
Concept explainers
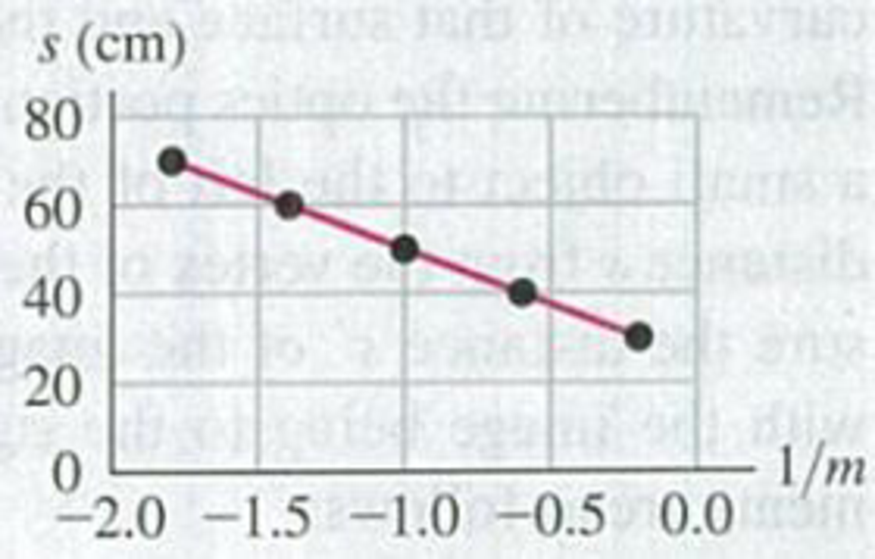
DATA In setting up an experiment for a high school biology lab, you use a concave spherical mirror to produce real images of a 4.00-mm-tall firefly. The firefly is to the right of the mirror, on the mirror’s optic axis, and serves as a real object for the mirror. You want to determine how far the object must be from the mirror’s vertex (that is, object distance s) to produce an image of a specified height. First you place a square of white cardboard to the right of the object and find what its distance from the vertex needs to be so that the image is sharply focused on it. Next you measure the height of the sharply focused images for five values of s. For each s value, you then calculate the lateral magnification m. You find that if you graph your data with s on the vertical axis and 1/m on the horizontal axis, then your measured points fall close to a straight line. (a) Explain why the data plotted this way should fall close to a straight line. (b) Use the graph in Fig. P34.102 to calculate the focal length of the mirror. (c) How far from the mirror’s vertex should you place the object in order for the image to be real, 8.00 mm tall, and inverted? (d) According to Fig. P34.102, starting from the position that you calculated in part (c), should you move the object closer to the mirror or farther from it to increase the height of the inverted, real image? What distance should you move the object in order to increase the image height from 8.00 mm to 12.00 mm? (e) Explain why l/m approaches zero as s approaches 25 cm. Can you produce a sharp image on the cardboard when s = 25 cm? (f) Explain why you can’t see sharp images on the cardboard when s < 25 cm (and m is positive).
Figure P34.102
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 34 Solutions
University Physics (14th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
- (i) When an image of an object is formed by a plane mirror, which of the following statements is always true? More than one statement may be correct. (a) The image is virtual. (b) The image is real. (c) The image is upright. (d) The image is inverted. (e) None of those statements is always true. (ii) When the image of an object is formed by a concave mirror, which of the preceding statements are always true? (iii) When the image of an object is formed by a convex mirror, which of the preceding statements are always true?arrow_forwardIn Figure P35.30, a thin converging lens of focal length 14.0 cm forms an image of the square abed, which is he = hb = 10.0 cm high and lies between distances of pd = 20.0 cm and pa = 30.0 cm from the lens. Let a, b, c. and d represent the respective corners of the image. Let qa represent the image distance for points a and b, qd represent the image distance for points c and d, hb, represent the distance from point b to the axis, and hc represent the height of c. (a) Find qa, qd, hb, and hc. (b) Make a sketch of the image. (c) The area of the object is 100 cm2. By carrying out the following steps, you will evaluate the area of the image. Let q represent the image distance of any point between a and d, for which the object distance is p. Let h represent the distance from the axis to the point at the edge of the image between b and c at image distance q. Demonstrate that h=10.0q(114.01q) where h and q are in centimeters. (d) Explain why the geometric area of the image is given by qaqdhdq (e) Carry out the integration to find the area of the image. Figure P35.30arrow_forwardWhy is the following situation impossible? Consider the lensmirror combination shown in Figure P35.55. The lens has a focal length of fL = 0.200 m, and the mirror has a focal length of fM = 0.500 m. The lens and mirror are placed a distance d = 1.30 m apart, and an object is placed at p = 0.300 m from the lens. By moving a screen to various positions to the left of the lens, a student finds two different positions of the screen that produce a sharp image of the object. One of these positions corresponds to light leaving the object and traveling to the left through the lens. The other position corresponds to light traveling to the right from the object, reflecting from the mirror and then passing through the lens. Figure P35.55 Problem 55 and 57.arrow_forward
- Consider the lensmirror arrangement shown in Figure P35.55. There are two final image positions to the left of the lens of focal length fL. One image position is due to light traveling from the object to the left and passing through the lens. The other image position is due to light traveling to the right from the object, reflecting from the mirror of focal length fM and then passing through the lens. For a given object position p between the lens and the mirror and measured with respect to the lens, there are two separation distances d between the lens and mirror that will cause the two images described above to be at the same location. Find both positions.arrow_forwardThe radius of curvature of the left-hand face of a flint glass biconvex lens (n = 1.60) has a magnitude of 8.00 cm, and the radius of curvature of the right-hand face has a magnitude of 11.0 cm. The incident surface of a biconvex lens is convex regardless of which side is the incident side. What is the focal length of the lens if light is incident on the lens from the left?arrow_forwardA floating strawberry illusion is achieved with two parabolic mirrors, each having a focal length 7.50 cm, facing each other as shown in Figure P33.58. If a strawberry is placed on the lower mirror, an image of the strawberry is formed at the small opening at the center of the top mirror, 7.50 cm above the lowest point of the bottom mirror. The position of the eye in Figure P35.58a corresponds to the view of the apparatus in Figure P35.58b. Consider the light path marked A. Notice that this light path is blocked by the upper mirror so that the strawberry itself is not directly observable. The light path marked B corresponds to the eye viewing the image of the strawberry that is formed at the opening at the top of the apparatus. (a) Show that the final image is formed at that location and describe its characteristics. (b) A very startling effect is to shine a flashlight beam on this image. Even al a glancing angle, the incoming light beam is seemingly reflected from the image! Explain. Figure P35.58arrow_forward
- A 1.80-m-tall person stands 9.00 m in front of a large, concave spherical mirror having a radius of curvature of 3.00 m. Determine (a) the mirrors focal length, (b) the image distance, and (c) the magnification. (d) Is the image real or virtual? (e) Is the image upright or inverted?arrow_forwardA lamp of height S cm is placed 40 cm in front of a converging lens of focal length 20 cm. There is a plane mirror 15 cm behind the lens. Where would you find the image when you look in the mirror?arrow_forwardA convex mirror with a radius of curvature of 25.0 cm is used to form an image of an arrow that is 10.0 cm away from the mirror. If the arrow is 2.00 cm tall and inverted (pointing below the optical axis), what is the height of the arrows image?arrow_forward
- A small convex mirror and a large concave mirror are separated by 1.00 m, and an object is placed 1.40 m to the left of the concave mirror (Fig. P37.69). The concave mirror forms an image of this object at distance di = 25.0 cm. This image is then reflected in the convex mirror, which forms an image a distance of 8.00 cm behind the convex mirror. What is the focal length of the small convex mirror? FIGURE P37.69arrow_forwardUnder what circumstances will an image be located at the focal point of a spherical lens or mirror?arrow_forwardAn object of height 3 cm is placed at a distance of 25 cm in front of a converging lens of focal length 20 cm, to be referred to as the first lens. Behind the lens there is another converging lens of focal length 20 cm placed 10 cm from the first lens. There is a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm placed 50 cm from the second lens. Find the location, orientation, and size of the final image.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





