
Concept explainers
(a)
The critical angle for total internal reflection for light in the diamond incident on the interface between the diamond and outside air.
(a)
Answer to Problem 28P
The critical angle of refraction at air-diamond interface is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown below.
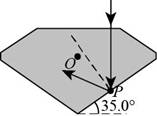
Figure (I)
From Snell’s law of refraction to air-diamond interface to find the critical angle is,
Here,
The value of
Substitute 1 for
Thus, the critical angle of refraction at air-diamond interface is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the critical angle of refraction at air-diamond interface is
(b)
To show: The light travelling towards point
(b)
Answer to Problem 28P
The angle of incidence is more than the critical angle all light is reflected from point P.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown in figure (I).
The critical angle for total internal reflection for light in the diamond incident on the interface between the diamond and outside air is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle of incidence is more than the critical angle all light is reflected from point P.
(c)
The critical angle for total internal reflection for light in the diamond when the diamond is immersed in the water.
(c)
Answer to Problem 28P
The critical angle of incidence at water-diamond interface is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown in figure (I).
From Snell’s law of refraction to water-diamond interface to find the critical angle is,
Here,
The value of
Substitute 1 for
Thus, the critical angle of incidence at water-diamond interface is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the critical angle of incidence at water-diamond interface is
(d)
The ray incident at point
(d)
Answer to Problem 28P
Yes, the light ray undergoes total internal reflection at point
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown in figure (I).
The critical angle for total internal reflection for light in the diamond incident on the interface between the diamond and water is
Thus, the light undergoes total internal reflection at
Conclusion:
Therefore, the light undergoes total internal reflection at
(e)
The direction in which the diamond is rotated such that the light at a point
(e)
Answer to Problem 28P
The diamond is rotated in clockwise direction on the axis perpendicular to the page through
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown in figure (I).
The critical angle for total internal reflection for light in the diamond incident on the interface between the diamond and water is
The light will exit from the diamond only when the incident angle is less than the critical angle. So, to reduce the angle of incidence the diamond should be rotated in clockwise direction on the axis perpendicular to the plane of paper.
Thus, the light will exit at point
Conclusion:
Therefore, the light will exit at point
(f)
The angle of rotation at which the light first exit the diamond at point
(f)
Answer to Problem 28P
The diamond is rotated by
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown in figure (I).
Let the angle is rotated clockwise by
Apply Snell’s law at the water-diamond interface.
The condition of the situation is shown below.
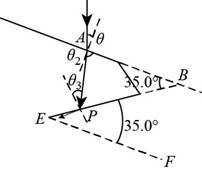
Figure (II)
The angle at the vertex
The requirement is that the angle of incidence
Apply Snell’s law and find angle
Substitute
Thus, the diamond is rotated by
Conclusion:
Therefore, the diamond is rotated by
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 34 Solutions
Bundle: Physics For Scientists And Engineers With Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 10th + Webassign Printed Access Card For Serway/jewett's Physics For Scientists And Engineers, 10th, Single-term
- Figure 29-43 Problem 12. ••13 In Fig. 29-44, point P₁ is at distance R = 13.1 cm on the perpendicular bisector of a straight wire of length L = 18.0 cm carrying current i = 58.2 mA. (Note that the wire is not long.) What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at P₁ due to i? P2° R R Larrow_forwardCheckpoint 1 The figure shows the current i in a single-loop circuit with a battery B and a resistance R (and wires of neg- ligible resistance). (a) Should the emf arrow at B be drawn pointing leftward or rightward? At points a, B C R b, and c, rank (b) the magnitude of the current, (c) the electric potential, and (d) the electric potential energy of the charge carriers, greatest first.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
- Pls help asaparrow_forwardPls help asaparrow_forward3. If the force of gravity stopped acting on the planets in our solar system, what would happen? a) They would spiral slowly towards the sun. b) They would continue in straight lines tangent to their orbits. c) They would continue to orbit the sun. d) They would fly straight away from the sun. e) They would spiral slowly away from the sun. 4. 1 The free-body diagram of a wagon being pulled along a horizontal surface is best represented by A F N B C 0 Ꭰ FN E a) A b) B c) C app app The app 10 app d) e) ס ח D E 10 apparrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





