
Concept explainers
Find the error in each of the following. (Note: There may be more than one error.)
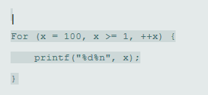
- The following code should print whether a given integer is odd or even:
- The following code should input an integer and a character and print them. Assume the usere types as input 100 A.
- The following code should output the odd integers from 999 to 1:
- The following code should output the even integers from 2 to 100:
- The following code should sum the integers from 100 to 150 (assume total is initialized to 0):
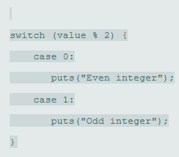
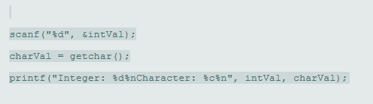
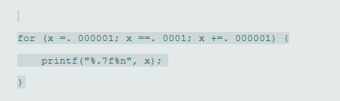

(a)
To find and debug the error using proper syntax and logic in the given program.
for (int x = 100; x >= 1;--x) {
printf ("%d\n", x);
}
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- For (x = 100, x >= 1, ++x) {
- printf ("%d%n", x);
- }
Explanation:
- Loop variable needs to be initialized as an intthat is int x.
- The syntax of a for loop is not followed as well as C is the case-sensitive language that is For and for are the different for C compiler.
- Therefore, For should be written as for and the commas need to be changed into the semi-colons (;) inside the for-loop parenthesis.
- The correct syntax of a for loop is:
- The logical error wasthat loop going to execute the infinite times as it’s variablestarts from 100 and is updating its value by incrementing 1 at every run. Therefore, at every update, the value of x is greater than 1. Thus, instead of updating x as ++x use -- x.
- The last error is that to print every integer in newline \n is used instead of %n .
for (Initializing variable; Testing condition; Updating variable){
//for block to write the statements
}
Output:
(b)
To find and debug the error using proper syntax and logic in the given program to print whether the given integer is odd or even.
switch (value % 2)
{
case 0:
puts ("Even integer");
break;
case 1:
puts ("Odd integer");
break;
}
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
switch (value % 2)
{
case 0:
puts ("Even integer");
case 1:
puts ("Odd integer");
}
Explanation:
The cases act as the start point for every switch and case block where the switch takes the data and matches it with the corresponding case. Therefore, if any case is matched then all the statements from that case will be executed till it terminates or breaks. Therefore, cases should have a break keyword to exit the switch and case block, once the case is matched.
(c)
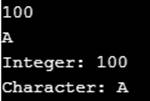
To find and debug the error using proper syntax and logic in the given program to print an integer value and the character value A as 100 A.
scanf ("%d", &intVal);
scanf ("\n%c", &charVal);
printf ("Integer: %d\nCharacter: %c\n", intVal, charVal);
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
scanf("%d", &intVal);
charVal = getchar ();
printf("Integer: %d\nCharacter: %c\n", intVal, charVal);
Explanation:
To stop reading the variable charValblank character, the second statement need to skip the preceding blanks when the user enters the integer value and press return, to rectify this scanf must be used. That is getchar() reads the next line after pressing by inputing the integer value.
Output:
(d)
To find and debug the error using proper syntax and logic in the given program
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
for (x = .000001; x == .0001; x += .000001)
printf("%.7f\n", x);
Explanation:
The numbers are quite small to be compared and the for-loop must not compare the floating-point number using == as it causes impression which might cause the infinite loop. Thus, it is recommended to use integer values as int datatype in the for-loop.
(e)
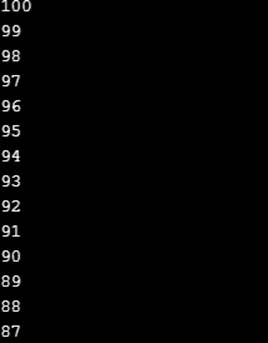
To find and debug the error using proper syntax and logic in the given program to print odd number from 999 to 1.
for (int x = 999; x >= 1; x -= 2)
if (x % 2 == 1)
printf ("%d\n", x);
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
for(x = 999; x >= 1; x += 2)
printf("%d\n", x);
Explanation:
- Loop variable need to be initialized as intthat is int x.
- To print the odd values from 999 to 1 the loop variable should decrease by two, instead of increasing by 2 as we need to decrease the value.
- The correct syntax of a for loop is:
- If condition is used to check whether the variable x is odd or not.
for (Initializing variable; Testing condition; Updating variable) {
//for block to write a statement
}
Output:

(f)
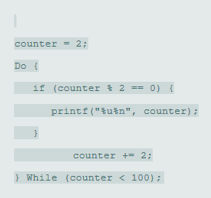
To find and debug the error using proper syntax and logic in the given program to print even numbers between 2 to 100.
int counter = 2;
do{
if(counter % 2== 0)
printf("%u\n", counter);
counter += 2;
} while(counter <= 100);
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
counter = 2;
Do {
if (counter % 2== 0) {
printf ("%u\n", counter);
}
counter += 2;
} While (counter < 100);
Explanation:
- The variable need to be initialized as intthat is int counter.
- The programming language - C is the case-sensitive language that is Do and do are different for C compiler and the same goes for While and while.
- To print the even values to 100 inclusively whileloop needs to <= instead of <.
Output:

(g)
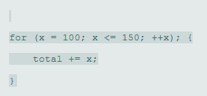
To find and debug the error using proper syntax and logic in the given programto find the sum of the numbers between 100 to 150.
int total = 0;
for(int x = 100; x <= 150; ++x){
total += x;
}
printf("%d",total);
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
for(x = 100; x <= 150; ++x);{
total += x;
}
Explanation:
- The declaration of the total variable is missing.
- Loop variable needs to be initialized as an intthat is int x.
- The syntax of a for loop is not followed as there should be no comma (,) after the parenthesis.
- The correct syntax of a for loop is:
- The logical error was that there is no print statement.
for (Initializing variable; Testing condition; Updating variable) {
//for block to write statement
}
Output:

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
MYPROGRAMMINGLAB WITH PEARSON ETEXT
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Modern Database Management
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Programming with Microsoft Visual Basic 2017Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102124Author:Diane ZakPublisher:Cengage LearningCOMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEComputer ScienceISBN:9780357392676Author:FREUND, StevenPublisher:CENGAGE L
Programming with Microsoft Visual Basic 2017Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102124Author:Diane ZakPublisher:Cengage LearningCOMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEComputer ScienceISBN:9780357392676Author:FREUND, StevenPublisher:CENGAGE L EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





