
Concept explainers
Ledger accounts,
The unadjusted
| Lakota Freight Co. Unadjusted Trial Balance March 31,2016 |
|||
| Debit Balances | Credit Balances | ||
| 11 | Cash.................................................... | 12,000 | |
| 13 | Supplies.................................................... | 30,000 | |
| 14 | Prepaid Insurance........................................... | 3,600 | |
| 16 | Equipment.................................................. | 110,000 | |
| 17 | 25,000 | ||
| 18 | Trucks...................................................... | 60,000 | |
| 19 | Accumulated Depreciation—Trucks........................... | 15,000 | |
| 21 | Accounts Payable........................................... | 4,000 | |
| 31 | Common Stock............................................. | 26,000 | |
| 32 | 70,000 | ||
| 33 | Dividends.................................................. | 15,000 | |
| 41 | Service Revenue............................................ | 160,000 | |
| 51 | Wages Expense............................................. | 45,000 | |
| 53 | Rent Expense............................................... | 10,600 | |
| 54 | Truck Expense............................................... | 9,000 | |
| 59 | Miscellaneous Expense...................................... | 4,800 | |
| 300,000 | 300,000 | ||
The data needed to determine year-end adjustments are as follows:
- a. Supplies on hand at March 31 are $7,500.
- b. Insurance premiums expired during year are $1,800.
- c. Depreciation of equipment during year is $8,350.
- d. Depreciation of trucks during year is $6,200.
- e. Wages, accrued but not paid at March 31 are $600.
Instructions
-
- 1. For each account listed in the trial balance, enter the balance in the appropriate Balance column of a four-column account and place a check mark (✓) in the Posting Reference column.
- 2. (Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on an end-of-period spreadsheet and complete the spreadsheet. Add the accounts listed in pan (3) as needed.
- 3. Journalize and post the adjusting entries, inserting balances in the accounts affected. Record the adjusting entries on Page 26 of the journal. The following additional accounts from Lakota Freight Co.’s chart of accounts should be used: Wages Payable, 22; Supplies Expense, 52; Depreciation Expense—Equipment, 55; Depreciation Expense— Trucks, 56; Insurance Expense, 57.
- 4. Prepare an adjusted trial balance.
- 5. Prepare an income statement, a retained earnings statement, and a
balance sheet . - 6. Journalize and
post the closing entries. Record the closing entries on Page 27 of the journal. (Income Summary is account *34 in the chart of accounts.) Indicate closed accounts by inserting a line in both Balance columns opposite the closing entry. - 7. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.
1, 3, and 6:
Journal:
Journal is the book of original entry. Journal consists of the day-to-day financial transactions in a chronological order. The journal has two aspects; they are debit aspect and the credit aspect.
T-Accounts:
T-accounts are referred as T-account because its format represents the letter “T”. The T-accounts consists of the following:
- The title of accounts.
- The debit side (Dr) and,
- The credit side (Cr).
Adjusted trial balance:
The unadjusted trial balance is the summary of all the ledger accounts that appears on the ledger accounts before making adjusting journal entries.
Adjusting entries:
An adjusting entry is prepared when the trial balance is not up-to-date, and complete, and they are usually prepared at the end of the accounting period. This adjusting entry is essential for preparing the financial statements of the business.
Spreadsheet:
A spreadsheet is a worksheet. It is used while preparing a financial statement. It is a type of form having multiple columns and it is used in the adjustment process. The use of a worksheet is optional for any organization. A worksheet can neither be considered as a journal nor a part of the general ledger.
Retained Earnings Statement:
It is one of the financial statements, which shows the amount of the net income retained by a company at a particular point of time for reinvestment and pay its debts and obligations. It shows the amount of retained earnings that is not paid as dividends to the shareholders.
Income statement:
An income statement is one of the financial statements which shows the revenues, and expenses of the company. The income statement is prepared to ascertain the net income/loss of the company, by deducting the expenses from the revenues.
Balance sheet:
A balance sheet is a financial statement consists of the assets, liabilities, and the stockholder’s equity of the company. The balance of the assets account must be equal to that of the liabilities and the stockholder’s equity account.
Closing entries:
Closing entries are recorded in order to close the temporary accounts such as incomes and expenses by transferring them to the permanent accounts. It is passed at the end of the accounting period, to transfer the final balance.
Post-Closing Trial Balance:
After passing all the journal entries and the closing entries of the permanent accounts and then further posting them to each of the respective accounts, a post-closing trial balance is prepared which consists of a list of all the permanent accounts. A post-closing trial balance serves as an evidence to prove that the balance of the permanent accounts is equal.
To prepare: The T-accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Record the transactions directly in their respective T-accounts, and determine their balances.
| Account: Cash Account no. 11 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 12,000 | |||
| Account: Supplies Account no. 13 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 30,000 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 22,500 | 7,500 | |||
| Account: Prepaid Insurance Account no. 14 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 3,600 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 1,800 | 1,800 | |||
| Account: Equipment Account no. 16 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 110,000 | |||
| Account: Accumulated Depreciation-Office equipment Account no. 17 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 25,000 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 8,350 | 33,350 | |||
| Account: Trucks Account no. 18 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 60,000 | |||
| Account: Accumulated Depreciation- Truck Account no. 19 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 15,000 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 6,200 | 21,200 | |||
| Account: Accounts Payable Account no. 21 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 4,000 | |||
| Account: Wages Payable Account no. 22 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 600 | 600 | ||
| Account: Common Stock Account no. 31 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 | Balance |
|
26,000 | 26,000 | ||
| Account: Retained Earnings Account no. 32 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 70,000 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 51,150 | 121,150 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 15,000 | 106,150 | |||
| Account: Dividends Account no. 33 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 | Balance |
|
15,000 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 15,000 | ||||
| Account: Income Summary Account no. 34 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 | Closing | 27 | 160,000 | 160,000 | ||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 108,850 | 51,150 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 51,150 | ||||
| Account: Service revenue Account no. 41 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 160,000 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 160,000 | ||||
| Account: Wages expense Account no. 51 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 45,000 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 600 | 45,600 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 45,600 | ||||
| Account: Supplies Expense Account no. 52 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 22,500 | 22,500 | ||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 22,500 | ||||
| Account: Rent expense Account no. 53 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 10,600 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 10,600 | ||||
| Account: Truck Expense Account no. 54 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 9,000 | |||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 9,000 | ||||
| Account: Depreciation Expense- Equipment Account no. 55 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 8,350 | 8,350 | ||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 8,350 | ||||
| Account: Depreciation Expense- Equipment Account no. 55 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 8,350 | 8,350 | ||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 8,350 | ||||
| Account: Depreciation Expense- Trucks Account no. 56 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2018 | |||||||
| March | 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 6,200 | 6,200 | ||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 6,200 | ||||
| Account: Insurance expense Account no. 57 | |||||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||||
| 2018 | |||||||||
| March | 31 | Adjusting | 26 | 1,800 | 1,800 | ||||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 1,800 | ||||||
| Account: Miscellaneous expense Account no. 59 | |||||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance | ||||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||||
| 2018 | |||||||||
| March | 31 |
|
✓ | 4,800 | |||||
| 31 | Closing | 27 | 4,800 | ||||||
2.
To enter: The unadjusted trial balance on an end-of-period spreadsheet, and complete the spreadsheet.
Explanation of Solution
The unadjusted trial balance on an end-of-period spreadsheet is prepared as follows:
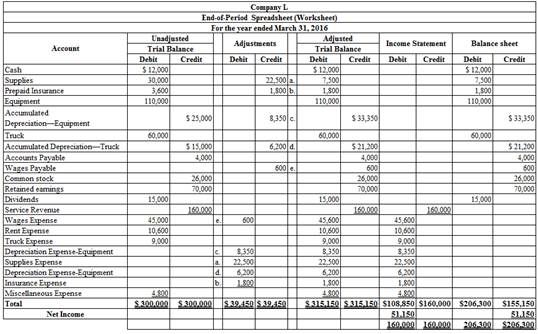
Table (1)
Hence, the unadjusted trial balance on an end-of-period spreadsheet is prepared and completed.
3.
To Journalize and post: The adjusting entries.
Explanation of Solution
The adjusting entries are journalized as follows:
| Date | Description | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | Supplies expense | 52 | 22,500 | ||
| March | 31 | Supplies
|
13 | 22,500 | |
| (To record the supplies used) | |||||
Table (2)
- Supplies expense is an expense account, and it is increased. Hence, debit the supplies expense account by $22,500.
- Supplies are the asset account, and it is increased. Hence, credit the supplies account by $22,500.
| Date | Description | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | Insurance expense | 57 | 1,800 | ||
| March | 31 | Prepaid insurance | 14 | 1,800 | |
| (To record the insurance expired) | |||||
Table (3)
- Insurance expense is an expense account, and it is increased. Hence, debit the insurance expense account by $1,800.
- Prepaid insurance is an asset account, and it is decreased. Hence, credit the prepaid insurance account by $1,800.
| Date | Description | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | Depreciation expense-Equipment | 55 | 8,350 | ||
| March | 31 | Accumulated depreciation- Equipment | 17 | 8,350 | |
| (To record the equipment depreciation) | |||||
Table (4)
- Depreciation expense is an expense account, and it is increased. Hence, debit the wages expense account by $8,350.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset account, and it is increased. Hence, credit the accumulated depreciation account by $8,350.
| Date | Description | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | Depreciation expense-Truck | 56 | 6,200 | ||
| March | 31 | Accumulated depreciation- Truck | 19 | 6,200 | |
| (To record the truck depreciation) | |||||
Table (5)
- Depreciation expense is an expense account, and it is increased. Hence, debit the wages expense account by $6,200.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset account, and it is increased. Hence, credit the accumulated depreciation account by $6,200.
| Date | Description | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | Wages expense | 51 | 600 | ||
| March | 31 | Wages payable | 22 | 600 | |
| (To record the wages accrued) | |||||
Table (6)
- Wages expense is an expense account, and it is increased. Hence, debit the wages expense account by $600.
- Wages payable is a liability account, and it is increased. Hence, credit the wages payable account by $600.
4.
To prepare: An adjusted trial balance for Company L, as of March 31, 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an adjusted trial balance for Company L, as of March 31, 2016.
| Company L | |||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | |||
| March 31, 2016 | |||
| Accounts | Account Number | Debit Balances | Credit Balances |
| Cash | 11 | 12,000 | |
| Supplies | 13 | 7,500 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 14 | 1,800 | |
| Equipment | 16 | 110,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation- Equipment | 17 | 33,350 | |
| Trucks | 18 | 60,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation- Trucks | 19 | 21,200 | |
| Accounts payable | 21 | 4,000 | |
| Wages Payable | 22 | 600 | |
| Common stock | 31 | 26,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 32 | 70,000 | |
| Dividends | 15,000 | ||
| Service revenue | 41 | 160,000 | |
| Wages expense | 51 | 45,600 | |
| Supplies expense | 52 | 22,500 | |
| Rent Expense | 53 | 10,600 | |
| Truck Expense | 54 | 9,000 | |
| Depreciation Expense- Equipment | 55 | 8,350 | |
| Depreciation Expense- Trucks | 56 | 6,200 | |
| Insurance Expense | 57 | 1,800 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 59 | 4,800 | |
| $315,150 | $315,150 | ||
Table (7)
The debit column and credit column of the adjusted trial balance are agreed, both having balance of $315,150.
5.
Explanation of Solution
The net income of Company L for the month of March is $51,150.
| Company L | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the year ended March 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenue: | ||
| Service revenue | $160,000 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Wages Expense | 45,600 | |
| Supplies Expense | 22,500 | |
| Rent Expense | 10,600 | |
| Truck Expense | 9,000 | |
| Depreciation Expense-Equipment | 8,350 | |
| Depreciation Expense-Trucks | 6,200 | |
| Insurance Expense | 1,800 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 4,800 | |
| Total Expenses | 108,850 | |
| Net Income | $51,150 | |
Table (8)
Hence, the net income of Company L for the year ended March 31, 2016 is $51,150.
6.
To Journalize: The closing entries for Company L.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entry for revenue and expense accounts:
| Date | Accounts title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 31, 2016 | Service revenue | 41 | 160,000 | |
| Income summary | 34 | 160,000 | ||
| (To close the balances of revenue account) | ||||
| March 31, 2016 | Income summary | 34 | 108,850 | |
| Wages expense | 51 | 45,600 | ||
| Supplies Expense | 52 | 22,500 | ||
| Rent Expense | 53 | 10,600 | ||
| Truck Expense | 54 | 9,000 | ||
| Depreciation Expense–Equipment | 55 | 8,350 | ||
| Depreciation Expense–Trucks | 56 | 6,200 | ||
| Insurance Expense | 57 | 1,800 | ||
| Miscellaneous Expense | 59 | 4,800 | ||
| (To close the balances of expense account) | ||||
| March 31, 2016 | Income summary | 34 | 51,150 | |
| Retained earnings | 32 | 51,150 | ||
| (To Close the excess of revenue to expenses) | ||||
| March 31, 2016 | Retained earnings | 32 | 15,000 | |
| Dividends | 33 | 15,000 | ||
| (To close the dividend account to retained earnings account) | ||||
Table (11)
- Laundry revenue is revenue account. Since the amount of revenue is closed and transferred to Income summary account. Here, Company L earned an income of $160,000. Therefore, it is debited.
- Wages Expense, Rent Expense, Insurance Expense, Supplies Expense, Depreciation Expenses, and Miscellaneous Expense are expense accounts. Since the amount of expenses are closed to Income Summary account. Therefore, it is credited.
- Closing entries are also passed in order to close the excess of revenue over the expenses, and the dividend account.
7.
To prepare: The post–closing trial balance of Company L for the month ended March 31, 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a post–closing trial balance of Company L for the month ended March 31, 2016 as follows:
Company L Post-closing Trial Balance March 31, 2016 |
|||
| Particulars | Account Number |
Debit $ | Credit $ |
| Cash | 11 | 12,000 | |
| Supplies | 13 | 7,500 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 14 | 1,800 | |
| Equipment | 16 | 110,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation- Equipment | 17 | 33,350 | |
| Trucks | 18 | 60,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation- Trucks | 19 | 21,200 | |
| Accounts payable | 21 | 4,000 | |
| Wages payable | 22 | 600 | |
| Common stock | 31 | 26,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 106,150 | ||
| Total | $191,300 | $191,300 | |
Table (12)
The debit column and credit column of the post–closing trial balance are agreed, both having balance of $191,300.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK FINANCIAL & MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College




