
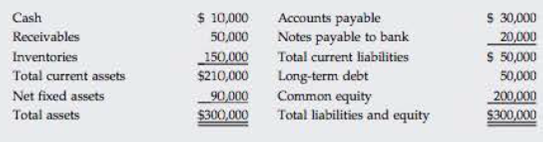
The new owner thinks that inventories are excessive and can be lowered to the point where the current ratio is equal to the industry average, 25×, without affecting sales or net income. If inventories are sold and not replaced (thus reducing the current ratio to 25×); if the funds generated are used to reduce common equity (stock can be repurchased at book value); and if no other changes occur, by how much will the ROE change? What will be the firm’s new quick ratio?
To identify: The change in return on equity and new quick ratio.
Quick Ratio: A part of liquidity ratios, quick ratio reflects the ability to oblige the short term debts of a company. It is calculated based on the liquid assets and current liabilities; a company has in an accounting period.
Return on Equity: Return on equity represents the amount earned as return by equity share holders; it can be calculated by dividing earnings available for equity share holders to total equity capital.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of return on equity
Items required for the calculation of return on equity are net income and common equity.
Given,
Net income is $15,000.
Common equity is $200,000.
Formula to calculate return on equity ratio,
Where,
- ROE is return on equity.
Substitute $15,000 for net income and $200,000 for common equity in the above formula,
Hence, the return on equity is 0.075 or 7.5%.
Compute the quick ratio
Given,
The current assets are $210,000.
The inventories are $150,000.
The current liabilities are $50,000.
Formula to compute quick ratio,
Substitute $210,000 for current assets, $150,000 for inventories and $50,000 for current liabilities in the above formula,
The quick ratio is 1.2 times.
In order to compute new quick ratio, old current ratio, new current assets and new return on equity need to calculate.
Computation of old current ratio
The items required for the calculation of current ratio are current liabilities and current assets.
Given,
Current assets are $210,000.
Current liabilities are $50,000.
Formula to calculate current ratio,
Substitute $210,000 for current assets and $50,000 for current liabilities in the above formula,
Hence, old current ratio is 4.2 times.
The new current ratio which is required to take is 2.5 times.
Compute the change in assets due to the current ratio as 2.5 times.
The current liabilities are $50,000. (Given)
The current ratio is 2.5 times.
Formula to calculate new current assets derives from the formula of current ratio,
Substitute $50,000 for current liabilities and 2.5 for current ratio in the above formula,
The new current assets are $125,000.
The difference between the currents assets refers the value of sold inventory.
Compute the sold inventory due to change in current assets
The current assets are $210,000. (Given)
The new current assets are $125,000. (Calculated)
Formula to calculate the sold inventory,
Substitute $210,000 for old current assets and $125,000 for new current assets in the above formula,
The value of inventor is curtailed by the $85,000.
Compute the balance inventory
The total inventory is $150,000. (Given)
The sold inventory is $85,000. (Calculated)
Formula to calculate the balance inventory,
Substitute $150,000 for inventory and $85,000 for sold inventory in the above formula,
The balanced inventory is $65,000.
Due to the sale the cash balance would also decrease by 65,000.
Computation of cash balance after the sale of inventory
Cash balance is $10,000.
The sale of inventory is $65,000.
Formula to calculate the new cash balance,
Substitute $10,000 for old balance and $65,000 for sold inventory in the above formula,
The cash balance after the sale of inventory is $55,000.
From the cash balance after sale of inventory, equity can be bought back. So the level of cash balance will reduce and equity will reduce by $65,000.
Compute the reduced equity:
The equity balance is $200,000. (Given)
The buyback equity share is $65,000. (Calculated)
Formula to calculate the reduced capital,
Substitute $200,000 for total equity shares and $65,000 for buyback shares in the above formula,
The reduced equity shares are $135,000.
Compute the new return on equity
The net income is $15,000. (Given)
The equity value is $135,000. (Calculated)
Formula to calculate the return on equity,
Where,
- ROE is return on equity.
Substitute $15,000 for net income and $135,000 for common equity in the above formula,
Hence, the return on equity is 0.1111 or 11.11%.
Compute the new quick ratio
The new current assets are $125,000.
The new inventories are $65,000.
The current liabilities are $50,000.
Formula to calculate quick ratio,
Substitute $125,000 for current assets, $65,000 for inventories and $50,000 for current liabilities in the above formula,
The new quick ratio is 1.2 times.
Quick ratio has remained same as there is no other current asset has changed except inventory and inventory is not the part of the terms used for the calculation of quick ratio.
Hence, the change in return on equity is 11.11% and there is no change in quick ratio and it is 1.2 times.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edition (MindTap Course List)
- If your Uncle borrows $60,000 from the bank at 10 percent interest over the seven-year life of the loan, what equal annual payments must be made to discharge the loan, plus pay the bank its required rate of interest? How much of his first payment will be applied to interest? To principal? How much of his second payment will be applied to each?arrow_forwardQ1: You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually.What is NEWER’s stock price?The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8.The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually.What is OLDER’s stock price?Now assume that both stocks have a required…arrow_forwardQ1: Blossom is 30 years old. She plans on retiring in 25 years, at the age of 55. She believes she will live until she is 105. In order to live comfortably, she needs a substantial retirement income. She wants to receive a weekly income of $5,000 during retirement. The payments will be made at the beginning of each week during her retirement. Also, Blossom has pledged to make an annual donation to her favorite charity during her retirement. The payments will be made at the end of each year. There will be a total of 50 annual payments to the charity. The first annual payment will be for $20,000. Blossom wants the annual payments to increase by 3% per year. The payments will end when she dies. In addition, she would like to establish a scholarship at Toronto Metropolitan University. The first payment would be $80,000 and would be made 3 years after she retires. Thereafter, the scholarship payments will be made every year. She wants the payments to continue after her death, therefore…arrow_forward
- Q1: Blossom is 30 years old. She plans on retiring in 25 years, at the age of 55. She believes she will live until she is 105. In order to live comfortably, she needs a substantial retirement income. She wants to receive a weekly income of $5,000 during retirement. The payments will be made at the beginning of each week during her retirement. Also, Blossom has pledged to make an annual donation to her favorite charity during her retirement. The payments will be made at the end of each year. There will be a total of 50 annual payments to the charity. The first annual payment will be for $20,000. Blossom wants the annual payments to increase by 3% per year. The payments will end when she dies. In addition, she would like to establish a scholarship at Toronto Metropolitan University. The first payment would be $80,000 and would be made 3 years after she retires. Thereafter, the scholarship payments will be made every year. She wants the payments to continue after her death, therefore…arrow_forwardJerome Moore invests in a stock that will pay dividends of $2.00 at the end of the first year; $2.20 at the end of the second year; and $2.40 at the end of the third year. also, he believes that at the end of the third year he will be able to sell the stock for $33. what is the present value of all future benefits if a discount rate of 11 percent is applied?arrow_forwardQ1: You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually.What is NEWER’s stock price?The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8.The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually.What is OLDER’s stock price?Now assume that both stocks have a required…arrow_forward
- Q1: You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually.What is NEWER’s stock price?The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8.The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually.What is OLDER’s stock price?Now assume that both stocks have a required…arrow_forwardQ1: Blossom is 30 years old. She plans on retiring in 25 years, at the age of 55. She believes she will live until she is 105. In order to live comfortably, she needs a substantial retirement income. She wants to receive a weekly income of $5,000 during retirement. The payments will be made at the beginning of each week during her retirement. Also, Blossom has pledged to make an annual donation to her favorite charity during her retirement. The payments will be made at the end of each year. There will be a total of 50 annual payments to the charity. The first annual payment will be for $20,000. Blossom wants the annual payments to increase by 3% per year. The payments will end when she dies. In addition, she would like to establish a scholarship at Toronto Metropolitan University. The first payment would be $80,000 and would be made 3 years after she retires. Thereafter, the scholarship payments will be made every year. She wants the payments to continue after her death, therefore…arrow_forwardTrue and False 1. There are no more than two separate phases to decision making and problem solving. 2. Every manager always has complete control over all inputs and factors. 3. Opportunity cost is only considered by accountants as a way to calculate profits 4. Standard error is always used to evaluate the overall strength of the regression model 5. The t-Stat is used in a similar way as the P-valued is used 6. The P-value is used as R-square is used. 7. R-square is used to evaluate the overall strength of the model. 8. Defining the problem is one of the last things that a manager considers Interpreting Regression Printouts (very brief answers) R² = .859 Intercept T N = 51 Coefficients 13.9 F= 306.5 Standard Error .139 SER=.1036 t Stat P value 99.8 0 .275 .0157 17.5 0 The above table examines the relationship between the nunber, of poor central city households in the U.S. and changes in the costs of college tuition from 1967 to 2019. 9. What is the direction of this relationship? 10.…arrow_forward
- CARS Auto Co. Ltd – Alpha Branch Unadjusted Trial Balance December 31, 2024 A/C NAME TRIAL BALANCE DR CR cash 240,000 Accounts receivables 120,000 supplies 41,100 Lease hold improvement 200,000 Accumulated depreciation – Lease hold improvement 80,000 Furniture and fixtures 800,000 Accumulated depreciation - furniture and fixtures 380,000 Accounts payable 30,000 Salary payable Unearned service revenue 44,100 Cars, capital 649,000 Cars, withdrawal 165,100 Service revenue 450,000 Salary expense 48,400 Supplies expense Rent expense Depreciation expense – leasehold improvement Depreciation expense – furniture and fixtures Advertising expense 18,500 1,633,100 1,633,100 Data presented for the adjusting entries include the following: Rent expense of $160,000…arrow_forwardScenario: Jim played football for a famous club but, due to a long term injury and on medical advice, he retired from the game in January 2007. The club, grateful for Jim’s contribution to their success over the years, held a testimonial match in Jim’s honour. Jim received €150,000 from this testimonial match and he decided to open a shop selling sporting goods with the proceeds. On 1 May 2007, Jim opened a business bank account into which he paid the €150,000. In the first year of trading, he undertook the following transactions: 2 May 2007: Jim signed a five year lease on a shop in the town centre and paid €50,000 to cover the lease for the whole five years 3 May 2007: Jim paid shop fitters €10,000 for shelves and racking and for the electronic till in which to record sales. Jim expects these assets will also have a useful life of 5 years. He hired a part time assistant at a cost of €250 per month paid monthly by cheque from the business bank account. While his main business is to…arrow_forwardHelp with questions 7-24arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning


