
Concept explainers
How fast can a racecar travel through a circular tum without skidding and hitting the wall? The answer could depend on several factors:
- The weight of the car;
- The friction between the tires and the road;
- The radius of the circle;
- The “steepness” of the turn.
In this project we investigate this question for NASCAR racecars at the Bristol Motor Speedway in Tennessee. Before considering this track in particular, we use
A car of mass m moves with constant angular speed to around a circular curve of radius R (Figure 3.20). The curve is banked at an angle
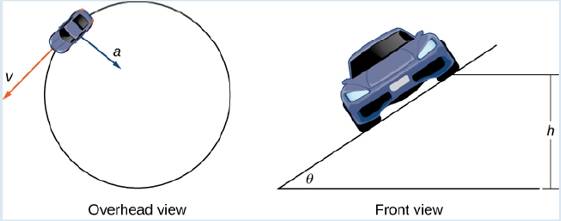
Figure 3.20 Views of a lace ear moving around a track.
As the car moves around the curve, three forces act on it: gravity, the force exerted by the road (this force is perpendicular to the ground), and the friction force (Figure 3.21). Because describing the frictional force generated by the tires and the road is complex, we use a standard approximation for the frictional force. Assume that
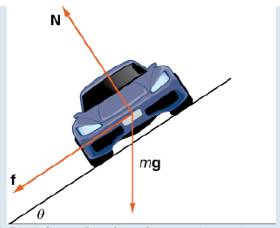
Figure 3.21 The car has three forces acting on it: gravity (denoted by mg), the friction force f, and the force exerted by the road N.
Let
The next three questions deal with developing a formula that relates the speed
Now that we have a formula
The Bristol Motor Speedway is a NASCAR short track in Bristol, Tennessee. The track has the approximate shape shown in Figure 3.22. Each end of the track is approximately semicircular, so when cars make turns they are traveling along an approximately circular curve. If a car takes the inside track and speeds along the bottom of turn 1, the car travels along a semicircle of radius approximately

Figure 3.22 At the Bristol Motor Speedway, Bristol, Tennessee (a), the turns have an inner radius of about
The coefficient of friction for a normal fire in Elly conditions is approximately
Before answering the following questions, note that it is easier to do computations in terms of feet and seconds, and then convert the answers to miles per hour as a final step.
9. In dry conditions, how fast can the car travel through the top of the turn without skidding?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Calculus Volume 3
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Graphical Approach To College Algebra
Precalculus
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- (6) ≤ a) Determine the following groups: Homz(Q, Z), Homz(Q, Q), Homz(Q/Z, Z) for n E N. Homz(Z/nZ, Q) b) Show for ME MR: HomR (R, M) = M.arrow_forwardAlready got wrong chatgpt answer Plz don't use chatgpt answer will upvote otherwise leave it .arrow_forwardy=f'(x) 1 8 The function f is defined on the closed interval [0,8]. The graph of its derivative f' is shown above. How many relative minima are there for f(x)? O 2 6 4 00arrow_forward
- 60! 5!.7!.15!.33!arrow_forwardUse Euler's summation formula to prove that, for x > 2, Σ log n n3 = A log x 2x2 n≤x where A is a constant. - 1 +0 4x2 log x x3 "arrow_forward• • Let > be a potential for the vector field F = (−2 y³, −6 xy² − 4 z³, −12 yz² + 4 2). Then the value of sin((-1.63, 2.06, 0.57) – (0,0,0)) is - 0.336 -0.931 -0.587 0.440 0.902 0.607 -0.609 0.146arrow_forward
- 1. If f(x² + 1) = x + 5x² + 3, what is f(x² - 1)?arrow_forward2. What is the total length of the shortest path that goes from (0,4) to a point on the x-axis, then to a point on the line y = 6, then to (18.4)?arrow_forwardThe value of cos(4M) where M is the magnitude of the vector field with potential ƒ = e² sin(лy) cos(π²) at x = 1, y = 1/4, z = 1/3 is 0.602 -0.323 0.712 -0.816 0.781 0.102 0.075 0.013arrow_forward
 Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
 Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





