU
AAU
AGU
AUC
Isoleucine (1)
Asparagine (N)
ACC
AAC
Threonine (T)
AUA
ACA
AAA
Methionine (M)
Lysine (K)
AUG
ACG
Start codon
AAG
AGC-Serine (S)
-Arginine (R)
AGA
AGG
GUU
GCU
GAU
GUC
GUA
GUG
GCC
Valine (V)
-Alanine (A)
GCA
GCG
GAC
GAA
GAG
Aspartic acid
(D)
GGU
Glutamic acid
(E)
GGC
GGA
GGG
Glycine (G)
In order to provide a complete answer to the question stated above, fill in the mRNA bases
and amino acid sequences by using the Genetic Code…
Chapter 4 Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes, 5th edition
Ch. 4 - Choose the best matching phrase in the right...Ch. 4 - Humans have 46 chromosomes in each somatic cell....Ch. 4 - The figure that follows shows the metaphase...Ch. 4 - XX males who are sex-reversed because they have a...Ch. 4 - Researchers discovered recently that the sole...Ch. 4 - One oak tree cell with 14 chromosomes undergoes...Ch. 4 - Indicate which of the cells numbered iv matches...Ch. 4 - a. What are the four major stages of the cell...Ch. 4 - Answer the questions that follow for each stage of...Ch. 4 - Does any reason exist that would prevent mitosis...
Ch. 4 - One oak tree cell with 14 chromosomes undergoes...Ch. 4 - Which types of cell division mitosis, meiosis I,...Ch. 4 - Complete the following statements using as many of...Ch. 4 - The five cells shown in figure a e on the next...Ch. 4 - One of the first microscopic observations of...Ch. 4 - A person is simultaneously heterozygous for two...Ch. 4 - Assuming i that the two chromosomes in homologous...Ch. 4 - In the moss Polytrichum commune, the haploid...Ch. 4 - Does any reason exist that would prevent meiosis...Ch. 4 - Sister chromatids are held together through...Ch. 4 - The pseudoautosomal regions PARs of the X and Y...Ch. 4 - Somatic cells of chimpanzees contain 48...Ch. 4 - In humans: a. How many sperm develop from 100...Ch. 4 - Women sometimes develop benign tumors called...Ch. 4 - In a certain strain of turkeys, unfertilized eggs...Ch. 4 - Imagine you have two pure-breeding lines of...Ch. 4 - A system of sex determination known as...Ch. 4 - In Drosophila, the autosomal recessive brown eye...Ch. 4 - Barred feather pattern is a Z-linked dominant...Ch. 4 - When Calvin Bridges observed a large number of...Ch. 4 - In a vial of Drosophila, a research student...Ch. 4 - In 1919, Calvin Bridges began studying an X-linked...Ch. 4 - In Drosophila, a cross was made between a...Ch. 4 - As we learned in this chapter, the white mutation...Ch. 4 - The following is a pedigree of a family in which a...Ch. 4 - Each of the four pedigrees that follow represents...Ch. 4 - The pedigree that follows indicates the occurrence...Ch. 4 - Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD is caused by a...Ch. 4 - The X-linked gene responsible for DMD encodes a...Ch. 4 - Males have hemophilia when they are hemizygous for...Ch. 4 - Consider the following pedigrees from human...Ch. 4 - Several different antigens can be detected in...Ch. 4 - The ancestry of a white female tiger bred in a...Ch. 4 - The pedigree at the bottom of the page shows the...Ch. 4 - In 1995, doctors reported a Chinese family in...Ch. 4 - In cats, the dominant 0 allele of the X-linked...Ch. 4 - In marsupials like the opposum or kangaroo, X...Ch. 4 - The pedigree diagram below shows a family in which...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- identify the indicated cell in white arrowarrow_forwardGloeocaspa Genus - diagram a colony and label the sheath, cell wall, and cytoplasm. Oscillatoria Genus - Diagram a trichome, and label the shealth and individual cells Nostoc Genus- diagram a sketch of the colonoy microscopically from low power to the left of the drawing. Draw a filament showing intercalary heterocysts, and vegatative cells to the right of the drawing Merismopedia Genus- diagram a sketch of the colony. draw and label a filament showing the colony, cell wall, and sheath. Gloeotrichia Genus- diagram a habit sketch of the colony. draw a filament showing the heterocyst, akimetes and vegatative cells of the filamentarrow_forwardOf this list shown, which genus does the image belong toarrow_forward
- As a medical professional, it is important to be able to discuss how genetic processes such as translation regulation can directly affect patients. Think about some situations that might involve translation regulation. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: Why is translation regulation important? What are some examples of translation regulation in humans? Select one of the examples you provided and explain what happens when translation regulation goes wrong.arrow_forwardThe metabolic pathway below is used for the production of the purine nucleotides adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and guanosine monophosphate (GMP) in eukaryotic cells. Assume each arrow represents a reaction catalyzed by a different enzyme. Using the principles of feedback inhibition, propose a regulatory scheme for this pathway that ensures an adequate supply of both AMP and GMP, and prevents the buildup of Intermediates A through G when supplies of both AMP and GMP are adequate.arrow_forwardQUESTION 27 Label the structures marked A, B, C and explain the role of structure A. W plasma membrane For the toolbar, press ALT+F10 (PC) or ALT+FN+F10 (Mac). BIUS ☐ Paragraph Π " ΩΘΗ Β Open Sans, a... 10pt EEarrow_forward
- examples of synamptomorphyarrow_forwardexamples of synamtomorphy.arrow_forwardE. Bar Graph Use the same technique to upload the completed image. We will use a different type of graph to derive additional information from the CO2 data (Fig A1.6.2) 1. Calculate the average rate of increase in COz concentration per year for the time intervals 1959-1969, 1969- 1979, etc. and write the results in the spaces provided. The value for 1959-1969 is provided for you as an example. 2. Plot the results as a bar graph. The 1959-1969 is plotted for you. 3. Choose the graph that looks the most like yours A) E BAR GRAPH We will use a different type of graph to derive additional information from the CU, data (rig. nive). Average Yearly Rate of Observatory, Hawall interval Rate of increase per year 1959-1969 0.9 1969-1979 1979-1989 1989-1999 1999-2009 Figure A1.6.2 1999-2009 *- mrame -11- -n4 P2 جية 1989-1999 1979-1989 1969-1979 1959-1969 This bar drawn for you as an example 1.0 CO, Average Increase/Year (ppmv) B) E BAR GRAPH We will use a different type of graph to derive…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Case Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
Case Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Case Studies In Health Information Management
Biology
ISBN:9781337676908
Author:SCHNERING
Publisher:Cengage

What are Mutations and what are the different types of Mutations?; Author: Science ABC;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I16YlE8qTBU;License: Standard youtube license