
Concept explainers
A.
To draw: Graph of the substrate concentration in the X axis versus the
Concept introduction: Enzymes are biological protein catalysts that alter the speed of the reaction in the biological system. The
A.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
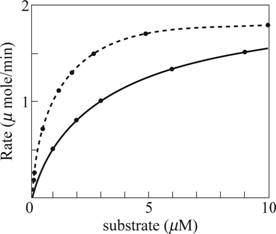
Fig. 1: A graph of the substrate concentration verses the rate of the reaction
Explanation:
| [S] µM | Rate µ mole/min |
| 0.08 | 0.15 |
| 0.12 | 0.21 |
| 0.54 | 0.70 |
| 1.23 | 1.1 |
| 1.82 | 1.3 |
| 2.72 | 1.5 |
| 4.94 | 1.7 |
| 10.00 | 1.8 |
With the above data, the graph is plotted. The black curve in Fig. 1 is the obtained graph from which the KMis evident as 1µM and the Vmax evident as 2 µmole/min.
B.
To explain: The results agree with the estimates made from the first graph of the raw data.
Concept introduction: Enzymes are biological protein catalysts that alter the speed of the reaction in the biological system. The chemical reactions that are catalyzed by these enzymes are studied under enzyme kinetics. The reaction rate is measure based on the rate at which the substrate of the enzymes combines with the enzyme and forms the products. KM is the Michaelis–Menton constant. KM value is not a direct measure of the affinity of the enzyme toward the substrate, but concentration of S where velocity at maximum is half. Vmax is the maximum velocity with which the enzyme catalyzes the reaction.
B.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
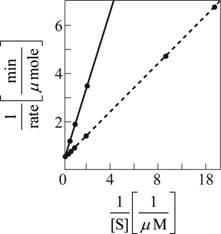
Fig. 2: A reciprocal graph of the substrate concentration verses the rate of the reaction
Explanation:
| 1/[S] (1/ µM) | 1/Rate min/ µ mole |
| 12.50 | 6.7 |
| 8.30 | 4.8 |
| 1.85 | 1.4 |
| 0.81 | 0.91 |
| 0.56 | 0.77 |
| 0.37 | 0.67 |
| 0.20 | 0.59 |
| 0.10 | 0.56 |
With the above data, the graph is plotted. The straight black line in Fig. 2 is the obtained graph from which the KMis evident as 1µM and the Vmax evident as 2 µmole/min. The data are easier to interpret in the second graph as the plot gives a straight line.
C.
To explain: The reason why the statement that very little product was formed in the given reaction condition is important.
Concept introduction: Enzymes are biological protein catalysts that alter the speed of the reaction in the biological system. The chemical reactions that are catalyzed by these enzymes are studied under enzyme kinetics. The reaction rate is measure based on the rate at which the substrate of the enzymes combines with the enzyme and forms the products. KM is the Michaelis–Menton constant. KM value is not a direct measure of the affinity of the enzyme toward the substrate, but concentration of S where velocity at maximum is half. Vmax is the maximum velocity with which the enzyme catalyzes the reaction.
C.
Explanation of Solution
D.
To explain: Plot of the graph for substrate concentration versus rate of the reaction and reciprocal of the substrate concentration versus the rate of the reaction when the enzyme upon regulated with phosphorylation, the KM value increases by a factor of 3 without any change in the Vmax.
Concept introduction: Enzymes are biological protein catalysts that alter the speed of the reaction in the biological system. The chemical reactions that are catalyzed by these enzymes are studied under enzyme kinetics. The reaction rate is measure based on the rate at which the substrate of the enzymes combines with the enzyme and forms the products. KM is the Michaelis–Menton constant. KM value is not a direct measure of the affinity of the enzyme toward the substrate, but concentration of S where velocity at maximum is half. Vmax is the maximum velocity with which the enzyme catalyzes the reaction.
D.
Explanation of Solution
KM value is directly proportional to the substrate concentration. Therefore, as the KM increases, the substrate concentration to give half of the maximum rate increases.
Since more concentration of the substrate is needed to produce the same rate of the reaction; the regulation with phosphorylation inhibits the enzyme-catalyzing reaction. The expected data plots for the same is plotted as dotted curve in Fig 1 for substrate concentration versus rate of the reaction and dotted line in Fig 2 for reciprocal plot of substrate concentration versus rate of the reaction.
| [S] µM | Rate µ mole/min |
| 0.24 | 0.15 |
| 0.36 | 0.21 |
| 1.62 | 0.70 |
| 3.69 | 1.1 |
| 5.46 | 1.3 |
| 8.16 | 1.5 |
| 14.82 | 1.7 |
| 30.00 | 1.8 |
| 1/[S] (1/ µM) | 1/Rate min/ µ mole |
| 4.16 | 6.7 |
| 2.78 | 4.8 |
| 0.61 | 1.4 |
| 0.27 | 0.91 |
| 0.18 | 0.77 |
| 0.12 | 0.67 |
| 0.06 | 0.59 |
| 0.03 | 0.56 |
With the above data, 3[S] is taken for X axis and the rate of the reaction remains the same. The expected data plots for the same is plotted as dotted curve in Fig. 1 for substrate concentration versus rate of the reaction and dotted line in Fig. 2 for reciprocal plot of substrate concentration versus rate of the reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Essential Cell Biology 5e
- What would happen if transcriptome analysis were done on liver and muscle cells?arrow_forwardBiology How many grams of sucrose would you add to 100mL of water to make a 100 mL of 5% (w/v) sucrosesolution?arrow_forwardWhich marker does this DNA 5ʹ AATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGC 3ʹ show?arrow_forward
- The Z value of LOD for two genes is 4, what does it mean for linkage and inheritance?arrow_forwardBiology How will you make a 50-ul reaction mixture with 2uM primer DNA using 10 uM primer DNA stocksolution and water?arrow_forwardBiology You’re going to make 1% (w/v) agarose gel in 0.5XTBE buffer 100 ml. How much agarose are you goingto add to 100 ml of buffer? The volume of agaroseis negligible.arrow_forward
- Biology How will you make a 50-ul reaction mixture with0.2 mM dNTP using 2-mM dNTP stock solution andwater?arrow_forwardBiology What is 200 pmole/uL in Molar concentration?arrow_forwardBiology How will you make a 50-ul reaction mixture with 1Xreaction buffer in it using water and 5X buffer stocksolution?arrow_forward
- Biology How would you make 200 uL of 10 pmole/uLprimer DNA solution using the 200 pmole/uLprimer DNA stock solution and distilled water?arrow_forwardBiology Now you have the 5 M of NaCl stock solution. Howwould you make one liter of 100 mM NaCl solutionusing the 5 M of NaCl solution and distilled water?arrow_forwardDevelopmental Biology Lab Question How to make one liter of 5 M NaCl stock solution?The molar weight of NaCl is 58.44 g/mol.(Molecular weight is 58.44 Dalton or amu).arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





