
Concept explainers
A spherical concave mirror has a radius of curvature of -400 cm. An object 2.00 cm tall is on the central axis 400 cm in front of the mirror. (a) Determine the focal length. (b) Locate the image. (c) Describe the image. (d) Determine the magnification. [Hint: Check out Fig. 36-5.]
(a)
The focal length of a
Answer to Problem 26SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The radius of curvature is
The height of the object is
The distance of the object from the concave mirror is
Formula used:
The thin mirror equation is written as,
Here,
Sign convention:
If R is negative, the centre of curvature is to the left of the mirror, and the mirror is concave.
If R is positive, the centre of curvature is to the right of the mirror, and the mirror is convex.
If f is positive, the mirror is concave.
If f is negative, the mirror is convex.
Explanation:
Recall the expression forthin mirror.
Solve for
Substitute
The positive sign indicates that the mirror is concave.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the focal length of the mirror is
(b)
The location of the image, when a
Answer to Problem 26SP
Solution:
The real image is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The radius of curvature is
The height of the object is
The distance of the object from the concave mirror is
From previous part, the focal length of the given concave mirror is
Formula used:
The thin mirror equation is written as,
Here,
Sign convention:
If
If
If
If f is positive, the mirror is concave.
If f is negative, the mirror is convex.
Explanation:
Consider the expression forthinmirror.
Understand that the object is placed at a distance of
Substitute
Solve for
The positive sign indicates that the image is real.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the location of t hereal image is
(c)
The nature of the image, when a
Answer to Problem 26SP
Solution:
The image is r eal, inverted, and of the same size as the object.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
From table 36-1 in the textbook, it is clear that when the object is at a distance of
Explanation:
Draw the diagram ofa concave mirror when the object is placed at a distance of
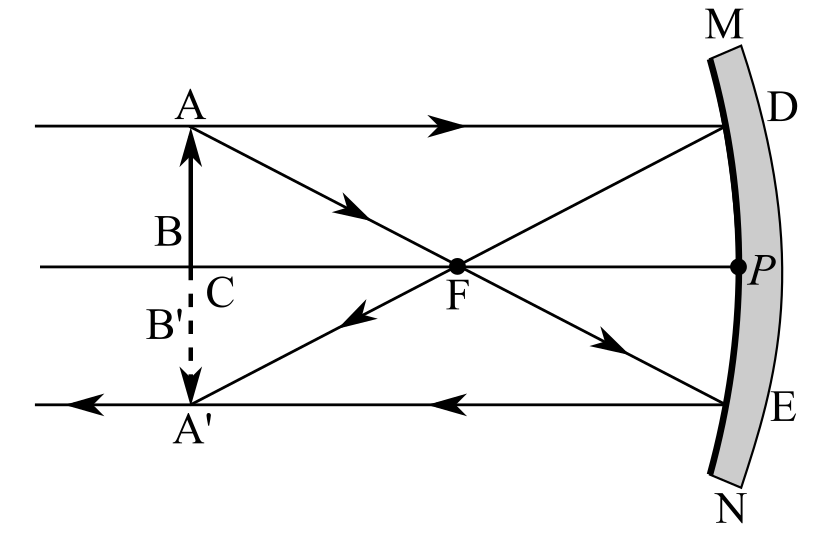
From the above figure, it is clear that when the object is placed at a distance of
Conclusion:
Therefore, the image formed by the concave mirror is real, inverted , and of the same size as the object.
(d)
The magnification, when a
Answer to Problem 26SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The radius of curvature is
The height of the object is
The distance of the object from the concave mirror is
From part (a), the focal length of the given concave mirror is
Formula used:
The formula for the magnification of the mirror is:
Here,
Explanation:
Consider the expression for the magnification of the mirror.
Obtain the value of
Substitute
The negative sign indicates that the image is inverted.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnification is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 36 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
- A converging lens made of crown glass has a focal length of 15.0 cm when used in air. If the lens is immersed in water, what is its focal length? (a) negative (b) less than 15.0 cm (c) equal to 15.0 cm (d) greater than 15.0 cm (e) none of those answersarrow_forwardHow far should you hold a 2.1 cm-focal length magnifying glass from an object to obtain a magnification of 10 x ? Assume you place your eye 5.0 cm from the magnifying glass.arrow_forwardThe disk of the Sun subtends an angle of 0.533 at the Earth. What are (a) the position and (b) the diameter of the solar image formed by a concave spherical mirror with a radius of curvature of magnitude 3.00 m?arrow_forward
- (i) When an image of an object is formed by a plane mirror, which of the following statements is always true? More than one statement may be correct. (a) The image is virtual. (b) The image is real. (c) The image is upright. (d) The image is inverted. (e) None of those statements is always true. (ii) When the image of an object is formed by a concave mirror, which of the preceding statements are always true? (iii) When the image of an object is formed by a convex mirror, which of the preceding statements are always true?arrow_forwardTwo lenses made of kinds of glass having different indices of refraction n1 and n2 are cemented together to form an optical doublet. Optical doublets are often used to correct chromatic aberrations in optical devices. The first lens of a certain doublet has index of refraction n1, one flat side, and one concave side with a radius of curvature of magnitude R. The second lens has index of refraction n2 and two convex sides with radii of curvature also of magnitude R. Show that the doublet can be modeled as a single thin lens with a focal length described by 1f=2n2n11Rarrow_forwardA diverging lens has a focal length of magnitude 20.0 cm. (a) Locate the image for object distances of (i) 40.0 cm, (ii) 20.0 cm, and (iii) 10.0 cm. For each case, state whether the image is (b) real or virtual and (c) upright or inverted.(d) For each case, find the magnification.arrow_forward
- If Joshs face is 30.0 cm in front of a concave shaving mirror creating an upright image 1.50 times as large as the object, what is the mirrors focal length? (a) 12.0 cm (b) 20.0 cm (c) 70.0 cm (d) 90.0 cm (e) none of those answersarrow_forwardThe radius of curvature of the left-hand face of a flint glass biconvex lens (n = 1.60) has a magnitude of 8.00 cm, and the radius of curvature of the right-hand face has a magnitude of 11.0 cm. The incident surface of a biconvex lens is convex regardless of which side is the incident side. What is the focal length of the lens if light is incident on the lens from the left?arrow_forwardUnder what circumstances will an image be located at the focal point of a spherical lens or mirror?arrow_forward
- An object 2.00 cm high is placed 40.0 cm to the left of a converging lens having a focal length of 30.0 cm. A diverging lens with a focal length of -20.0 cm is placed 110 cm to the right of the converging lens. Determine (a) the position and (b) the magnification of the final image, (c) Is the image upright or inverted? (d) What If? Repeat parts (a) through (c) for the case in which the second lens is a converging lens having a focal length of 20.0 cm.arrow_forward1) Suppose a concave spherical mirror has a focal length of 4.0 cm. Find the image location and magnification both graphically (with ray diagrams) and analytically (using equations) for the following cases. In each case state whether the image is real/virtual and upright/inverted. (a) First case: An object of height 4.0 cm located a distance 12.0 cm from the mirror. (b) Second case: An object of height 2.0 cm located a distance 2.0 cm from the mirror. (c) Third case: Repeat 1(a) for a convex mirror using the same focal length.arrow_forwardA dentist uses a mirror to examine a tooth that is 1.25 cm in front of the mirror. The image of the tooth is formed 10.0 cm behind the mirror. (a) Determine the mirror's radius of curvature. cm (b) Determine the magnification of the image. ✕arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





