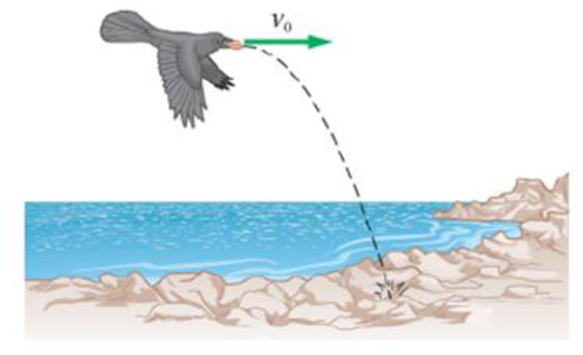
Problem 1CQ: What is the acceleration of a projectile when it reaches its highest point? What is its acceleration... Problem 2CQ: A projectile is launched with an initial speed of v0 at an angle above the horizontal. It lands at... Problem 3CQ: A projectile is launched from level ground. When it lands, its direction of motion has rotated... Problem 4CQ: In a game of baseball a player hits a high fly ball to the outfield. (a) Is there a point during the... Problem 5CQ: A projectile is launched with an initial velocity of v=(4m/s)x+(3m/s)y. What is the velocity of the... Problem 6CQ: A projectile is launched from a level surface with an initial velocity of v=(2m/s)x+(4m/s)y. What is... Problem 7CQ: Do projectiles for which air resistance is nonnegligible, such as a bullet fired from a rifle have... Problem 8CQ: Two projectiles are launched from the same point at the same angle above the horizontal Projectile 1... Problem 9CQ: A child rides on a pony walking with constant velocity. The boy leans over to one side and a scoop... Problem 10CQ: Driving down the highway, you find yourself behind a heavily loaded tomato truck. You follow close... Problem 11CQ: A projectile is launched from the origin of a coordinate system where the positive x axis points... Problem 1PCE: Predict/Explain As you walk briskly down the street, you toss a small ball into the air. (a) If you... Problem 2PCE: A sailboat runs before the wind with a constant speed of 4.2 m/s in a direction 32 north of west.... Problem 3PCE: As you walk to class with a constant speed of 1.75 m/s, you are moving in a direction that is 18.0... Problem 4PCE: Starting from rest, a car accelerates at 2.0 m/s2 up a hill that is inclined 5.5 above the... Problem 5PCE: Predict/Calculate A particle passes through the origin with a velocity of (6.2 m/s)y. If the... Problem 6PCE: A skateboarder travels on a horizontal surface with an initial velocity of 3.8 m/s toward the south... Problem 7PCE: A hot-air balloon is drifting in level flight due east at 2.5 m/s due to a light wind. The pilot... Problem 8PCE: An electron in a cathode-ray tube is traveling horizontally at 2.10 109cm/s when deflection plates... Problem 9PCE: Two canoeists start paddling at the same time and head toward a small island in a lake, as shown in... Problem 10PCE: Predict/Explain Two divers run horizontally off the edge of a low cliff. Diver 2 runs with twice the... Problem 11PCE: Predict/Explain Two youngsters dive off an overhang into a lake Diver 1 drops straight down, and... Problem 12PCE: An archer shoots an arrow horizontally at a target 15 m away. The arrow is aimed directly at the... Problem 13PCE: Victoria Falls The great, gray-green, greasy Zambezi River flows over Victoria Falls in south... Problem 14PCE: A diver runs horizontally off the end of a diving board with an initial speed of 1.85 m/s. If the... Problem 15PCE: An astronaut on the planet Zircon tosses a rock horizontally with a speed of 6.95 m/s. The rock... Problem 16PCE: Predict/Calculate Pitchers Mounds Pitchers mounds are raised to compensate for the vertical drop of... Problem 17PCE: Playing shortstop, you pick up a ground ball and throw it to second base. The ball is thrown... Problem 18PCE: Predict/Calculate A crow is flying horizontally with a constant speed of 2.70 m/s when it releases a... Problem 19PCE: A mountain climber jumps a 2.8-m-wide crevasse by leaping horizontally with a speed of 7.8 m/s. (a)... Problem 20PCE: Predict/Calculate A white-crowned sparrow flying horizontally with a speed of 1.80 m/s folds its... Problem 21PCE: Pumpkin Toss In Denver, children bring their old jack-o-lanterns to the top of a tower and compete... Problem 22PCE: Fairgoers ride a Ferris wheel with a radius of 5.00 m (Figure 4-22). The wheel completes one... Problem 23PCE: Predict/Calculate A swimmer runs horizontally off a diving board with a speed of 3.32 m/s and hits... Problem 24PCE: Baseball and the Washington Monument On August 25, 1894, Chicago catcher William Schriver caught a... Problem 25PCE: A basketball is thrown horizontally with an initial speed of 4.20 m/s (Figure 4-23). A straight line... Problem 26PCE: Predict/Calculate A ball rolls off a table and falls 0.75 m to the floor, landing with a speed of... Problem 27PCE: A certain projectile is launched with an initial speed v0. At its highest point its speed is 12v0.... Problem 28PCE: Three projectiles (A, B, and C) are launched with the same initial speed but with different launch... Problem 29PCE: Three projectiles (A, B, and C) are launched with different initial speeds so that they reach the... Problem 30PCE: A cannonball is launched at an angle above level ground, giving it an initial vertical and... Problem 31PCE: A second baseman tosses the ball to the first baseman, who catches it at the same level from which... Problem 32PCE: A soccer ball is kicked with a speed of 15.6 m/s at an angle of 32.5 above the horizontal. If the... Problem 33PCE: In a game of basketball a forward makes a bounce pass to the center. The ball is thrown with an... Problem 34PCE: Predict/Calculate Snowballs are thrown with a speed of 13 m/s from a roof 7.0 m above the ground.... Problem 35PCE: In Problem 34, find the direction of motion of the two snowballs just before they land. Problem 36PCE: A golfer gives a ball a maximum initial speed of 51 4 m/s. (a) What is the longest possible... Problem 37PCE: What is the highest tree the ball in the previous problem could clear on its way to the longest... Problem 38PCE: The hang time of a punt is measured to be 4.50 s. If the ball was kicked at an angle of 63.0 above... Problem 39PCE: In a friendly game of handball, you hit the ball essentially at ground level and send it toward the... Problem 40PCE: On a hot summer day a young girl swings on a rope above the local swimming hole (Figure 4-27). When... Problem 41PCE: A certain projectile is launched with an initial speed v0. At its highest point its speed is v0/4.... Problem 42PCE: Punkin Chunkin In Dover, Delaware, a post-Halloween tradition is Punkin Chunkin, in which... Problem 43PCE: A dolphin jumps with an initial velocity of 12.0 m/s at an angle of 40.0 above the horizontal. The... Problem 44PCE: A player passes a basketball to another player who catches it at the same level from which it was... Problem 45PCE: A golf ball is struck with a five iron on level ground. It lands 92.2 m away 4.30 s later. What were... Problem 46PCE: Predict/Explain You throw a ball into the air with an initial speed of 10 m/s at an angle of 60... Problem 47PCE: A football quarterback shows off his skill by throwing a pass 45.70 m downfield and into a bucket.... Problem 48PCE: A clever inventor has created a device that can launch water balloons with an initial speed of 85.0... Problem 49PCE: Predict/Calculate Volcanoes on lo Astronomers have discovered several volcanoes on lo, a moon of... Problem 50PCE: Predict/Calculate A soccer ball is kicked with an initial speed of 10.2 m/s in a direction 25.0... Problem 51PCE: A soccer ball is kicked with an initial speed of 8.25 m/s. After 0.750 s it is at its highest point.... Problem 52PCE: An archer shoots an arrow over a castle wall by launching it with an initial speed of 28 m/s at 65... Problem 53GP: CE Child 1 throws a snowball horizontally from the top of a roof; child 2 throws a snowball straight... Problem 54GP: CE The penguin to the left in the accompanying photo is about to land on an ice floe. Just before it... Problem 55GP: CE Dolphins may leap from the water just for the fun of it. At the instant a leaping dolphin lands,... Problem 56GP: CE Predict/Explain A person flips a coin into the air and it lands on the ground a few feet away.... Problem 57GP: CE Predict/Explain Suppose the elevator in the previous problem is rising with a constant upward... Problem 58GP: A train moving with constant velocity travels 170 m north in 12 s and an undetermined distance to... Problem 59GP: A tennis ball is struck in such a way that it leaves the racket with a speed of 4.87 m/s in the... Problem 60GP: A person tosses a ball for her puppy to retrieve. The ball leaves her hand horizontally with a speed... Problem 61GP: An osprey flies horizontally with a constant speed of 6.8 m/s when it drops the fish it was... Problem 62GP: Predict/Calculate A hot-air balloon rises from the ground with a velocity of (2.00 m/s)y. A... Problem 63GP: In a friendly neighborhood squirt gun contest a participant runs at 7.8 m/s horizontally off the... Problem 64GP: BIO Spitting Llamas An agitated llama may spit to assert dominance, or to ward off threats. Llamas... Problem 65GP: A particle leaves the origin with an initial velocity v=(2.40m/s)x, and moves with constant... Problem 66GP: BIO When the dried-up seed pod of a scotch broom plant bursts open, it shoots out a seed with an... Problem 67GP: Trick Shot In an Internet video an athlete launches a basketball from a stadium platform that is... Problem 68GP: A shot-putter throws the shot with an initial speed of 12.2 m/s from a height of 5.15 ft above the... Problem 69GP: Two marbles are launched at t = 0 in the experiment illustrated in Figure 4-29. Marble 1 is launched... Problem 70GP: Rescue Swimmers Coast Guard rescue swimmers are trained to leap from helicopters into the sea to... Problem 71GP: A football player kicks a field goal, launching the ball at an angle of 48 above the horizontal.... Problem 72GP: A ball thrown straight upward returns to its original level in 2.75 s. A second ball is thrown at an... Problem 73GP: Predict/Calculate To decide who pays for lunch, a passenger on a moving train tosses a coin straight... Problem 74GP: Predict/Calculate A cannon is placed at the bottom of a cliff 61.5 m high. If the cannon is fired... Problem 75GP: A golfer hits a shot to an elevated green. The ball leaves the club with an initial speed of 16 m/s... Problem 76GP: Shot Put Record A mens world record for the shot put, 23.12 m, was set by Randy Barnes of the United... Problem 77GP: Referring to Conceptual Example 4-13, suppose the two cats jump from an elevation of 2.5 m with an... Problem 78GP: A Lob Pass Versus a Bullet A quarterback can throw a receiver a high, lazy lob pass or a low, quick... Problem 79GP: For summertime fun, you decide to combine diving from a board with shooting a basketball through a... Problem 80GP: Landing on Mars When the twin exploration rovers, Spirit and Opportunity, landed on Mars, their... Problem 81GP: Collision Course A useful rule of thumb in piloting is that if the heading from your airplane to a... Problem 82GP: As discussed in Example 4-14, the archerfish hunts by dislodging an unsuspecting insect from its... Problem 83GP: Find the launch angle for which the range and maximum height of a projectile are the same. Problem 84GP: A mountain climber jumps a crevasse of width W by leaping horizontally with speed v0. (a) If the... Problem 85GP: Landing on a Different Level A projectile fired from y = 0 with initial speed v0 and initial angle ... Problem 86GP: A mountain climber jumps a crevasse by leaping horizontally with speed v0. If the climbers direction... Problem 87GP: Projectiles: Coming or Going? Most projectiles continually move farther from the origin during their... Problem 88PP: Caterpillar Pellets The larvae (caterpillars) of certain species of butterflies and moths construct... Problem 89PP: Caterpillar Pellets The larvae (caterpillars) of certain species of butterflies and moths construct... Problem 90PP: Caterpillar Pellets The larvae (caterpillars) of certain species of butterflies and moths construct... Problem 91PP: Caterpillar Pellets The larvae (caterpillars) of certain species of butterflies and moths construct... Problem 92PP: Referring to Example 4-9 (a) At what launch angle greater than 54.0 does the golf ball just barely... Problem 93PP: Referring to Example 4-9 Suppose that the golf ball is launched with a speed of 15.0 m/s at an angle... Problem 94PP: Referring to Example 4-11 Suppose the ball is dropped at the horizontal distance of 5.50 m, but from... Problem 95PP: Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 4-11 Suppose we change the dolphins launch angle to 45.0, but... format_list_bulleted


 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning




