
Concept explainers
1,3, 5 and 8
Prepare T-accounts for the necessary accounts.
1,3, 5 and 8
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increases or decreases in the value of specific asset, liability,
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
(a)The title of the account
(b)The left or debit side
(c)The right or credit side
Prepare T-accounts for the necessary accounts as follows:
| Cash (A) | |||
| Beg. | $3 | ||
| a | 12 | b | $9 |
| c | 23 | d | 10 |
| h | 120 | f | 13 |
| j | 24 | i | $85 |
| Bal. | $65 | ||
| Land(A) | |||
| Beg. | $0 | ||
| b | 9 | ||
| Bal. | $9 | ||
| Software (A) | |||
| Beg. | $15 | ||
| d | 10 | ||
| Bal. | $25 | ||
| Accounts Payable (L) | |||
| Beg. | $5 | ||
| f | $13 | e | 18 |
| Bal. | $10 | ||
| Salaries and Wages Payable (L) | |||
| Beg. | $0 | ||
| o | 12 | ||
| Bal. | $12 | ||
| Common Stock (SE) | |||
| Beg. | $71 | ||
| c | 23 | ||
| Bal. | $94 | ||
| Accounts Receivable(A) | |||
| Beg. | $5 | ||
| h | 40 | j | 24 |
| Bal. | $21 | ||
| Equipment (A) | |||
| Beg. | $60 | ||
| Bal. | $60 | ||
| Accumulated Amortization (xA) | |||
| Beg. | $5 | ||
| k | 5 | ||
| Bal. | $10 | ||
| Notes Payable (short-term) (L) | |||
| Beg | $0 | ||
| a | 12 | ||
| Bal. | $12 | ||
| Interest Payable (L) | |||
| Beg. | $0 | ||
| n | 1 | ||
| Bal. | $1 | ||
| Beg. | $8 | ||
| CE1 | 23 | ||
| Bal. | $31 | ||
| Supplies (A) | |||
| Beg. | $12 | ||
| e | 18 | ||
| 30 | |||
| l | 20 | ||
| Bal. | $10 | ||
| Accumulated | |||
| Beg. | $6 | ||
| m | 6 | ||
| Bal. | $12 | ||
| Income Tax Payable (L) | |||
| Beg. | $0 | ||
| p | 8 | ||
| Bal. | $8 | ||
| Service Revenue (R) | |||
| Beg. | 0 | ||
| h | $160 | ||
| CE1 | $160 | ||
| Bal. | $0 | ||
| Salaries and Wages Expense (E) | |||
| Beg. | $0 | ||
| i | 85 | ||
| o | 12 | ||
| 97 | |||
| CE1 | $97 | ||
| Bal. | $0 | ||
| Depreciation Expense (E) | |||
| Beg. | $0 | ||
| m | 6 | ||
| CE1 | $6 | ||
| Bal. | $0 | ||
| Amortization Expense (E) | |||
| Beg. | $0 | ||
| k | 5 | ||
| CE1 | $5 | ||
| Bal. | $0 | ||
| Income Tax Expense (E) | |||
| Beg. | $0 | ||
| p | 8 | ||
| CE1 | $8 | ||
| Bal. | $0 | ||
| Interest Expense (E) | |||
| Beg. | $0 | ||
| n | 1 | ||
| CE1 | $1 | ||
| Bal. | $0 | ||
| Supplies Expense (E) | |||
| Beg. | $0 | ||
| l | 20 | ||
| CE1 | $20 | ||
| Bal. | $0 | ||
2.
Record the necessary
2.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entries for the transactions (a) to (j) as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| a) | Cash (+A) | 12 | |||
| Notes payable (Short-term) (+L) | 12 | ||||
| (To record borrowed cash on note) | |||||
| b) | Land (+A) | 9 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 9 | ||||
| (To record purchase of land for building site) | |||||
| c) | Cash (+A) | 23 | |||
| Common Stock (+SE) | 23 | ||||
| (To record issued common stock for cash) | |||||
| d) | Software (+A) | 10 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 10 | ||||
| (To record Purchase of additional software) | |||||
| e) | Supplies (+A) | 18 | |||
| Accounts payable (+L) | 18 | ||||
| (To record supplies purchased for future use) | |||||
| f) | Accounts payable (-L) | 13 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 13 | ||||
| (To record cash paid to creditors) | |||||
| g) | No entry required, Because no revenue has been earned in 2018 | ||||
| h) | Cash (+A) | 120 | |||
| 40 | |||||
| Service Revenue (+R, +SE) | 160 | ||||
| (To record service revenue earned during the year 2018) | |||||
| i) | Salaries and Wages Expense (+E, -SE) | 85 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 85 | ||||
| (To record salaries and wages expense incurred during 2018) | |||||
| j) | Cash (+A) | 24 | |||
| Accounts Receivable (-A) | 24 | ||||
| (To record cash collected on customer’s account) | |||||
Table (1)
3.
Prepare an unadjusted
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an unadjusted trial balance of Incorporation H&H as follows:
| Incorporation H&H | ||
| Unadjusted Trial Balance | ||
| At December 31, 2018 | ||
| (in thousands) | ||
| Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 65 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 21 | |
| Supplies | 30 | |
| Land | 9 | |
| Equipment | 60 | |
| 6 | ||
| Software | 25 | |
| Accumulated Amortization | 5 | |
| Accounts Payable | 10 | |
| Notes Payable (short–term) | 12 | |
| Salaries and Wages Payable | ||
| Interest Payable | ||
| Income Taxes Payable | ||
| Common Stock | 94 | |
| Retained Earnings | 8 | |
| Service Revenue | 160 | |
| Salaries and Wages Expense | 85 | |
| Supplies Expense | ||
| Depreciation Expense | ||
| Interest Expense | ||
| Income Tax Expense | ||
| Total | 295 | 295 |
Table (2)
4.
Record the adjusting journal entries (k) to (p).
4.
Explanation of Solution
Record the adjusting journal entries (k) to (p) as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| k. | Amortization Expense (+E, -SE) | 5 | |||
| Accumulated Amortization (+xA, -A) | 5 | ||||
| (To record | |||||
| l. | Supplies expense (+E, -SE) (refer working note 1) | 20 | |||
| Supplies(-A) | 20 | ||||
| (To record the use of supplies) | |||||
| m. | Depreciation expense (+E, -SE) | 6 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation –Equipment (+xA, -A) | 6 | ||||
| (To record adjusting entry for depreciation expense) | |||||
| n. | Interest expense (+E, -SE) | 1 | |||
| Interest payable(+L) | 1 | ||||
| (To record the adjusting entry for interest expense) | |||||
| o. | Salaries and wages expense (+E, -SE) | 12 | |||
| Salaries and wages payable (+L) | 12 | ||||
| (To record the adjusting entry for salaries and wages expenses) | |||||
| p. | Income tax expense(+E, -SE) | 8 | |||
| Income tax payable(+L) | 8 | ||||
| (To record the adjusting entry for income tax expense) | |||||
Table (3)
Working notes 1:
Calculate the value of supplies expenses:
5.
Prepare an adjusted trial balance from requirement 4.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an adjusted trial balance for Incorporation H&H for December 31, 2018 as follows:
| Incorporation H&H | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| At December 31, 2018 | ||
| (in thousands) | ||
| Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 65 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 21 | |
| Supplies | 10 | |
| Land | 9 | |
| Equipment | 60 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation–Equipment | 12 | |
| Software | 25 | |
| Accumulated Amortization | 10 | |
| Accounts Payable | 10 | |
| Notes Payable (short–term) | 12 | |
| Salaries and Wages Payable | 12 | |
| Interest Payable | 1 | |
| Income Taxes Payable | 8 | |
| Common Stock | 94 | |
| Retained Earnings | 8 | |
| Service Revenue | 160 | |
| Salaries and Wages Expense | 97 | |
| Supplies Expense | 20 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 6 | |
| Amortization expense | 5 | |
| Interest Expense | 1 | |
| Income Tax Expense | 8 | |
| Total | 327 | 327 |
Table (4)
6.
Prepare an income statement, statement of retained earnings and balance sheet.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an income statement for the year ended December 31, 2018 as follows:
| Incorporation H&H | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| (in thousands) | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Service revenue | 160 | |
| Total revenues | 160 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Salaries and wage expense | 97 | |
| Supplies expense | 20 | |
| Depreciation expense | 6 | |
| Amortization expense | 5 | |
| Interest expense | 1 | |
| Income tax expense | 8 | |
| Total expenses | 137 | |
| Net income | 23 | |
Table (5)
Prepare a statement of retained earnings as follows:
| Incorporation H&H | ||
| Statement of Retained Earnings | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| (in thousands) | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Balance, January 1, 2018 | 8 | |
| Add: Net income | 23 | |
| 31 | ||
| Less: Dividends | (0) | |
| Balance, December 31, 2018 | 31 | |
Table (6)
Prepare a balance sheet for the year December 31, 2018 as follows:
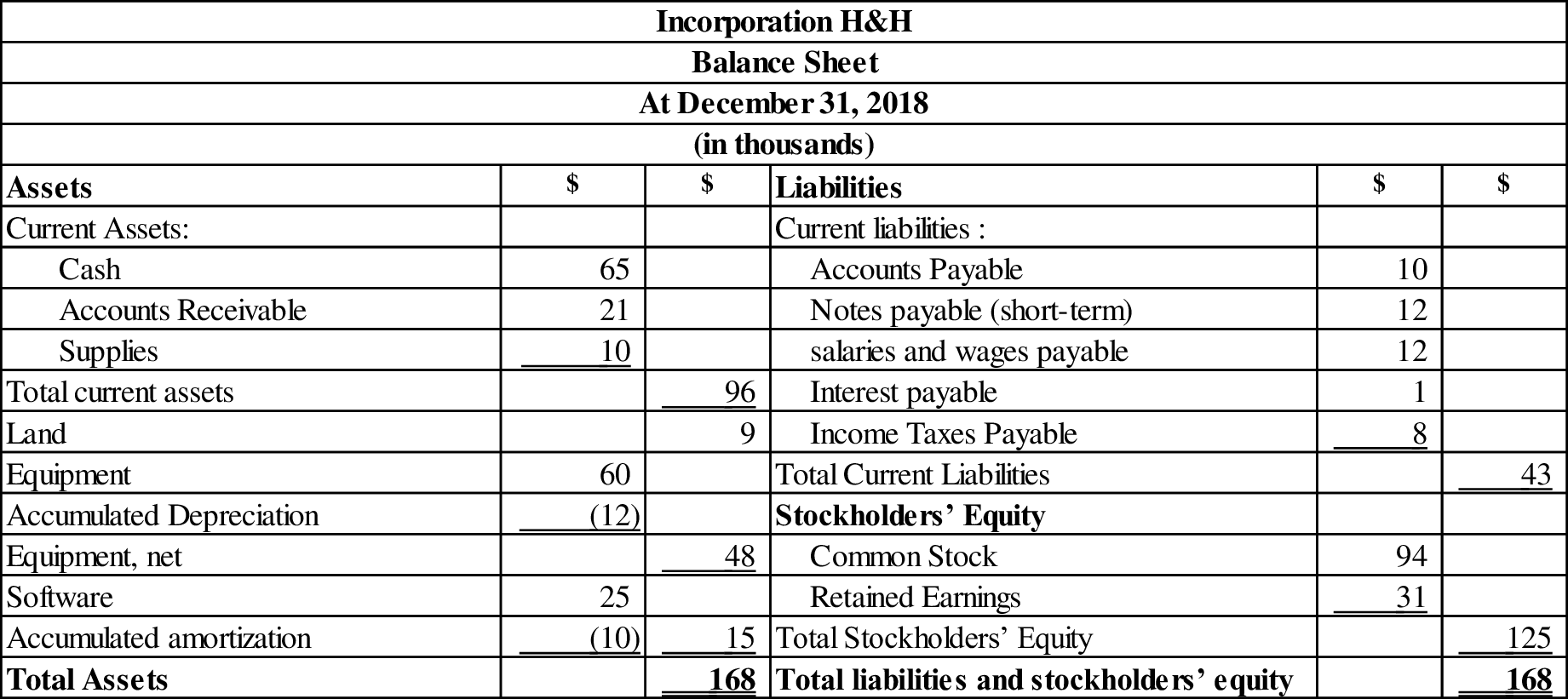
Table (7)
7.
Prepare the closing entry for Incorporation H&H on December 31, 2018.
7.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare closing entries for Incorporation H&H on December 31, 2018:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2018 | Sales revenue(-R) | 160 | |
| Salaries and wages expense(-E) | 97 | ||
| Depreciation expense(-E) | 6 | ||
| Supplies expense(-E) | 20 | ||
| Amortization expense (-E) | 5 | ||
| Income tax expense(-E) | 8 | ||
| Interest expense (-E) | 1 | ||
| Retained earnings(+SE) (refer table 5) | 23 | ||
| (To record the closing entries for Incorporation H&H) |
Table (8)
For closing of temporary accounts, the balances of revenues, expenses, and dividend accounts are transferred to retained earnings in order to bring zero balance for expenses and revenues accounts.
8.
Prepare post-closing trial balance from the requirement 7.
8.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a Post-closing trial balance for Incorporation H&H for December 31, 2018 as follows:
| Incorporation H&H | ||
| Post-closing Trial Balance | ||
| At December 31, 2018 | ||
| (in thousands) | ||
| Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 65 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 21 | |
| Supplies | 10 | |
| Land | 9 | |
| Equipment | 60 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation–Equipment | 12 | |
| Software | 25 | |
| Accumulated Amortization | 10 | |
| Accounts Payable | 10 | |
| Notes Payable (short–term) | 12 | |
| Salaries and Wages Payable | 12 | |
| Interest Payable | 1 | |
| Income Taxes Payable | 8 | |
| Common Stock | 94 | |
| Retained Earnings | 31 | |
| Dividends | 0 | |
| Service Revenue | 0 | |
| Salaries and Wages Expense | 0 | |
| Supplies Expense | 0 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 0 | |
| Amortization expense | 0 | |
| Interest Expense | 0 | |
| Income Tax Expense | 0 | |
| Total | 190 | 190 |
Table (9)
9.
Ascertain the net income of Incorporation H&H that has been generated during 2018 and calculate the net profit margin. Explain the company has been financed primarily by liabilities or stockholders’ equity, and find the current ratio.
9.
Explanation of Solution
The net income of Incorporation H&H for 2018:
Incorporation H&H generated net income of $23(thousand) in the year 2018
Calculate the net profit margin:
The net profit margin of Incorporation H&H is 14.4%.
Whether the Incorporation H&H is financed primarily by liabilities or stockholders’ equity:
Incorporation H&H is financed primarily by stockholders’ equity, where by providing stockholders’ equity for $125(thousand) with the total assets and liabilities providing for $43(thousand).
The invested amount of assets primarily come from stockholder’s’ equity of Incorporation H&H, because the stockholder’s equity (common stock) has financed $125 thousand of the Incorporation H&H’s total assets, whereas liabilities has financed $34 thousand.
Calculate the current ratio:
The current ratio is 2.23:1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING LL
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





