
Concept explainers
(a)
Find the number of branches present in the circuit.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1P
The number of branches present in the circuit is 11 branches.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure given in the textbook.
The voltage source is
The current source is
The given circuit is modified as shown in Figure 1.
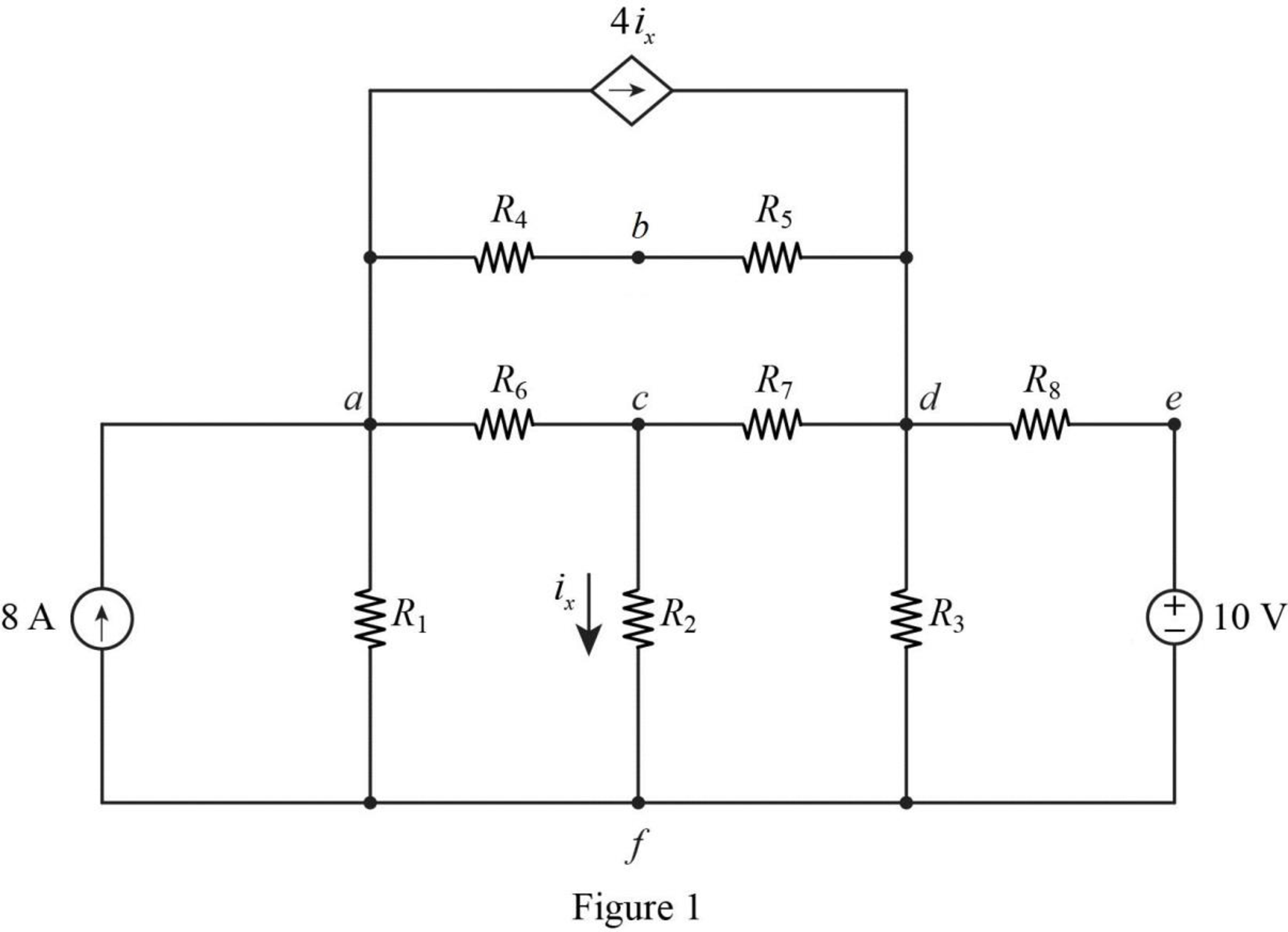
A branch is defined as a single electrical device or elements.
In Figure 1, there are 11 branches in the circuit. They are,
That is, 1 branch with a dependent source, 2 branches with independent sources, and 8 branches with resistors.
Conclusion:
Thus, the number of branches present in the circuit is 11 branches.
(b)
Find the number of branches where the current is unknown.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1P
The number of branches in which the current is unknown is 10 branches.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 1 in Part (a).
In Figure 1, the only one known current in the circuit is the
Conclusion:
Thus, the number of branches in which the current is unknown is 10 branches.
(c)
Find the number of essential branches in the circuit.
(c)
Answer to Problem 1P
The number of essential branches in the circuit is 9 essential branches.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 1 in Part (a).
Essential branch: It is defined as a path that attaches essential nodes without passing through an essential node.
The essential branches in the circuit are,
In the circuit,
Therefore, the circuit has 9 essential branches.
Conclusion:
Thus, the number of essential branches in the circuit is 9 essential branches.
(d)
Find the number of essential branches where the current is unknown in the circuit.
(d)
Answer to Problem 1P
The number of essential branches where the current is unknown is 8 essential branches.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 1 in Part (a).
From Part (c), the circuit has 9 essential branches.
In Figure 1, the current is known only in the essential branch that containing the
Conclusion:
Thus, the number of essential branches where the current is unknown is 8 essential branches.
(e)
Find the number of nodes present in the circuit.
(e)
Answer to Problem 1P
The number of nodes present in the circuit is 6 nodes.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 1 in Part (a).
Node: It is defined as a connection point between two or more branches.
In Figure 1, the nodes present in the circuit are,
Conclusion:
Thus, the number of nodes present in the circuit is 6 nodes.
(f)
Find the number of essential nodes present in the circuit.
(f)
Answer to Problem 1P
The number of essential nodes present in the circuit is 4 essential nodes.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 1 in Part (a).
Essential node: It is a node that joins three or more electrical element or devices
In Figure 1, the essential nodes present in the circuit are,
Conclusion:
Thus, the number of essential nodes present in the circuit is 4 essential nodes.
(g)
Find the number of meshes present in the circuit.
(g)
Answer to Problem 1P
The number of meshes present in the circuit is 6 meshes.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 1 in Part (a).
Mesh: It is defined as a closed loop path that has no any other smaller loops present inside.
In Figure 1, the closed loops present in the circuit are,
Conclusion:
Thus, the number of meshes present in the circuit is 6 meshes.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Electric Circuits Plus Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText 2.0 - Access Card Package (11th Edition) (What's New in Engineering)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- NO AI PLEASEarrow_forwardApply Routh stability criteria to compute the range of values of K such that the following close loop unity negative feedback control syst m is stable. The open-loop transfer function of th system is given by: G(s)H(s) 90(1+0.5s) (1+s) 1+2s)(1+Ks) *arrow_forwardNO AI. Thank Youarrow_forward
- NO AI. Thank Youarrow_forwardPlease solve in detailarrow_forwardHere the Req is 8 my prof solved it and got R3 is parallel to R4 in series with R2 and this combination is parallel to R1. i don't understand how he got these relationships. initially i did the opposite i took (R1//R4 + R2 ) + R3 but got the wrong answer why is it wrong? can you explain to me if there's a trick i can do to understand these questions better and know the configurations of the resistors in a better manner?arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





