
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
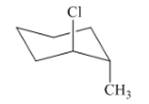
Concept Introduction: If the conformer shows the minimum steric hindrance of the substituent and minimum torsional strain then that conformer is in stable form.
(b)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
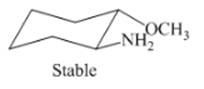
Concept Introduction: Trans-isomer has opposite attachment of all groups on the ring.
(c)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.

Concept Introduction:All groups are situated in one side, it is cis-isomer. Stability is defined in terms of axial interactions.
(d)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
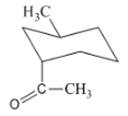
Concept Introduction:In trans-isomer all groups are attached in opposite side of the ring.
(e)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
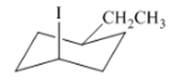
Concept Introduction:When groups are on one side then that isomer is cis-isomer.
(f)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
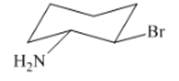
Concept Introduction:Trans-isomer consist all different groups on the opposite side of the ring.
(g)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
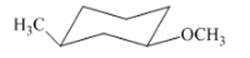
Concept Introduction:If all groups of the ring are attached on same side then that isomer is cis-isomer.
(h)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
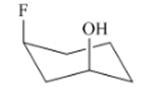
Concept Introduction:If the groups are attached on the same side then that isomer is cis-isomer.
(i)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
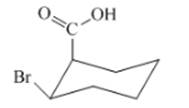
Concept Introduction:In cis-isomer the all different groups are situated on the same side of the ring.
(j)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
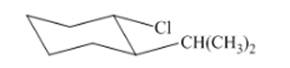
Concept Introduction:Trans-isomers have the different groups on the opposite side of the ring.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- esc Draw the Markovnikov product of the hydration of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. Explanation Check BBB + X 0 1. Hg (OAc)2, H₂O 2. Na BH 5 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bl P 豆 28 2 28 N 9 W E R T Y A S aps lock G H K L Z X C V B N M T central H command #e commandarrow_forwardC A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. . If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. (X) This transformation can't be done in one step. + Tarrow_forwardく Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. Explanation Check OH + + ✓ 2 H₂SO 4 O xs H₂O 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- Draw the skeletal ("line") structure of 1,3-dihydroxy-2-pentanone. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Parrow_forwardPredicting edict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. + No reaction. Explanation Check HO Na O H xs H₂O 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Iarrow_forwardChoosing reagents and conditions for acetal formation or hydrolysis 0/5 A student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + This transformation can't be done in one step. 5 I H Autumn alo 值 Ar Barrow_forward
- A block of copper of mass 2.00kg(cp = 0.3851 .K) and g temperature 0°C is introduced into an insulated container in which there is 1.00molH, O(g) at 100°C and 1.00 2 atm. Note that C P = 4.184. K for liquid water, and g that A H = 2260 for water. vap g Assuming all the steam is condensed to water, and that the pressure remains constant: (a) What will be the final temperature of the system? (b) What is the heat transferred from the water to the copper? (c) What is the entropy change of the water, the copper, and the total system?arrow_forwardIdentify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: H+ X + Y OH H+ O O Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H₂O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cente ? Earrow_forwardCalculate the solubility of CaF2 in g/L (Kp = 4.0 x 10-8). sparrow_forward
- For the following reaction with excess reagent, predict the product. Be sure your answer accounts for stereochemistry. If multiple stereocenters are formed, be sure to draw all products using appropriate wedges and dashes. 1. EtLi, Et₂O CH₁ ? 2. H₂O*arrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure 요 OH ہو۔ HO OH name X S ☐ ☐arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. D ㄖˋ ید H No reaction. + 5 H₂O.* Click and drag to start drawing a structure. OH H₂Oarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

