
Rainbow. Figure 33-67 shows a light ray entering and then leaving a falling, spherical raindrop after one internal reflection (see Fig, 33-21a). The final direction of travel is deviated (turned) from the initial direction of travel by angular deviation θdev(a) Show that θdev.(a) Show that θdev is
θdev = 180°+2θi-4θr,
where θi is the angle of incidence of the ray on the drop and θr is the angle of refraction of the ray within the drop, (b) Using Snell's law, substitute for θr in terms of θi, and the index of refraction n of the water. Then, on a graphing calculator or with a computer graphing package, graph θdev versus θi for the range of possible θi, values and for n = 1.331 for red light (at one end of the visible spectrum) and n = 1.333 for blue light (at the other end).
The red-light curve and the blue-light curve have different minima, which means that there is a different angle of minimum deviation for each color. The light of any given color that leaves the drop at that color’s angle of minimum deviation is especially bright because rays bunch up at that angle and the bright red light leaves the drop at one angle and the bright blue light leaves it at another angle.
Determine the angle of minimum deviation from the θdev curve for (c) red light and (d) blue light. (e) If these colors form the inner and outer edges of a rainbow (Fig. 33-21a), what is the angular width of the rainbow?
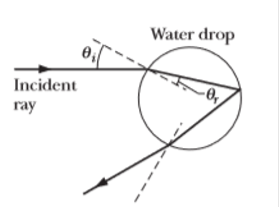
Figure 33-67 Problem 77.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 33 Solutions
FUND.OF PHYSICS(LL)-PRINT COMP-W/ACCESS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
- 8. With the aid of a diagram draw the following electric circuit and use the resistor as the load, (a) Closed circuit (b) Open circuitarrow_forwardLab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





