
Concept explainers
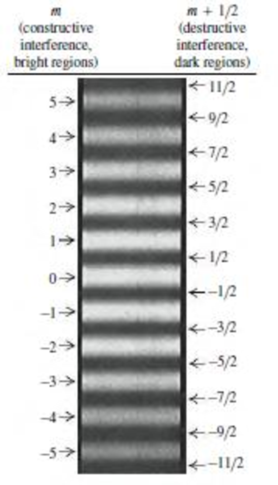
You shine a tunable laser (whose wavelength can be adjusted by turning a knob) on a pair of closely spaced slits. The light emerging from the two slits produces an interference pattern on a screen like that shown in Fig. 35.6. If you adjust the wavelength so that the laser light changes from red to blue, how will the spacing between bright fringes change? (i) The spacing increases; (ii) the spacing decreases; (iii) the spacing is unchanged; (iv) not enough information is given to decide.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 35 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Physics with eText -- Access Card Package (14th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
- In Figure P27.7 (not to scale), let L = 1.20 m and d = 0.120 mm and assume the slit system is illuminated with monochromatic 500-nm light. Calculate the phase difference between the two wave fronts arriving at P when (a) = 0.500 and (b) y = 5.00 mm. (c) What is the value of for which the phase difference is 0.333 rad? (d) What is the value of for which the path difference is /4?arrow_forwardTable P35.80 presents data gathered by students performing a double-slit experiment. The distance between the slits is 0.0700 mm, and the distance to the screen is 2.50 m. The intensity of the central maximum is 6.50 106 W/m2. What is the intensity at y = 0.500 cm? TABLE P35.80arrow_forwardCoherent light rays of wavelength strike a pair of slits separated by distance d at an angle 1, with respect to the normal to the plane containing the slits as shown in Figure P27.14. The rays leaving the slits make an angle 2 with respect to the normal, and an interference maximum is formed by those rays on a screen that is a great distance from the slits. Show that the angle 2 is given by 2=sin1(sin1md) where m is an integer.arrow_forward
- Light from a laser with a wavelength of 5.50 ✕ 102 nm is incident on (and perpendicular to) a pair of slits separated by 0.310 mm. An interference pattern is formed on a screen 1.70 m from the slits. Find the distance (in mm) between the first and second dark fringes of the interference pattern.arrow_forwardA double slit experiment using 532 nm light produces an interference pattern with the 1st order maxima separated by an angle of 0.115º from the central maxima. By what distance are the slits separated?arrow_forwardA spacer is cut from a playing card of thickness 2.88 x 10-“ m and used to separate one end of two rectangular, optically flat, 3.20 cm long glass plates with n = 1.60, as in the figure below. Laser light at 633 nm shines straight down on the top plate. HINT (a) Count the number of phase reversals for the interfering waves. (b) Calculate the separation (in m) between dark interference bands observed on the top plate. marrow_forward
- Monochromatic light with wavelength 620 nm passes through a circular aperture with diameter 7.4 mm. The resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen that is 4.5 m from the aperture. What is the diameter of the Airy disk on the screen?arrow_forwardA beam of light is diffracted by a slit of width 0.55mm. The diffraction pattern is formed on a wall 2m beyond the slit. The distance between the positions of zero intensity on both sides of the central bright fringe is 4.1mm. Calculate the wavelength of the laser light. (Diffraction and polarization)arrow_forwardA red He-Ne laser and a green Kr-Ar laser shine through a double slit, where the spacing between the slits is 50.0 um. The red laser has a wavelength of 632.8 nm while the green laser has a wavelength of 514.5 nm. The distance between the central bright spot and the first red fringe is 3.1 cm. The small angle approximation can be assumed in this question. Recall u = 10-6 n = 2 n = 1 n = 1 Central bright spot Part A What is the distance between the screen and the double slit? Hνα ΑΣφ D = m Submit Request Answer Part B How far (in centimeters) from each side of the first red fringe is a green fringe located? (Find r1 and rz on the screen illustrated above) ? T1, r2 = cm Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- Using the equation for the distance between fringes, Δy = x? d , calculate the distance (in cm) between fringes for 578 nm light falling on double slits separated by 0.0350 mm, located 3.20 m from a screen as in the figure.arrow_forwardTwo narrow slits separated by 0.38 mm are positioned a distance 4.5 m away from a screen. Two lasers illuminate the slits with wavelengths 655 nm and 524 nm, creating a pattern of overlapping interference patterns on the screen. The central maxima (m = 0) of both colors overlap at y = 0. What is the next higher position y > 0 where maxima for both colors overlap again? Give your answer in units of mm.arrow_forwardThe yellow light from a sodium vapor lamp seems to be of pure wave- length, but it produces two first-order maxima at 36.093◦ and 36.129◦ when projected on a 10,000 line per centimeter diffraction grating. What are the two wavelengths to an accuracy of 0.1 nm?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill


