
EBK FOUNDATIONS OF COLLEGE CHEMISTRY
15th Edition
ISBN: 9781118930144
Author: Willard
Publisher: JOHN WILEY+SONS INC.
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 4, Problem 1RQ
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The physical state of acetic acid at
Expert Solution & Answer
Explanation of Solution
The table is,
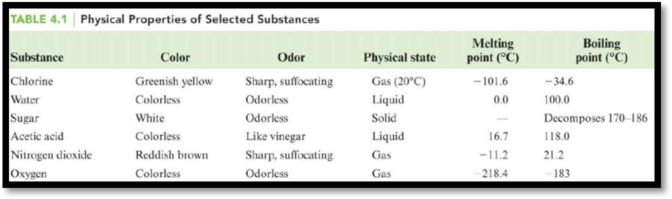
Figure 1
The boiling point of acetic acid is
The boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid boils at a fixed pressure under standard atmospheric conditions and it remains gas.
The given temperature is
The temperature in Kelvin has to be converted to Celsius.
The temperature of the acetic acid is higher than the boiling point of the acetic acid so the physical sate of the acetic acid at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
7. Help
11. Help
8. Help
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK FOUNDATIONS OF COLLEGE CHEMISTRY
Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.1PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.2PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.3PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.4PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.5PCh. 4 - Prob. 1RQCh. 4 - Prob. 2RQCh. 4 - Prob. 3RQCh. 4 - Prob. 4RQCh. 4 - Prob. 5RQ
Ch. 4 - Prob. 6RQCh. 4 - Prob. 7RQCh. 4 - Prob. 8RQCh. 4 - Prob. 9RQCh. 4 - Prob. 10RQCh. 4 - Prob. 11RQCh. 4 - Prob. 12RQCh. 4 - Prob. 13RQCh. 4 - Prob. 14RQCh. 4 - Prob. 15RQCh. 4 - Prob. 1PECh. 4 - Prob. 2PECh. 4 - Prob. 3PECh. 4 - Prob. 4PECh. 4 - Prob. 5PECh. 4 - Prob. 6PECh. 4 - Prob. 7PECh. 4 - Prob. 8PECh. 4 - Prob. 9PECh. 4 - Prob. 10PECh. 4 - Prob. 11PECh. 4 - Prob. 12PECh. 4 - Prob. 13PECh. 4 - Prob. 14PECh. 4 - Prob. 15PECh. 4 - Prob. 16PECh. 4 - Prob. 17PECh. 4 - Prob. 18PECh. 4 - Prob. 19PECh. 4 - Prob. 20PECh. 4 - Prob. 21PECh. 4 - Prob. 22PECh. 4 - Prob. 23AECh. 4 - Prob. 24AECh. 4 - Prob. 25AECh. 4 - Prob. 26AECh. 4 - Prob. 27AECh. 4 - Prob. 28AECh. 4 - Prob. 29AECh. 4 - Prob. 30AECh. 4 - Prob. 31AECh. 4 - Prob. 32AECh. 4 - Prob. 33AECh. 4 - Prob. 34AECh. 4 - Prob. 35AECh. 4 - Prob. 36AECh. 4 - Prob. 37AECh. 4 - Prob. 38AECh. 4 - Prob. 39AECh. 4 - Prob. 44CECh. 4 - Prob. 45CECh. 4 - Prob. 46CE
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Which of the following are descriptions of possible starting material for this reaction? H ? trace acid an ester a ketone an imine an aldehyde a carboxylic acid an enamine a primary amine a secondary amine a tertiary aminearrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardWhat are the reagents needed for this and the third structure I only got the top right structure rightarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning


World of Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618562763
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl
Publisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div