
Concept explainers
a.
Find
a.
Answer to Problem 13PS
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
When you stand in shallow water and look at an object below the surface of the water, the object will look farther away from you than it really is. This is because when light rays pass between air and water, the water refracts, or bends, the light rays. The index of refraction for water is
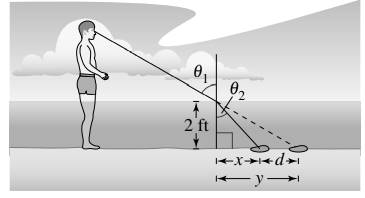
While standing in water that is
Calculation:
Here, we will consider the following figure:
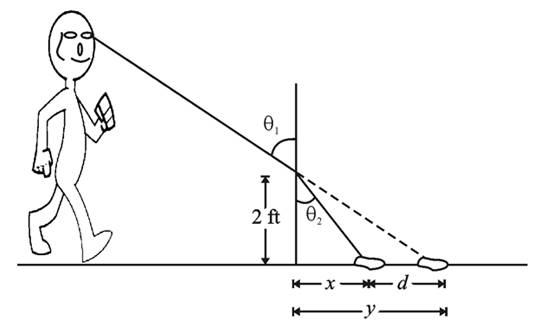
We are given the ratio:
Now, for
Hence,
b.
Find the distances
b.
Answer to Problem 13PS
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
When you stand in shallow water and look at an object below the surface of the water, the object will look farther away from you than it really is. This is because when light rays pass between air and water, the water refracts, or bends, the light rays. The index of refraction for water is
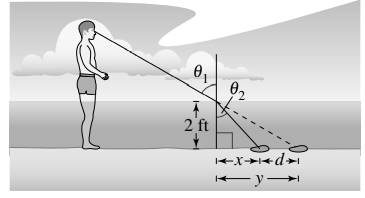
Find the distances
Calculation:
Here, we will find
Now, we will find
c.
Find the distance
c.
Answer to Problem 13PS
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
When you stand in shallow water and look at an object below the surface of the water, the object will look farther away from you than it really is. This is because when light rays pass between air and water, the water refracts, or bends, the light rays. The index of refraction for water is
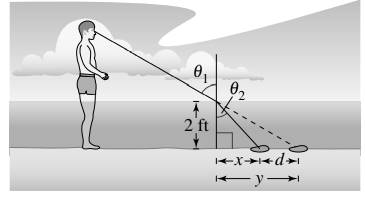
Find the distance
Calculation:
Here, as we move close to the rock,
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- A factorization A = PDP 1 is not unique. For A= 7 2 -4 1 1 1 5 0 2 1 one factorization is P = D= and P-1 30 = Use this information with D₁ = to find a matrix P₁ such that - -1 -2 0 3 1 - - 1 05 A-P,D,P P1 (Type an integer or simplified fraction for each matrix element.)arrow_forwardMatrix A is factored in the form PDP 1. Use the Diagonalization Theorem to find the eigenvalues of A and a basis for each eigenspace. 30 -1 - 1 0 -1 400 0 0 1 A= 3 4 3 0 1 3 040 3 1 3 0 0 4 1 0 0 003 -1 0 -1 Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. (Use a comma to separate vectors as needed.) A basis for the corresponding eigenspace is { A. There is one distinct eigenvalue, λ = B. In ascending order, the two distinct eigenvalues are λ₁ ... = and 2 = Bases for the corresponding eigenspaces are { and ( ), respectively. C. In ascending order, the three distinct eigenvalues are λ₁ = = 12/2 = and 3 = Bases for the corresponding eigenspaces are {}, }, and { respectively.arrow_forwardN Page 0.6. 0.4. 0.2- -0.2- -0.4- -6.6 -5 W 10arrow_forward
- Diagonalize the following matrix, if possible. 8 0 6 - 8 Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. 8 0 OA. For P= D= 0 3 6 0 B. For P = D= 0 -6 8 0 C. For P = D= 0 - 8 D. The matrix cannot be diagonalized.arrow_forwardCalculus lll May I please have the solutions for the following exercises? Thank youarrow_forwardCalculus lll May I please have the solution for the following question? Thank youarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





