
A plane frame (see figure) consists of column AB and beam BC that carries a triangular distributed load (see figure part a). Support A is fixed, and there is a roller support at C. Beam BC has a shear release just right of joint B.
- Find the support reactions at A and C then plot axial-force (N), shear-force (V), and bending-moment (M) diagrams for both members. Label all critical N,K and M values and also the distance to points where any critical ordinates are zero.
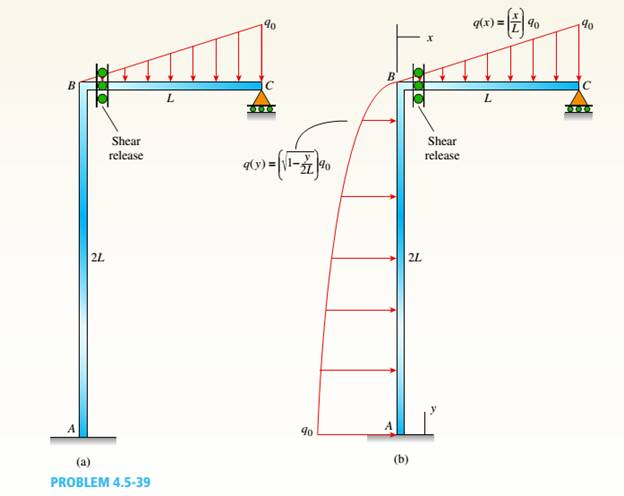
a.
The support reaction at point A and C and plot the shear, moment, and axial force diagram.
Answer to Problem 4.5.39P
Explanation of Solution
Given: .
The given figure.
AB column and BC beam forms the plane frame that carries a load that is distributed in the triangular shape. At C there is roller support and support A is fixed. Below the B joint there is a moment release at column AB
Concept Used:
Vertical force equilibrium is given as,
Horizontal force equilibrium is given as,
Calculation: .
Vertical force equilibrium is given as,
Horizontal force equilibrium is given as,
At the top of the moment release the moment is given as,
In equation (1),
Below B there is moment release at point A,
At x the shear force is given and equated to 0,
At point x bending moment is maximum,
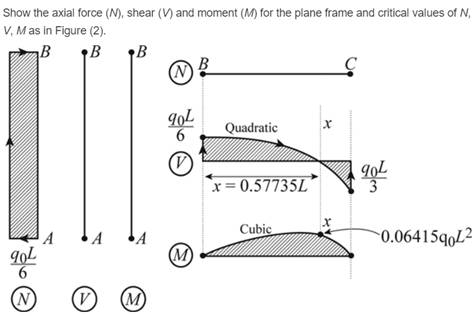
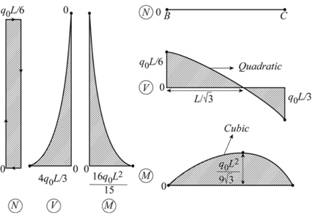
Axial force critical values
Shear force critical values
Moment critical values
Conclusion: .
Thus, the support reaction at point A and C and plot the shear, moment and axial force diagram.
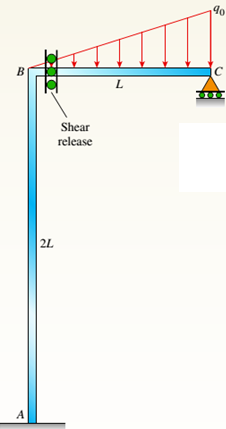
b.
For the load that is parabolic, lateral acts to the right added to AB column and part (a) is repeated.
Answer to Problem 4.5.39P
Explanation of Solution
Given: .
The given figure:.
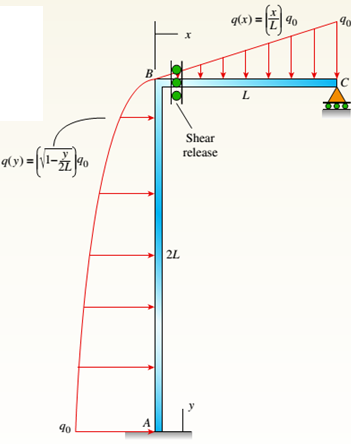
AB column and BC beam forms the plane frame that carries a load that is distributed in the triangular shape. At C there is roller support and support A is fixed. Below the B joint, there is a moment release at column AB.
Concept Used:
Vertical force equilibrium is given as,
Horizontal force equilibrium is given as,
Calculation: .
With the equilibrium force being vertical,
Moment at point B above moment release,
In (2) substitute
With the equilibrium force being horizontal,
As left of x axis is negative,
At A moment below the moment release,
At x shear force is calculated and equated to 0,
At x bending moment is calculated
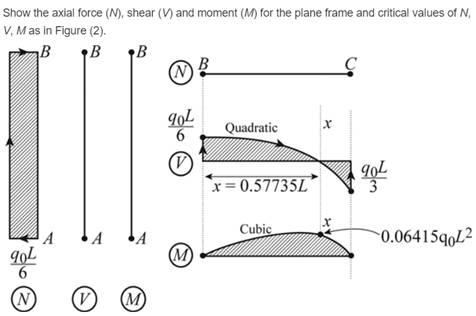
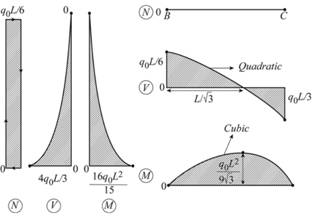
For plane frame and critical values of N, V, M, the axial, shear and moment is given.
Axial force critical values
Shear force critical values in beam
Shear force critical values in column
Moment critical values in beam
Moment critical values in column
Conclusion: .
Thus, for the load that is parabolic lateral acts to the right added to AB column and part (a) is repeated.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- A piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the change in the volume of the cylinder of the refrigerant-134a if the specific volume and enthalpy of R-134a at the initial state of 90.4 kPa and -10°C and at the final state of 90.4 kPa and 15°C are as follows: = 0.2418 m³/kg, h₁ = 247.77 kJ/kg 3 v2 = 0.2670 m³/kg, and h₂ = 268.18 kJ/kg The change in the volume of the cylinder is marrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the final pressure of the refrigerant-134a. The final pressure is kPa.arrow_forwardThe hydraulic cylinder BC exerts on member AB a force P directed along line BC. The force P must have a 560-N component perpendicular to member AB. A M 45° 30° C Determine the force component along line AB. The force component along line AB is N.arrow_forward
- ! Required information A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB. The tension in the left-hand portion of the cable is given to be T₁ = 815 lb. A 15° 25° B T₂ Using trigonometry, determine the required tension T₂ in the right-hand portion if the resultant R of the forces exerted by the cable at A is to be vertical. The required tension is lb.arrow_forwardWhat are examples of at least three (3) applications of tolerance fitting analysis.arrow_forwardThe primary material used in the production of glass products is silica sand. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Which one of the following is the most common polymer type in fiber-reinforced polymer composites? thermosets thermoplastics elastomers none of the abovearrow_forwardA pattern for a product is larger than the actual finished part. True or Falsearrow_forwardIn the lost foam process, the pattern doesn’t need to be removed from the mold. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Tempering eliminates internal stresses in glass. True or Falsearrow_forwardThermoset polymers can be recycled with little to no degradation in properties. True or Falsearrow_forwardTwo forces are applied as shown to a hook support. The magnitude of P is 38 N. 50 N 25° DG a 터 Using trigonometry, determine the required angle a such that the resultant R of the two forces applied to the support will be horizontal. The value of a isarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
