
Concept explainers
Consider a horizontal interface between air above and glass of index of refraction 1.55 below. (a) Draw a light ray incident from the air at angle of incidence 30.0°. Determine the angles of the reflected and refracted rays and show them on the diagram. (b) What If? Now suppose the light ray is incident from the glass at an angle of 30.0°. Determine the angles of the reflected and refracted rays and show all three rays on a new diagram. (c) For rays incident from the air onto the air–glass surface, determine and tabulate the angles of reflection and refraction for all the angles of incidence at 10.0° intervals from 0° to 90.0°. (d) Do the same for light rays coming up to the interface through the glass.
(a)
Answer to Problem 35.52AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The index of refraction of glass is
From, law of reflection, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Thus, angle of reflection is
From Snell’s law,
Here,
Substitute
The figure below shows the angle of incidence, the angle of reflection and the angle of refraction.
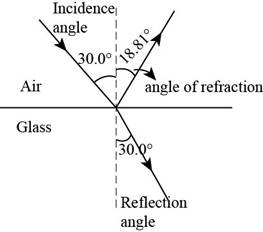
Figure (1)
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle of reflection is
(b)
Answer to Problem 35.52AP
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The index of refraction of glass is
From, law of reflection, angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
Thus, angle of reflection is
From, Snell’s law,
Here,
Substitute
The figure below shows the angle of incidence, the angle of reflection and the angle of refraction.
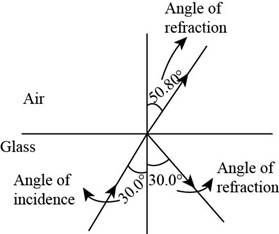
Figure (2)
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle of reflection is
(c)
Answer to Problem 35.52AP
| Angle of incidence | Angle of reflection | Angle of refraction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Explanation of Solution
From, law of reflection, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. So for all value of angles between
The formula to calculate the angle of refraction is,
From, Snell’s law,
Substitute
Substitute
The remaining values of the angle of refraction can be calculated by the same method.
The table for angle of reflection and angle of refraction for all angles of incidence at
| Angle of incidence | Angle of reflection | Angle of refraction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle of reflection is same as the angle of incidence and the of angle of refraction for rays incident from air onto the air-glass surface is increasing as angle of incidence is increasing.
The table for angle of reflection and angle of refraction for all angles of incidence at
| Angle of incidence | Angle of reflection | Angle of refraction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d)
Answer to Problem 35.52AP
The table for angle of reflection and angle of refraction for all angles of incidence at
|
Angle of incidence(
(
|
Angle of reflection(
|
Angle of refraction(
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Explanation of Solution
From, the law of reflection, angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. So, for all value of angles between
The formula to calculate the angle of refraction is,
From, Snell’s law,
Substitute
Substitute
The remaining values of the angle of refraction can be calculated by the same method.
The formula to calculate the critical angle is,
Here,
Substitute
The angle of incidence is greater than
The table for angle of reflection and angle of refraction for all angles of incidence at
|
Angle of incidence(
(
|
Angle of reflection(
|
Angle of refraction(
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle of reflection is same as the angle of incidence and the of angle of refraction for rays coming up to the interface through the glass will increase up to angle of incidence
The table for angle of reflection and angle of refraction for all angles of incidence at
|
Angle of incidence(
(
|
Angle of reflection(
|
Angle of refraction(
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 35 Solutions
PHYSICS 1250 PACKAGE >CI<
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Iarrow_forwardHow would partial obstruction of an air intake port of an air-entrainment mask effect FiO2 and flow?arrow_forward14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forwardCheckpoint 4 The figure shows four orientations of an electric di- pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta- tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di- pole, greatest first. (1) (2) E (4)arrow_forward
- What is integrated science. What is fractional distillation What is simple distillationarrow_forward19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax





