
Solve Prob. 3.55, assuming that the shaft AB is replaced by a hollow shaft of the same outer diameter and 25-mm inner diameter.
3.55 Two solid steel shafts (G = 77.2 GPa) are connected to a coupling disk B and to fixed supports at A and C. For the loading shown, determine (a) the reaction at each support, (b) the maximum shearing stress in shaft (c) the maximum shearing stress in shaft BC.
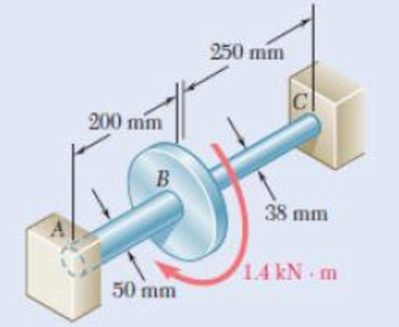
Fig. p3.55
(a)
The reaction at the supports.
Answer to Problem 56P
The reaction at the supports are
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The modulus of rigidity of solid shafts is
Inner diameter of the shaft AB is 25 mm.
Calculation:
The outer radius of the shaft AB is
The inner radius of the shaft AB is
The polar moment of inertia of shaft AB of outer radius
The torque carried by the shaft AB
Here,
Substitute
The radius of the shaft BC is
The polar moment of inertia of shaft BC of radius
The torque carried by the shaft BC
Here,
Substitute
The value of total torque in the shaft is
The total torque
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the reaction at the supports are
(b)
The maximum shearing stress in the shaft AB.
Answer to Problem 56P
The maximum shearing stress in the shaft AB is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The modulus of rigidity of solid shafts is
Calculation:
Refer (a).
The value of torque in the shaft AB is
The polar moment of inertia of shaft AB is
The maximum shearing stress in the shaft AB
Substitute
Therefore, the maximum shearing stress in the shaft AB is
(c)
The maximum shearing stress in the shaft BC.
Answer to Problem 56P
The maximum shearing stress in the shaft BC is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The modulus of rigidity of solid shafts is
Calculation:
Refer (a).
The value of torque in the shaft BC is
The polar moment of inertia of shaft BC of radius
The maximum shearing stress in the shaft BC
Substitute
Therefore, the maximum shearing stress in the shaft BC is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- Calculate the force in cable AB and the angle θ for the support system shown. Round your final answers to two decimal places.arrow_forward1.53 In the steel structure shown, a 6-mm-diameter pin is used at C and 10-mm-diameter pins are used at B and D. The ultimate shearing stress is 150 MPa at all connections, and the ultimate normal stress is 400 MPa in link BD. Knowing that a factor of safety of 3.0 is desired, determine the largest load P that can be applied at A. Note that link BD is not reinforced around the pin holes. Front view D D 6 mm 18 mm B A B Side view 160 mm 120 mm A B Top viewarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 16: Determine (a) the maximum bending stress, (b)the maximum shearing stress, (c) compressive bending stress atthe roller support, and (d) the shearing stress 1 in below the topsurface of the beam at the location 1 ft to the right of the rollersupport in the simply supported beam shown in Fig. 8-70.ANS: (a) 21,945.313 lb/in2; (b) 1656.25 lb/in2; (c) 10,000 lb/in2; (d) 190.972 lb/in2arrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 20: A 2022 Porsche 911 (992) GT3 is crossing a 20 ft bridge. The specification of the car is shown below.Determine the maximum shear (in lb) and moment (in lb-ft) on the bridge. ANS: Vmax = 2,680.850 lb ; Mmax = 11,233.13 lb-ftarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. Answers: P1 = 208.625 KN/M P2 = 281.310 KN/M P = 15.491 KN/M FB = 463.402 MPA FV = 55.034 MPAarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 18: Determine the maximum shear and moment that would be experienced by a 10 m beam if a three-wheelmoving load of 10 kN, 30 kN, and 5 kN respectively will pass it by. The distance between the 1st and 2nd load is 1 m and the distance between the 2nd and 3rd load is 3 m.ANS: Vmax = 40 kN ; Mmax = 100.014 kN-marrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 5: A 12-m simply supported bridge is constructed with 100-mm concrete slab deck supported by precastconcrete stringers spaced 800 mm on center. Analyze the stringers when subjected to a moving load consisting of 3 evenly spaced axle loads at 3 m and equivalent to 20 kN, 30 kN and 40 kN respectively. The self-weight of the stringers is 8.5 kN/m and the concrete deck has a unit weight of 24 kN/m3 . Neglect all other superimposed loads. Calculate: (a) the maximum shear force in the stringers; (b) the maximum bending moment in the stringers. Answer: Vmax = 135.020 KN, Mmax = 477.388 KN-Marrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 19: A 22-wheeler truck is crossing over 25 m bridge. The dimensions between the axles of the truck are shownin the figure below. Axles 1 to 3 carry a 90 kN load each, axles 4 and 5 carry a 65 kN load each, and the axle directly below the cab of the truck has a load of 100 kN. Determine the maximum shear and moment on the bridge.ANS: Vmax = 374.92 kN ; Mmax = 1,702.229 kN-marrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 1. A H = 6 m cantilever retaining wall is subjected to a soil pressurelinearly varying from zero at the top to 90 kPa at the bottom. As an additionalsupport, it is anchored at depth y = 2 m. with maximum tension equal to 25kN. Assume that the stem provides fully retrained support. Draw the shearand moment diagram of the wall to calculate the following: (a) Maximumpositive bending moment per linear meter; (b) maximum negative bendingmoment per linear meter; (c) maximum shear force per linear meter. answer: +MMax = 440 kn-m, -Mmax = 0kn-M, Vmax = 245 KNarrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 17: A simply supported beam with the section shown below has an allowableflexural shearing stress of 43 MPa. (a) Determine the maximum allowable shearing force onthe section. And (b) what is the minimum thickness of plate that should be welded at theflanges if the section is to withstand a total shearing force of 200 kN. The additional plate willhave its base dimension equal to the flange dimension.ANS: V = 179.333 kN ; t = 23.181 mmarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. Answer: A = 0.207 L(M)arrow_forwardQu 4 The 12-kg slender rod is attached to a spring, which has an unstretched length of 2 m. If the rod is released from rest when 0 = 30°, determine its angular velocity at the instant 0 = 90°. 2 m B k = 40 N/m 2 marrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





