
Concept explainers
A Fermat’s principle of least time for refraction. A ray of light traveling in a medium with speed v1 leaves point A and strikes the boundary between the incident and transmitted media a horizontal distance x from point A as shown in Figure P38.98. The refracted ray travels with speed v2 in the second medium, eventually reaching point B. The horizontal distance between points A and B is L. a. Calculate the time t required for the light to travel from A to B in terms of the parameters labeled in the figure. b. Now take the derivative of t with respect to x. What is the condition for which the ray of light will take the shortest time to travel from A to B?
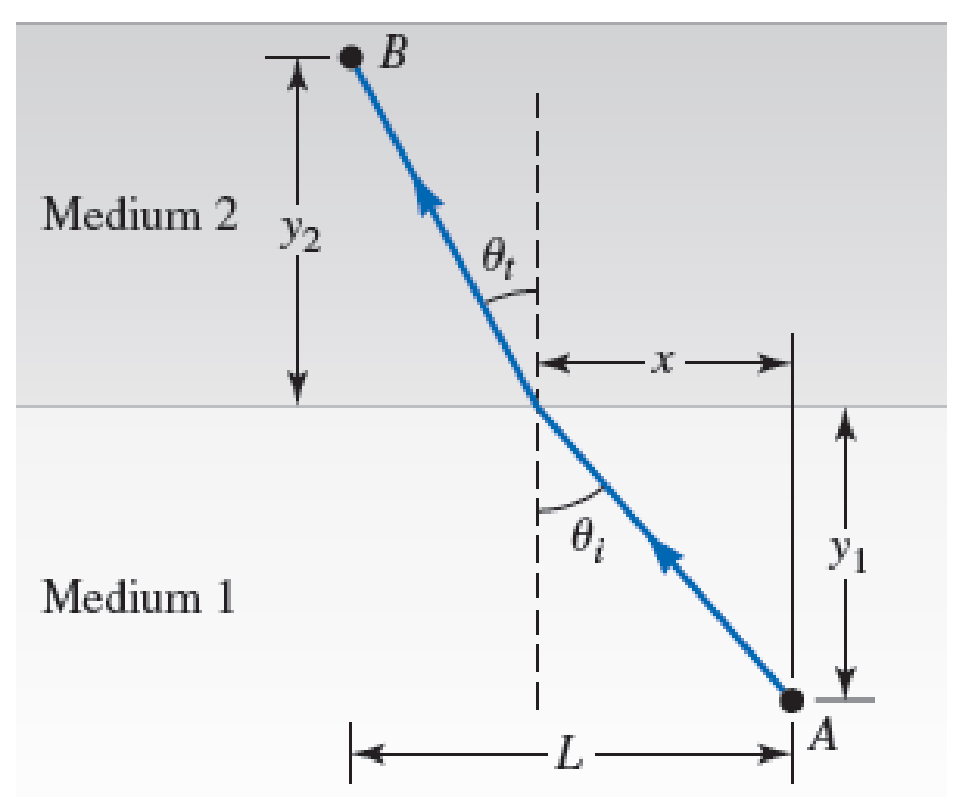
Figure P38.98
(a)
The time required for the light ray to travel from the points A to B.
Answer to Problem 98PQ
The time taken for the light to travel from point
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the time taken for the light ray in the second medium.
Here,
Write the expression for distance travelled by the light in the second medium.
Here,
Write the expression for the time taken for the light ray in the first medium.
Here,
Write the expression for distance travelled by the light in the first medium.
Here,
Write the equation for total time taken for the light is.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the time taken for the light to travel from point
(b)
The required condition to travel for getting the shortest time to reach the point
Answer to Problem 98PQ
The required condition for getting the minimum time to reach the point
Explanation of Solution
Take the derivative of
From the formula
The light ray in which its shortest time taken is.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Simplify the above equation.
Therefore, the required condition for getting the minimum time to reach the point
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 38 Solutions
Physics For Scientists And Engineers: Foundations And Connections, Extended Version With Modern Physics
- 9. A spring has a force constant of 100 N/m and an unstretched length of 0.07 m. One end is attached to a post that is free to rotate in the center of a smooth. table, as shown in the top view in the figure below. The other end is attached to a 1kg disc moving in uniform circular motion on the table, which stretches the spring by 0.03 m. Friction is negligible. What is the centripetal force on the disc? Top View (a) 0.3 N (b) 3.0 N (c) 10 N (d) 300 N (e) 1000 Narrow_forward4. A child has a ball on the end of a cord, and whirls the ball in a vertical circle. Assuming the speed of the ball is constant (an approximation), when would the tension in the cord be greatest? (a) At the top of the circle. (b) At the bottom of the circle. (c) A little after the bottom of the circle when the ball is climbing. (d) A little before the bottom of the circle when the ball is descending quickly. (e) Nowhere; the cord is pulled the same amount at all points.arrow_forward3. In a rotating vertical cylinder (Rotor-ride) a rider finds herself pressed with her back to the rotating wall. Which is the correct free-body diagram for her? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)arrow_forward
- 8. A roller coaster rounds the bottom of a circular loop at a nearly constant speed. At this point the net force on the coaster cart is (a) zero. (b) directed upward. (c) directed downward. (d) Cannot tell without knowing the exact speed.arrow_forward5. While driving fast around a sharp right turn, you find yourself pressing against the left car door. What is happening? (a) Centrifugal force is pushing you into the door. (b) The door is exerting a rightward force on you. (c) Both of the above. (d) Neither of the above.arrow_forward7. You are flung sideways when your car travels around a sharp curve because (a) you tend to continue moving in a straight line. (b) there is a centrifugal force acting on you. (c) the car exerts an outward force on you. (d) of gravity.arrow_forward
- 1. A 50-N crate sits on a horizontal floor where the coefficient of static friction between the crate and the floor is 0.50. A 20-N force is applied to the crate acting to the right. What is the resulting static friction force acting on the crate? (a) 20 N to the right. (b) 20 N to the left. (c) 25 N to the right. (d) 25 N to the left. (e) None of the above; the crate starts to move.arrow_forward3. The problem that shall not be named. m A (a) A block of mass m = 1 kg, sits on an incline that has an angle 0. Find the coefficient of static friction by analyzing the system at imminent motion. (hint: static friction will equal the maximum value) (b) A block of mass m = 1kg made of a different material, slides down an incline that has an angle 0 = 45 degrees. If the coefficient of kinetic friction increases is μ = 0.5 what is the acceleration of the block? karrow_forward2. Which of the following point towards the center of the circle in uniform circular motion? (a) Acceleration. (b) Velocity, acceleration, net force. (c) Velocity, acceleration. (d) Velocity, net force. (e) Acceleration, net force.arrow_forward
- Problem 1. (20 pts) The third and fourth stages of a rocket are coastin in space with a velocity of 18 000 km/h when a smal explosive charge between the stages separate them. Immediately after separation the fourth stag has increased its velocity to v4 = 18 060 km/h. Wha is the corresponding velocity v3 of the third stage At separation the third and fourth stages hav masses of 400 and 200 kg, respectively. 3rd stage 4th stagearrow_forwardMany experts giving wrong answer of this question. please attempt when you 100% sure . Otherwise i will give unhelpful.arrow_forwardDetermine the shear and moment diagram for the beam shown in Fig.1. A 2 N/m 10 N 8 N 6 m B 4m Fig.1 40 Nm Steps: 1) Determine the reactions at the fixed support (RA and MA) (illustrated in Fig 1.1) 2) Draw the free body diagram on the first imaginary cut (fig. 1.2), and determine V and M. 3) Draw the free body diagram on the second imaginary cut (fig. 1.3), and determine V and M. 4) Draw the shear and moment diagramarrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





