
Concept explainers
Answers to all problems are at the end of this book. Detailed solutions are available in the Student Solutions Manual, Study Guide, and Problems Book.
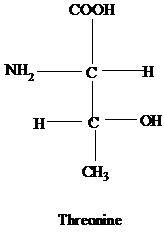
- Drawing Fischer Projection Formulas for Amino Acids Without consulting chapter figures, draw Fischer projection formulas for glycine, aspartate, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, and threonine.
Interpretation:
The Fischer projection formulas for the following amino acids should be drawn.
Glycine, Aspartate, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine and Threonine.
Concept Introduction:
Fisher projection formula is the method used to predict a stereo formula within two dimensions without hampering the stereochemical information.
Explanation of Solution
All amino acids contain
The R group of glycine is hydrogen.

Glycine:
The R group of aspartates is a -CH2COOH.
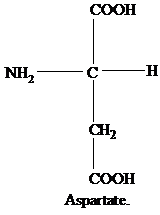
The R group of leucine is an isobutyl group.
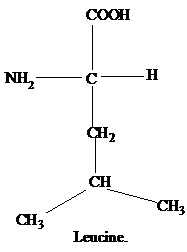
The R group of isoleucine is a sec-butyl group.
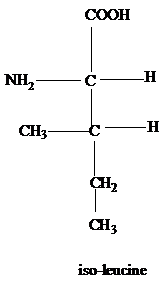
The R group of methionine is a thioether of methyl and ethyl groups.
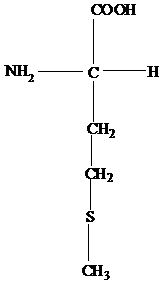
The R group of threonine contains another chiral carbon attached to methyl and a hydroxyl group.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Biochemistry
- Show the fate of the proton on the 4-Oxygen molecule of F-1,6-BP. Please include a drawing showing the electron flow that occurs.arrow_forward1. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following aldol condensation? O NaOH, H₂O heat A B C D Earrow_forwardAn organic chemist ordered the wrong item. She wanted to obtain 1-hydroxy-2-butanone, butinstead ordered 2-hydroxybutyraldehyde. As a good biochemist, show how the organic chemistcould use biological catalysis to make her desired compound. Please show the mechanism by drawing.arrow_forward
- Show the fate of the hydrogen on carbon-2 of glucose. Please draw out the structure using curve arrows to show electron flow.arrow_forward3. Which one of the compounds below is the major product formed by the reaction sequence shown here? CH3 + CH3NO2 NaOH H2, Ni ? nitromethane acetophenone OH OH HO HN- u x x x x Ph A HO -NH2 HO H Ph Ph Ph N- H B Ph NH2 D Earrow_forward4. Only ONE of the five compounds below can be prepared by an aldol condensation in which a single carbonyl compound is treated with base. Which one is it? To solve this problem, reverse the aldol condensation that formed each of these molecules to find out what two molecules came together to make the products. The one in which the two molecules are identical is the answer. Ph Ph ཚིག གནས ག ནཱ ཀ ན ཀནཱ A Ph H B Ph Ph H D Ph. Ph Ph E Harrow_forward
- 5. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? First, equimolar amounts of cyclopentanone and LDA are mixed at -78°C. Then propionaldehyde (propanal) is added. Addition of aqueous acid completes the process. LDA, -78°C. 1. 2. H₂O* H A B H 0 D H H Earrow_forward2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? NaOH, H₂O heat A B C D Earrow_forwardCH3CH2CHO + propanal PhCH2CHO 2-phenylacetaldehyde mixture of four products NaOH 10. In the crossed aldol reaction of propanal and 2-phenylacetaldehyde shown above, a mixture of four products will be formed. Which ONE of the compounds below will NOT be formed in this crossed aldol reaction? OH Ph A H OH OH Ph H B OH OH H H H Ph Ph C Ph D Earrow_forward
- An organic chemist ordered the wrong item. She wanted to obtain 1-hydroxy-2-butanone, butinstead ordered 2-hydroxybutyraldehyde. As a good biochemist, show how the organic chemistcould use biological catalysis to make her desired compound.arrow_forwardPredict the products of aldolase catalyzing the reaction with acetone and (S)-3-hydroxybutyraldehyde.arrow_forwardA cancer patient undergoing chemotherapy is taking a protein kinase inhibitor drug. The patientis an avid marathon runner and does not want to miss his upcoming race. Is it a good idea forthis patient to attempt a marathon while on this medication? Explain why or why not.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
